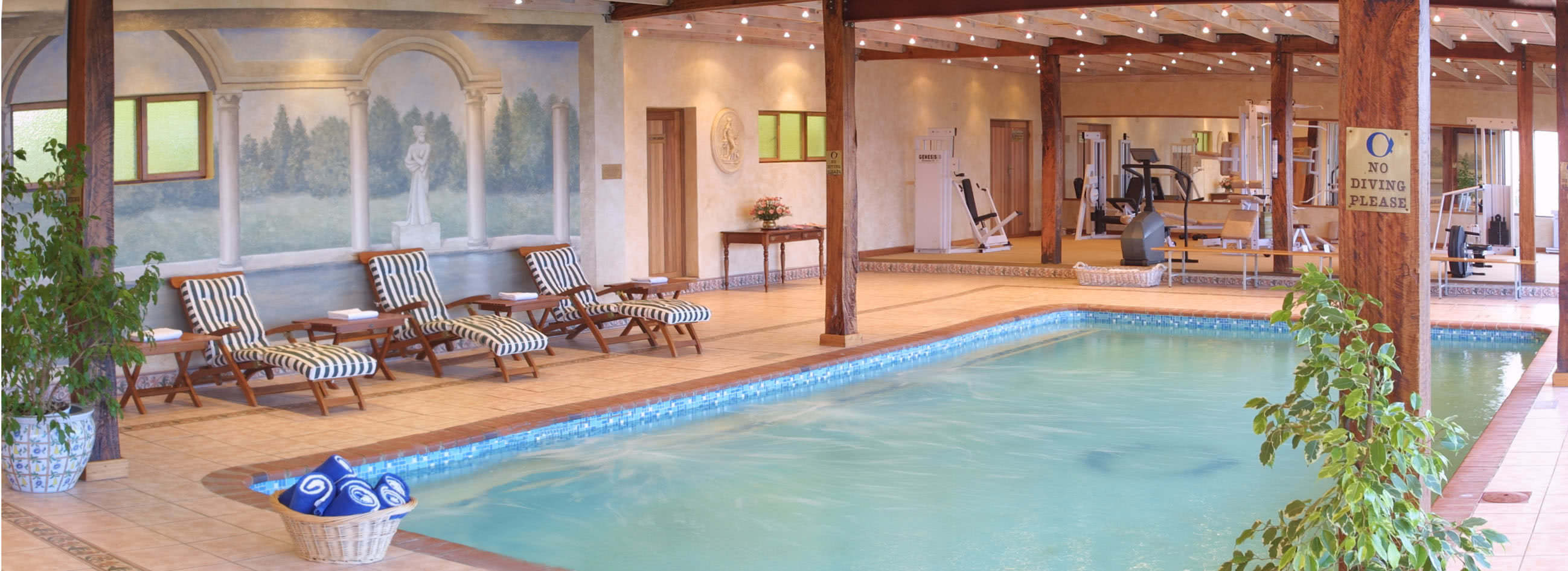
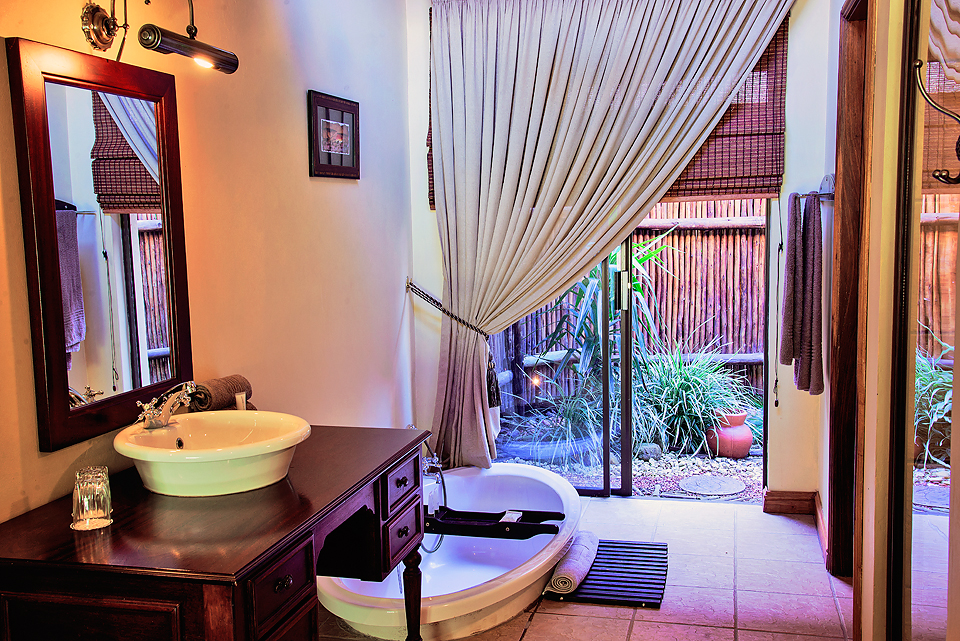
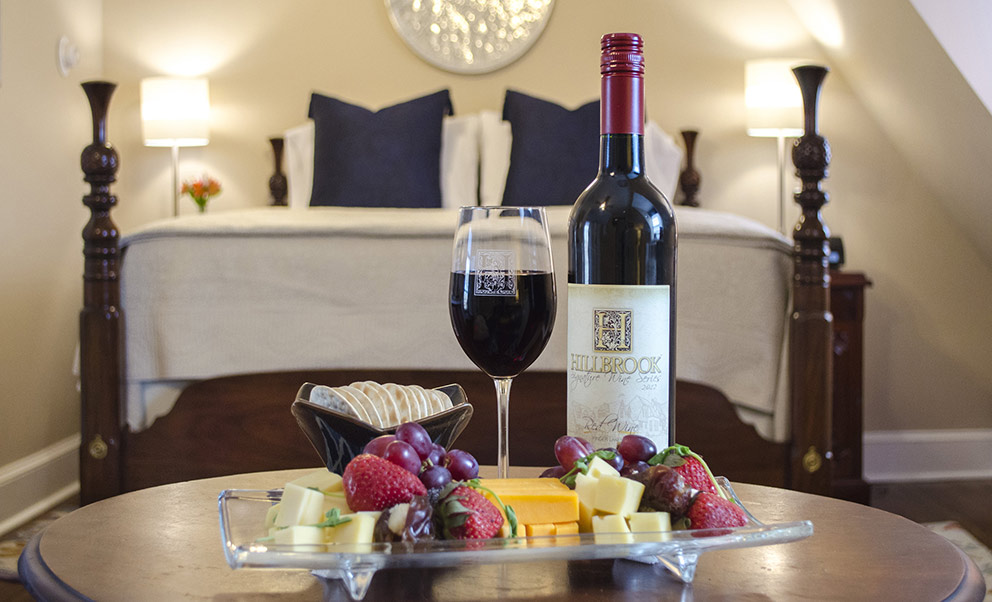
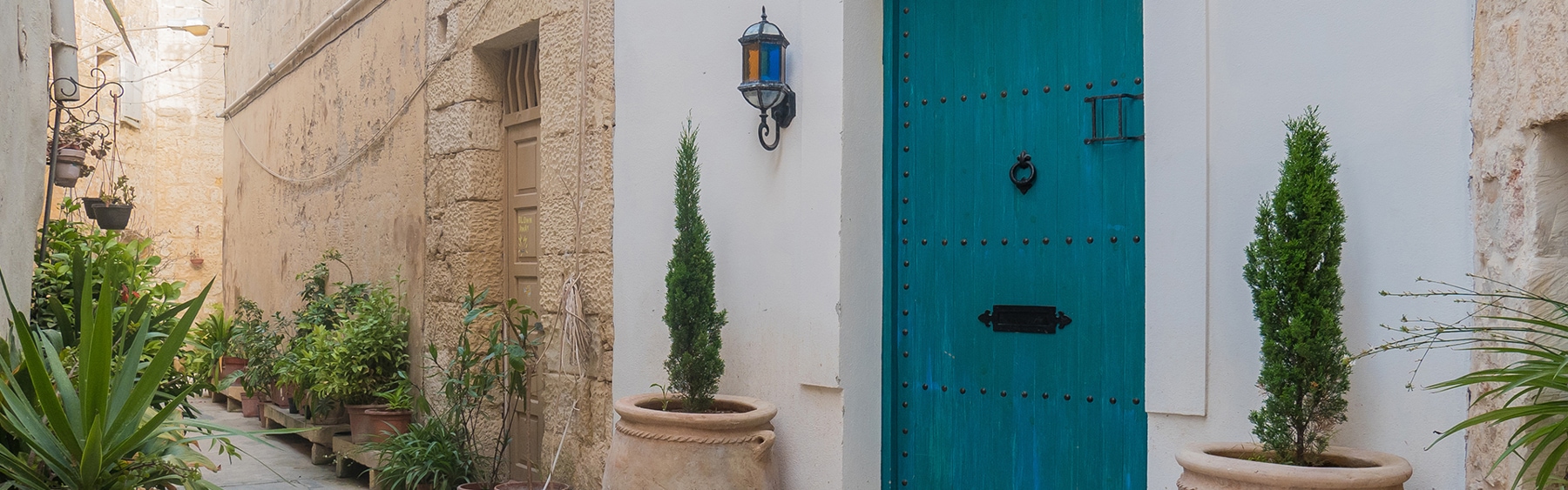
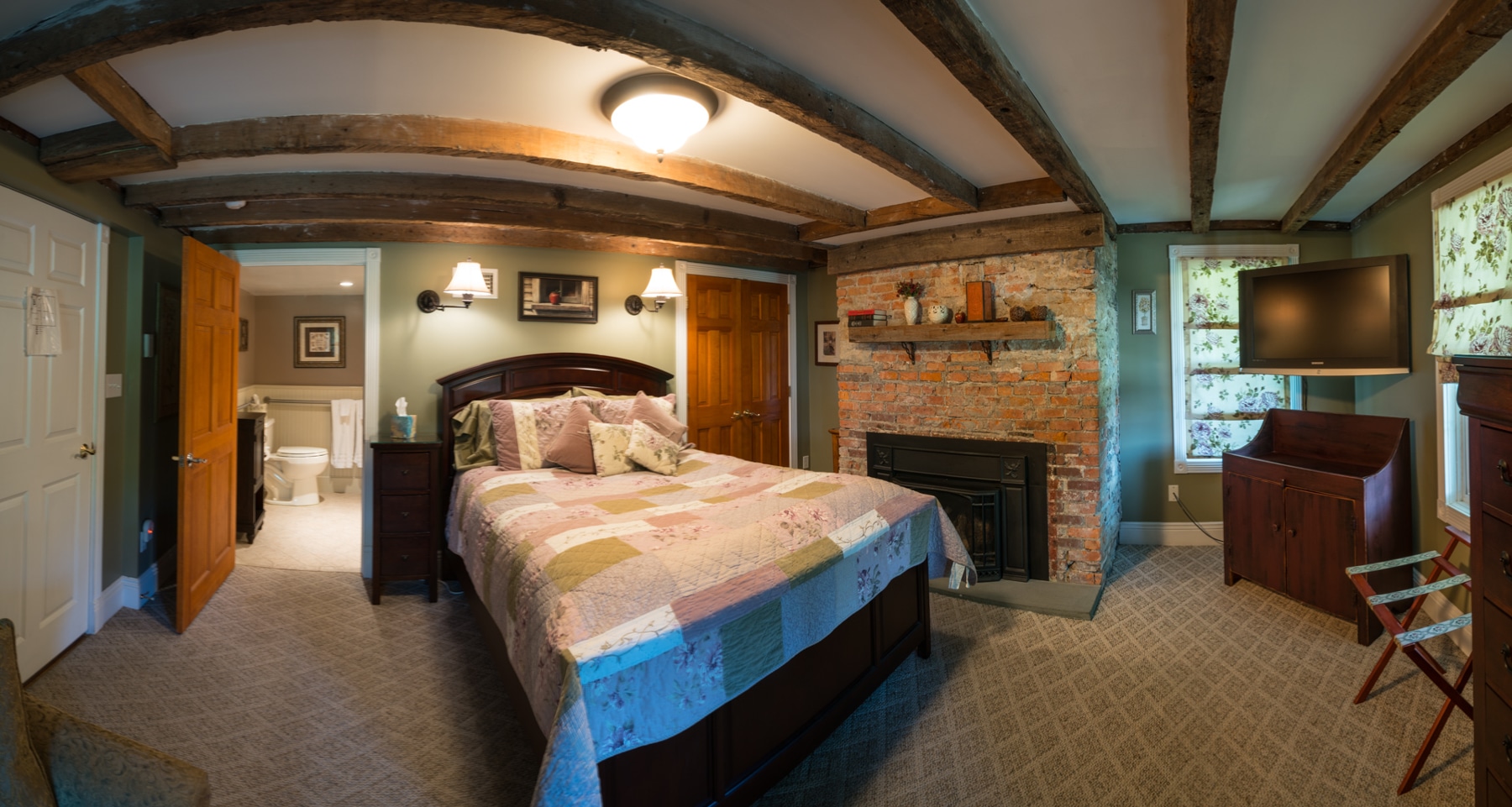
