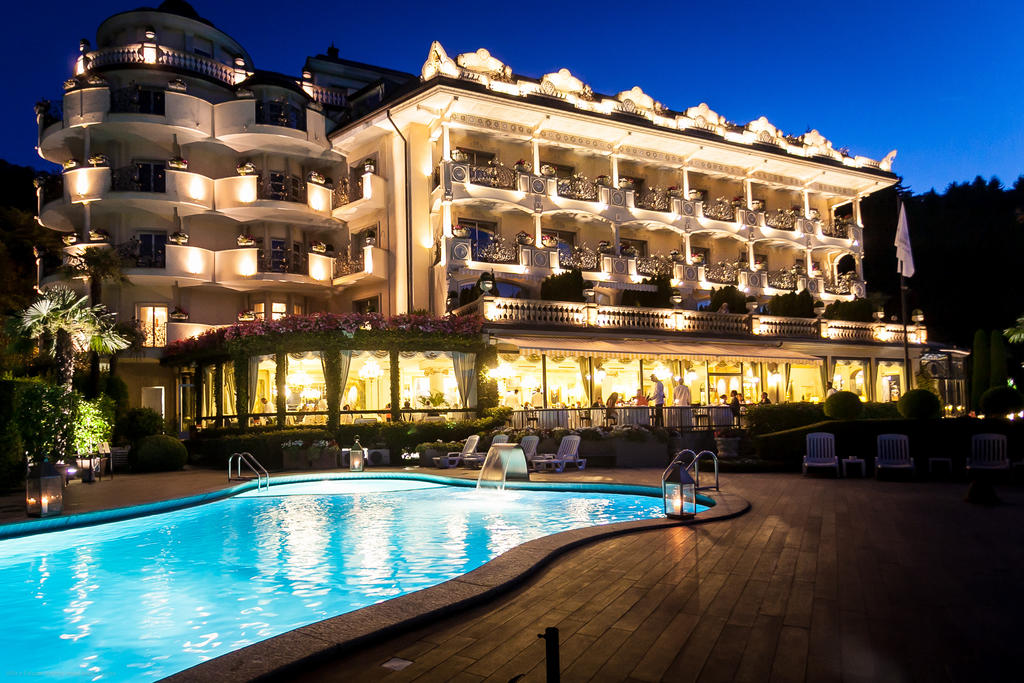
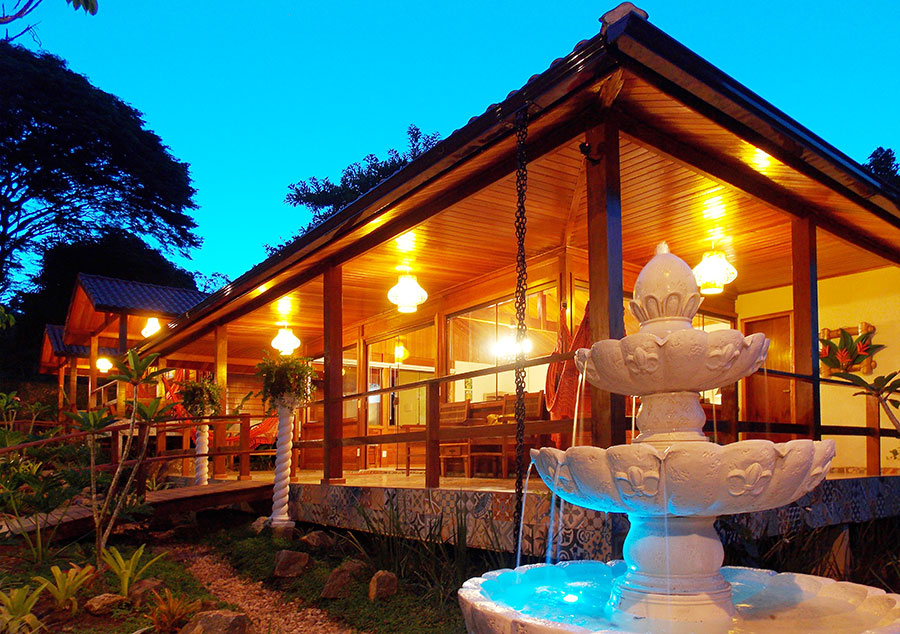