This room is equipped with one big bed, comfortable workspace,Private Computer, bathroom with jacuzzi,bidet, sauna,hair-drier,refrigerator, cable TV, wireless internet connection, safe, CD-player, air-conditioner and tea/coffee making facilities.
Restaurant
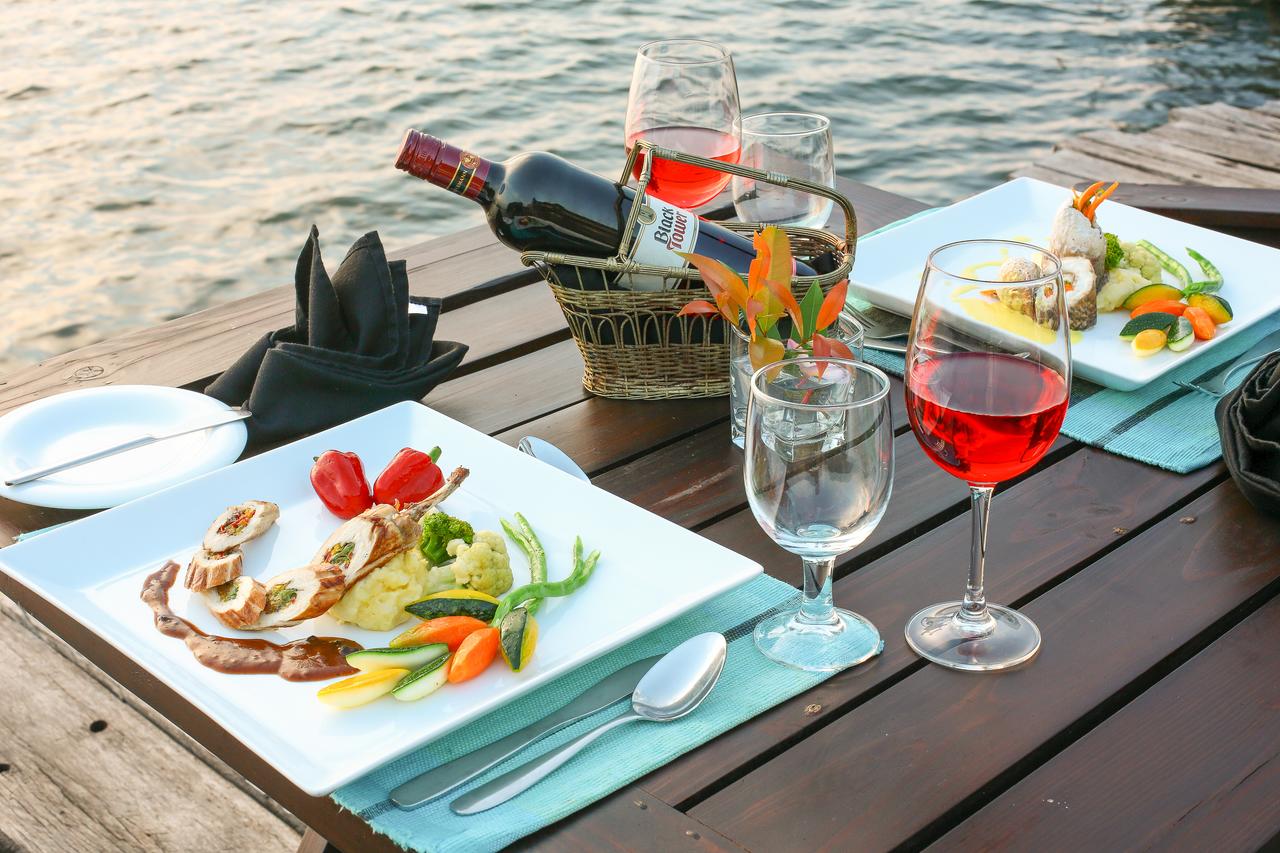
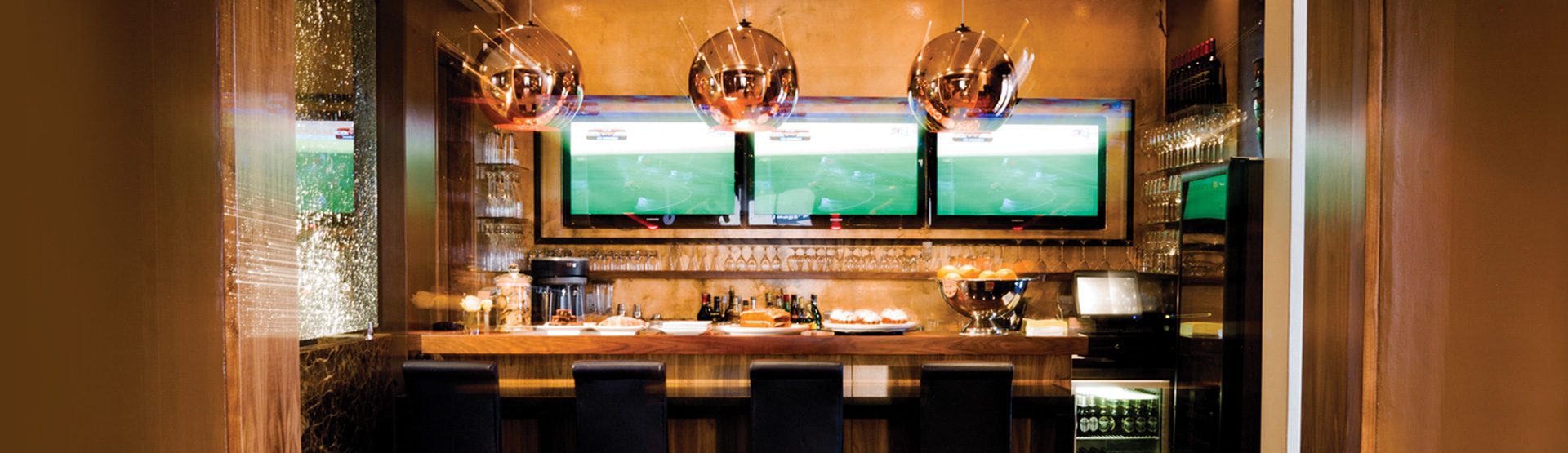
Our boutique hotel offers restaurant services with rich choice of drinks. The modern European cuisine with great choice of dishes on any taste will be at your disposal.
Our Chef will prepare fantastic banquet for any occasion. You can trust our experience.
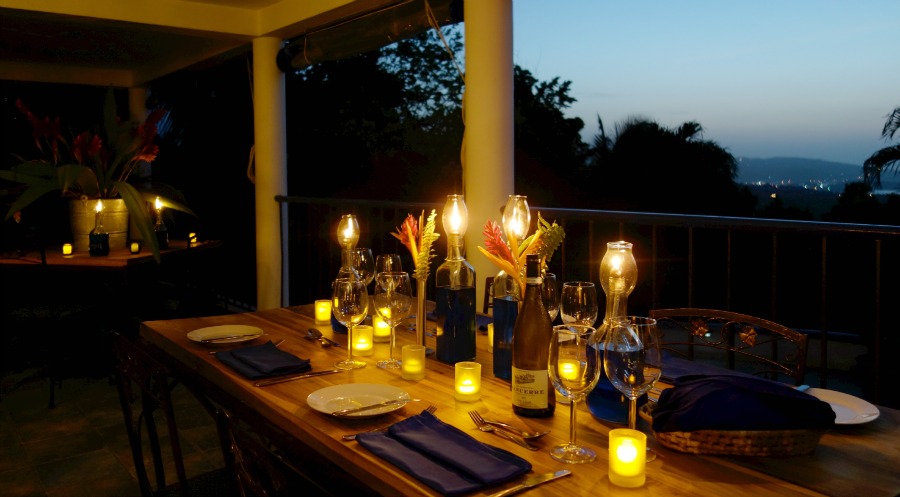