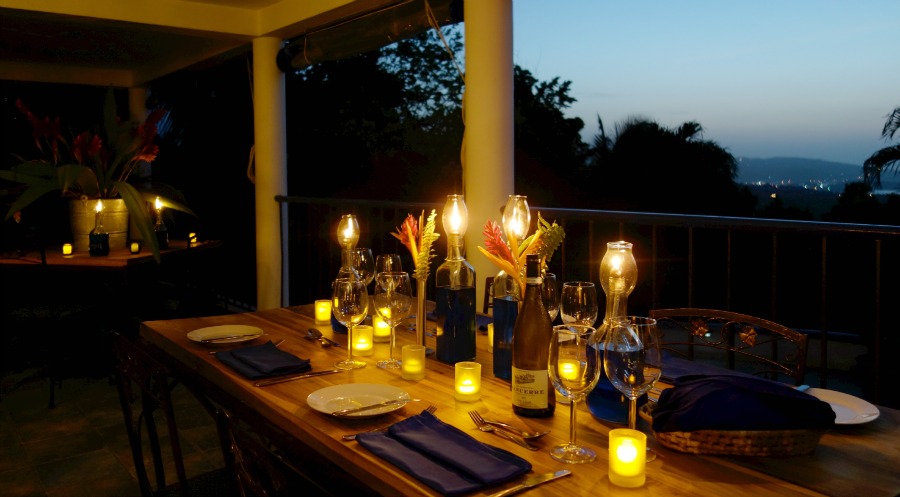
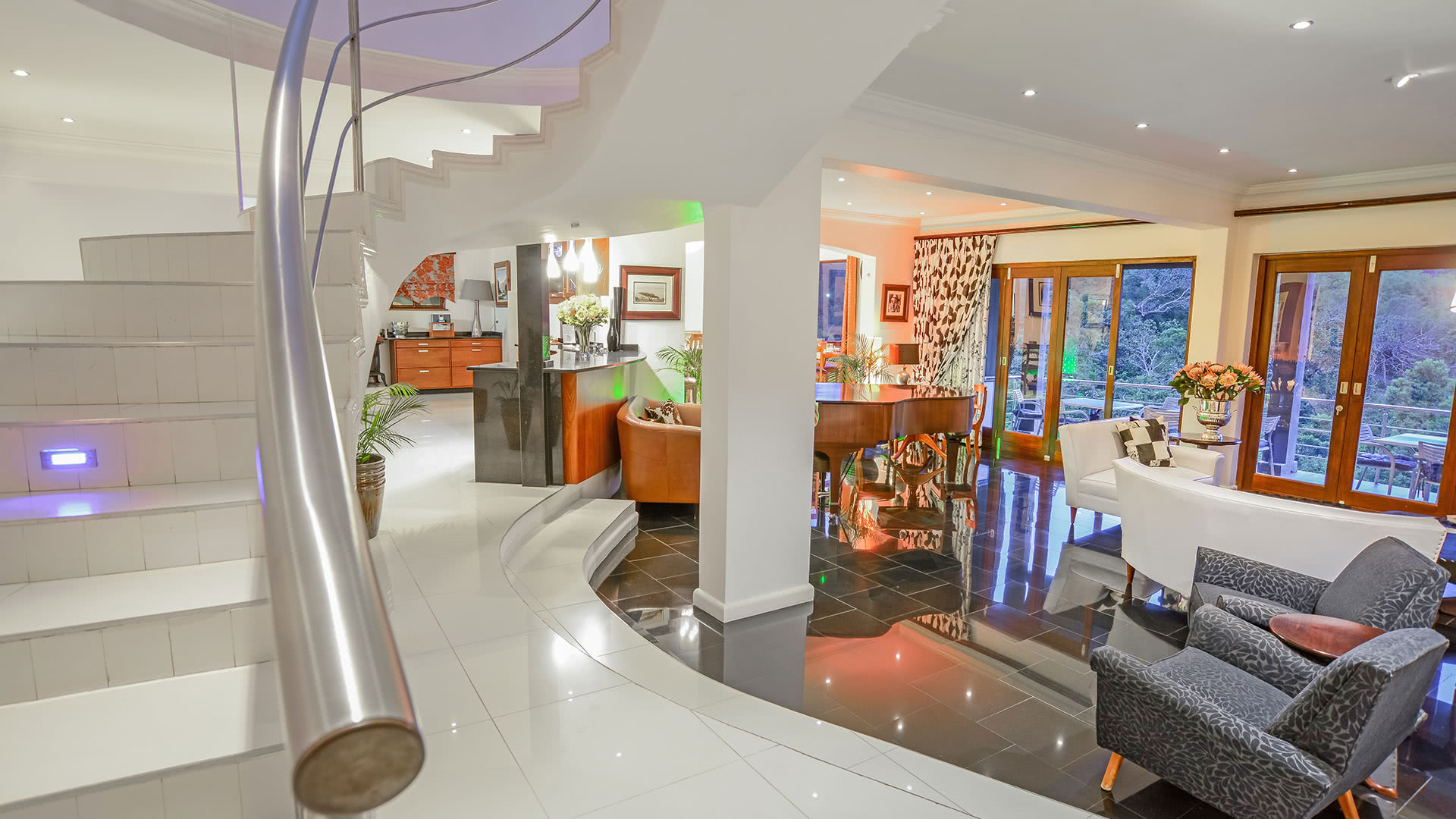