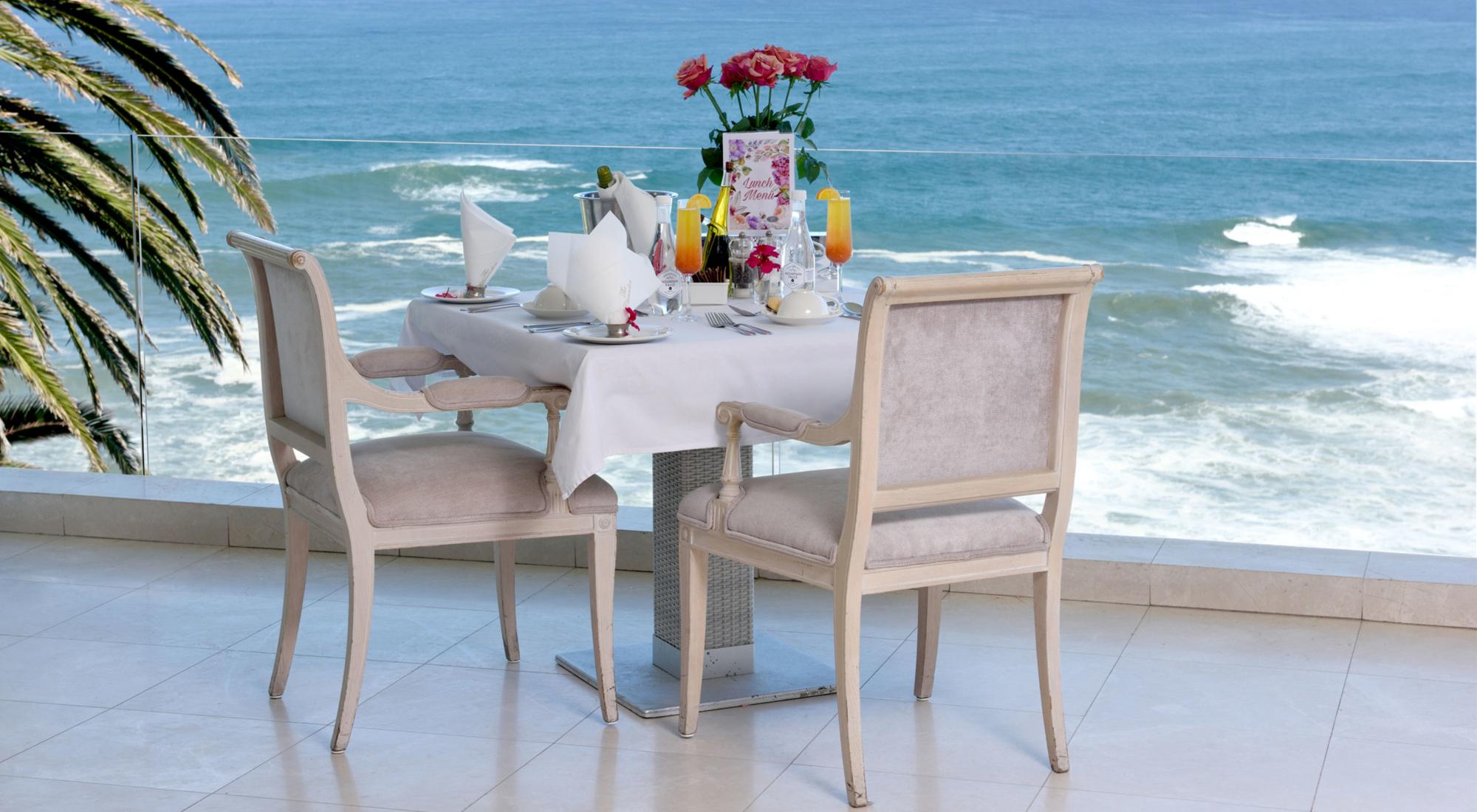
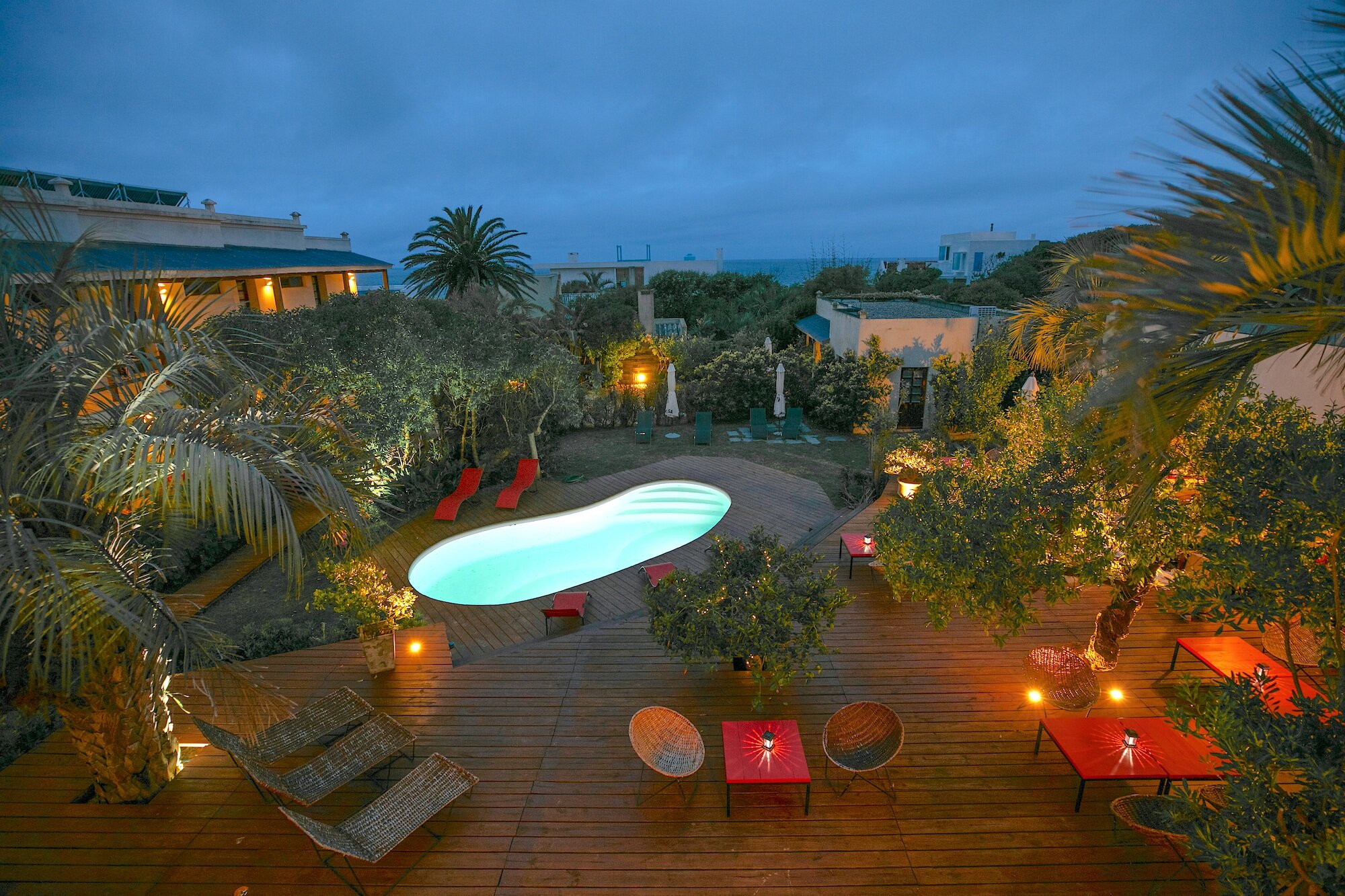
Our hotel has a nice summer terrace where you can feel in romance and peaceful atmosphere. Guests can have dinner or supper outside and try a waterpipe.
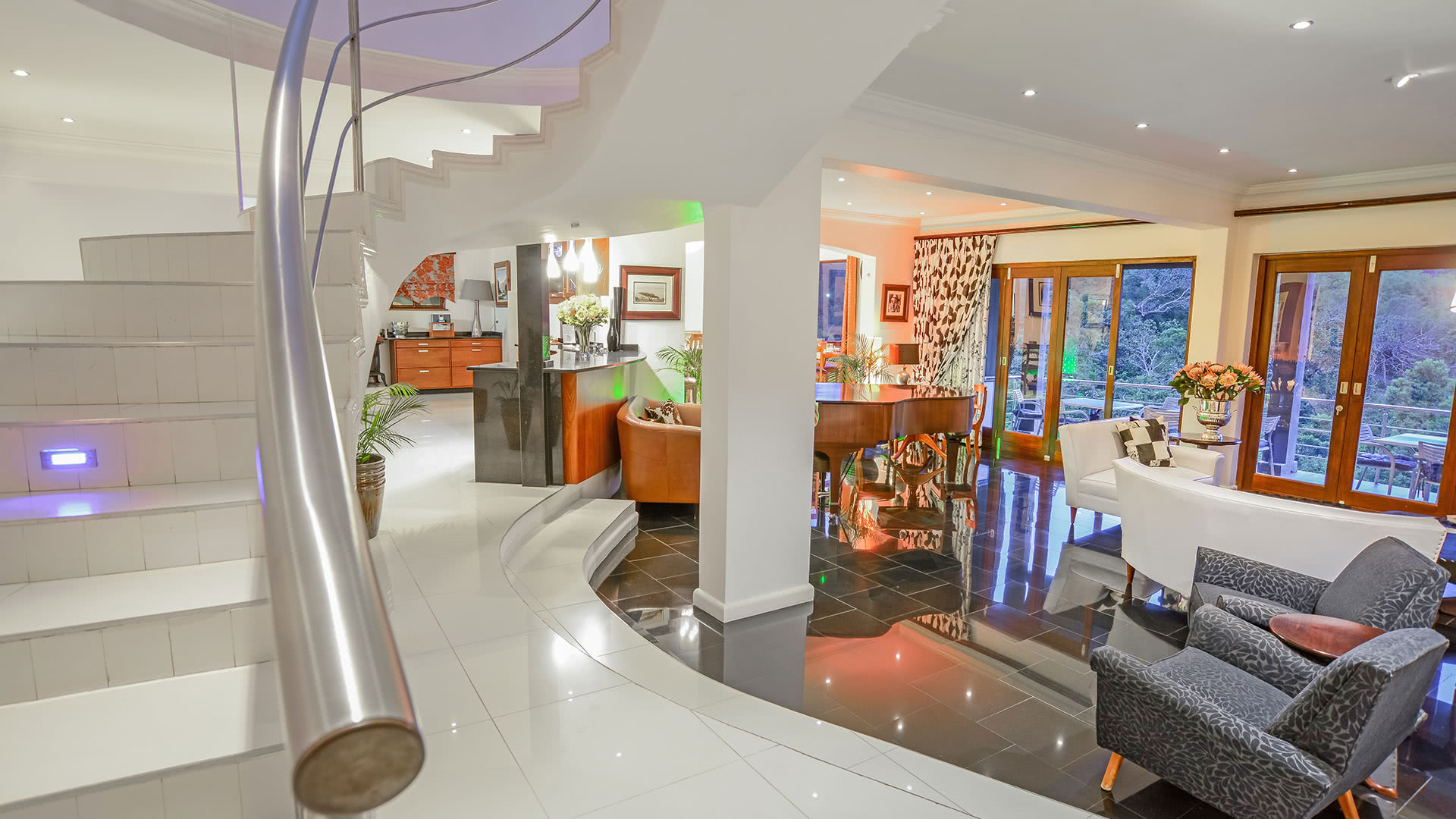
Services
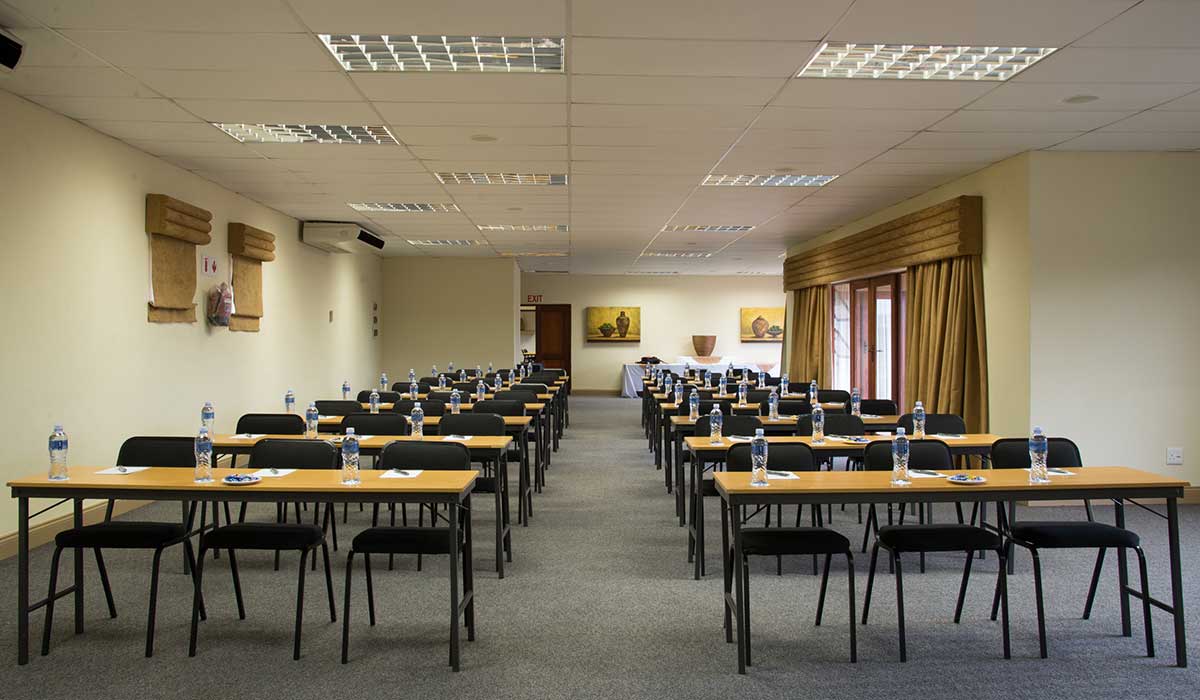
Hotel Monte Kristo offers meeting and conference room. Our conference room have high-speed Internet access, board, DVD equipment and television.
It is the ideal setting for any special occasion — from conferences up to 20 participants.
Riga
Riga is the capital and largest city of Latvia and is home to 605,802 inhabitants which is a third of Latvia's population. The city lies on the Gulf of Riga at the mouth of the Daugava river where it meets the Baltic Sea. Riga's territory covers 307.17 km2 (118.60 sq mi) and lies 1–10 m (3.3–32.8 ft) above sea level, on a flat and sandy plain.
Riga was founded in 1201 and is a former Hanseatic League member. Riga's historical centre is a UNESCO World Heritage Site, noted for its Art Nouveau/Jugendstil architecture and 19th century wooden architecture. Riga was the European Capital of Culture in 2014, along with Umeå in Sweden. Riga hosted the 2006 NATO Summit, the Eurovision Song Contest 2003, the 2006 IIHF Men's World Ice Hockey Championships, 2013 World Women's Curling Championship and the 2021 IIHF World Championship. It is home to the European Union's office of European Regulators for Electronic Communications (BEREC). In 2017, it was named the European Region of Gastronomy.
In 2016, Riga received over 1.4 million visitors. The city is served by Riga International Airport, the largest and busiest airport in the Baltic states. Riga is a member of Eurocities, the Union of the Baltic Cities (UBC) and Union of Capitals of the European Union (UCEU).
Etymology
There are numerous and speculative theories for the origin of the name Riga:
- It is an adapted borrowing from the Livonian ringa meaning loop, referring to the ancient natural harbour formed by the tributary loop of the Daugava River.
- It could be derived from Riege, the German name for the River Rīdzene, a former tributary of the Daugava.
- Bishop Albert claimed credit from his campaign to conquer and convert the local populace, as coming from the Latin rigata ("irrigated"), symbolising an "irrigation of dry pagan souls by Christianity".
However, the most reliably documented explanation is the affirmation by German historian Dionysius Fabricius (1610) that Riga's name comes from its already established role in trade: "Riga nomen sortita est suum ab aedificiis vel horreis quorum a litus Dunae magna fuit copia, quas livones sua lingua Rias vocare soliti." (in Latin) ("Riga obtained its name from the buildings or warehouses found in great number along the banks of the Duna, which the Livs in their own language are accustomed to call Riae."). The "j" in Latvian rīja hardened to a "g" in German. English geographer Richard Hakluyt (1589) corroborates this account, calling Riga Rie, as pronounced in Latvian.
History
Founding
The river Daugava has been a trade route since antiquity, part of the Vikings' Dvina–Dnieper navigation route to Byzantium. A sheltered natural harbour 15 km (9.3 mi) upriver from the mouth of the Daugava—the site of today's Riga—has been recorded, as Duna Urbs, as early as the 2nd century. It was settled by the Livs, a Finnic tribe.
Riga began to develop as a centre of Viking trade during the early Middle Ages. Riga's inhabitants occupied themselves mainly with fishing, animal husbandry, and trading, later developing crafts (in bone, wood, amber, and iron).
The Livonian Chronicle of Henry testifies to Riga having long been a trading centre by the 12th century, referring to it as portus antiquus (ancient port), and describes dwellings and warehouses used to store mostly flax, and hides. German traders began visiting Riga, establishing a nearby outpost in 1158.
Along with German traders the monk Meinhard of Segeberg arrived to convert the Livonian pagans to Christianity. Catholic and Orthodox Christianity had already arrived in Latvia more than a century earlier, and many Latvians had been baptised. Meinhard settled among the Livs, building a castle and church at Uexküll (now known as Ikšķile), upstream from Riga, and established his bishopric there. The Livs, however, continued to practice paganism and Meinhard died in Uexküll in 1196, having failed in his mission. In 1198, the Bishop Berthold arrived with a contingent of crusaders and commenced a campaign of forced Christianisation. Berthold died soon afterwards and his forces were defeated.
The Church mobilised to avenge this defeat. Pope Innocent III issued a bull declaring a crusade against the Livonians. Bishop Albert was proclaimed Bishop of Livonia by his uncle Hartwig of Uthlede, Prince-Archbishop of Bremen and Hamburg in 1199. Albert landed in Riga in 1200 with 23 ships and 500 Westphalian crusaders. In 1201, he transferred the seat of the Livonian bishopric from Uexküll to Riga, extorting agreement to do this from the elders of Riga by force.
21st Century
In 2004, the arrival of low-cost airlines resulted in cheaper flights from other European cities such as London and Berlin, and consequently a substantial increase in numbers of tourists.
Riga was the European Capital of Culture in 2014. During Latvia's Presidency of the Council of the European Union in 2015, the 4th Eastern Partnership Summit took place in Riga.
Latvia
Latvia, officially the Republic of Latvia[ (Latvian: Latvijas Republika, Latgalian: Latvejas Republika, Livonian: Lețmō Vabāmō), is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is one of the Baltic states; and is bordered by Estonia to the north, Lithuania to the south, Russia to the east, Belarus to the southeast, and shares a maritime border with Sweden to the west. Latvia covers an area of 64,589 km2 (24,938 sq mi), with a population of 1.9 million. The country has a temperate seasonal climate. Its capital and largest city is Riga. Latvians belong to the ethno-linguistic group of the Balts and speak Latvian, one of the only two surviving Baltic languages. Russians are the most prominent minority in the country, at almost a quarter of the population.
After centuries of Teutonic, Swedish, Polish-Lithuanian and Russian rule, which was mainly executed by the local Baltic German aristocracy, the independent Republic of Latvia was established on 18 November 1918 when it broke away from the German Empire and declared independence in the aftermath of World War I. However, by the 1930s the country became increasingly autocratic after the coup in 1934 establishing an authoritarian regime under Kārlis Ulmanis. The country's de facto independence was interrupted at the outset of World War II, beginning with Latvia's forcible incorporation into the Soviet Union, followed by the invasion and occupation by Nazi Germany in 1941, and the re-occupation by the Soviets in 1944 to form the Latvian SSR for the next 45 years. As a result of extensive immigration during the Soviet occupation, ethnic Russians became the most prominent minority in the country, now constituting nearly a quarter of the population. The peaceful Singing Revolution started in 1987, and ended with the restoration of de facto independence on 21 August 1991. Since then, Latvia has been a democratic unitary parliamentary republic.
Latvia is a developed country, with a high-income advanced economy; ranking very high 39th in the Human Development Index. Latvia is a member of the European Union, Eurozone, NATO, the Council of Europe, the United Nations, the Council of the Baltic Sea States, the International Monetary Fund, the Nordic-Baltic Eight, the Nordic Investment Bank, the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe, and the World Trade Organization.












































































 Name: BondExcel
Name: BondExcel  Name: Businessentials For Hospitality
Name: Businessentials For Hospitality  Name: Capital Efficiency Group
Name: Capital Efficiency Group  Name: D E I R D R E R E N N I E R S Interior Design
Name: D E I R D R E R E N N I E R S Interior Design  Name: De Leeuw Valuers Cape Town
Name: De Leeuw Valuers Cape Town  Name: E C Mobility
Name: E C Mobility  Name: Edward Tokolo Kasete
Name: Edward Tokolo Kasete  Name: Electrolux Professional
Name: Electrolux Professional  Name: Exquisite Hotel Consultants' Hospitality Training Department
Name: Exquisite Hotel Consultants' Hospitality Training Department  Name: FVE Interiors
Name: FVE Interiors  Name: Healing Earth
Name: Healing Earth  Name: Hospro
Name: Hospro  Name: Hotel Revenue Management
Name: Hotel Revenue Management  Name: Indigo Real Estate Agency
Name: Indigo Real Estate Agency  Name: Lisa Dunn - Tourism Grading Assessor
Name: Lisa Dunn - Tourism Grading Assessor  Name: Ooba (Pty) Ltd
Name: Ooba (Pty) Ltd  Name: SK Sambu Tours & Transfers
Name: SK Sambu Tours & Transfers  Name: Soul Private Collection
Name: Soul Private Collection  Name: The Dumb Butler Hospitality Suppliers
Name: The Dumb Butler Hospitality Suppliers  Name: The High Street Auction Company
Name: The High Street Auction Company  Name: Touch Point Retail
Name: Touch Point Retail