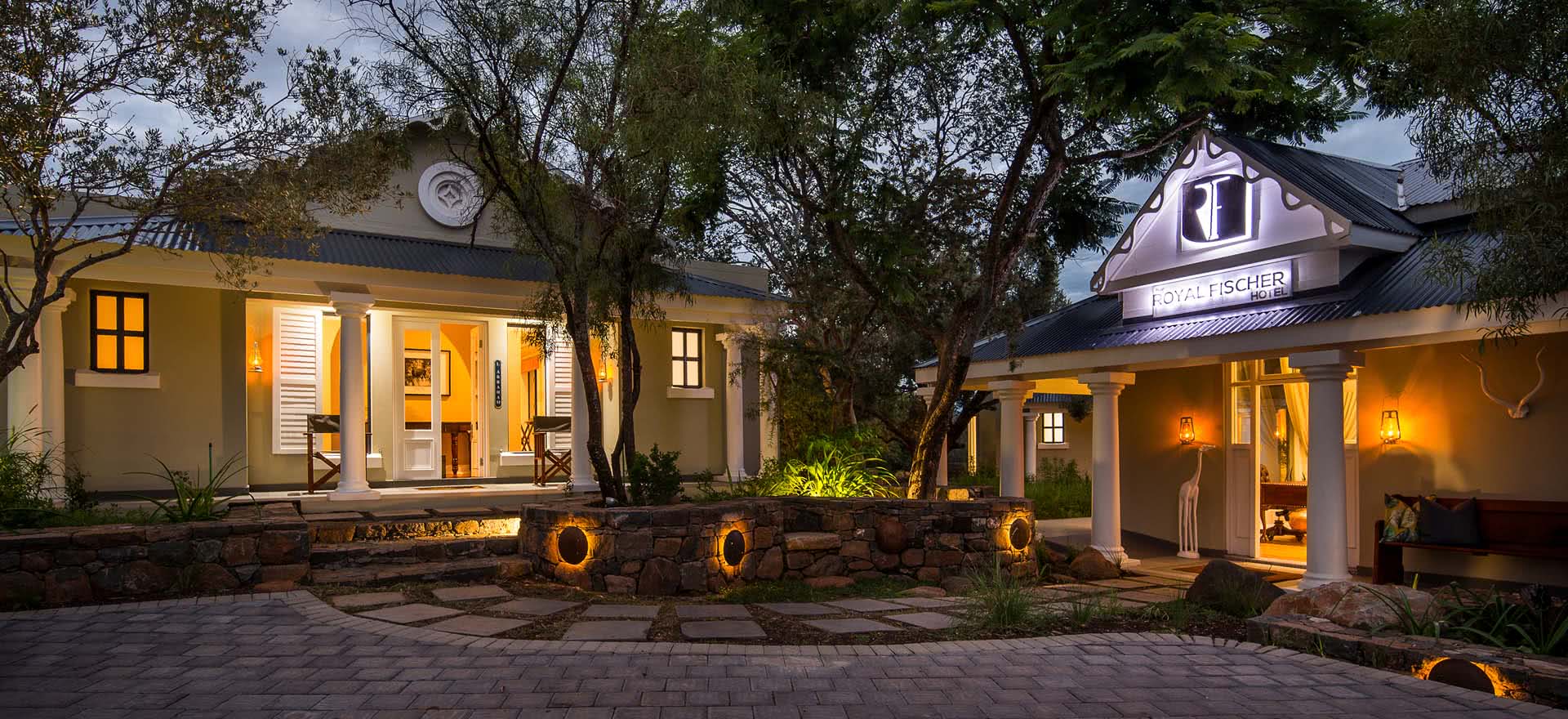
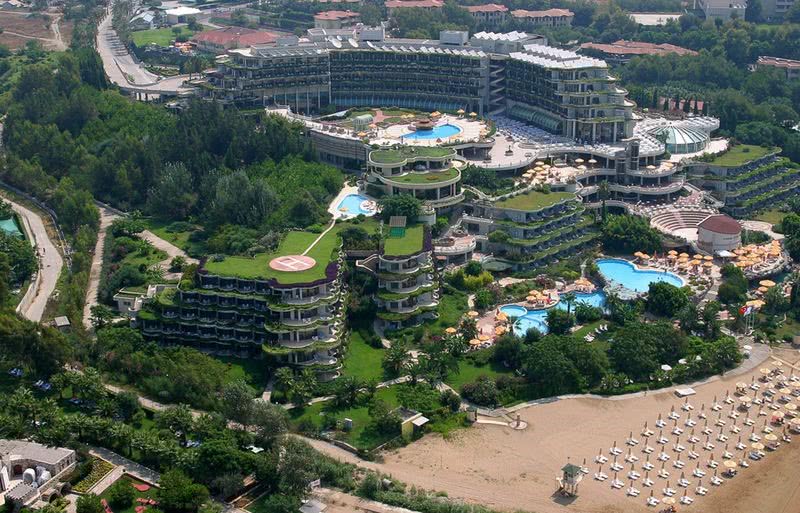
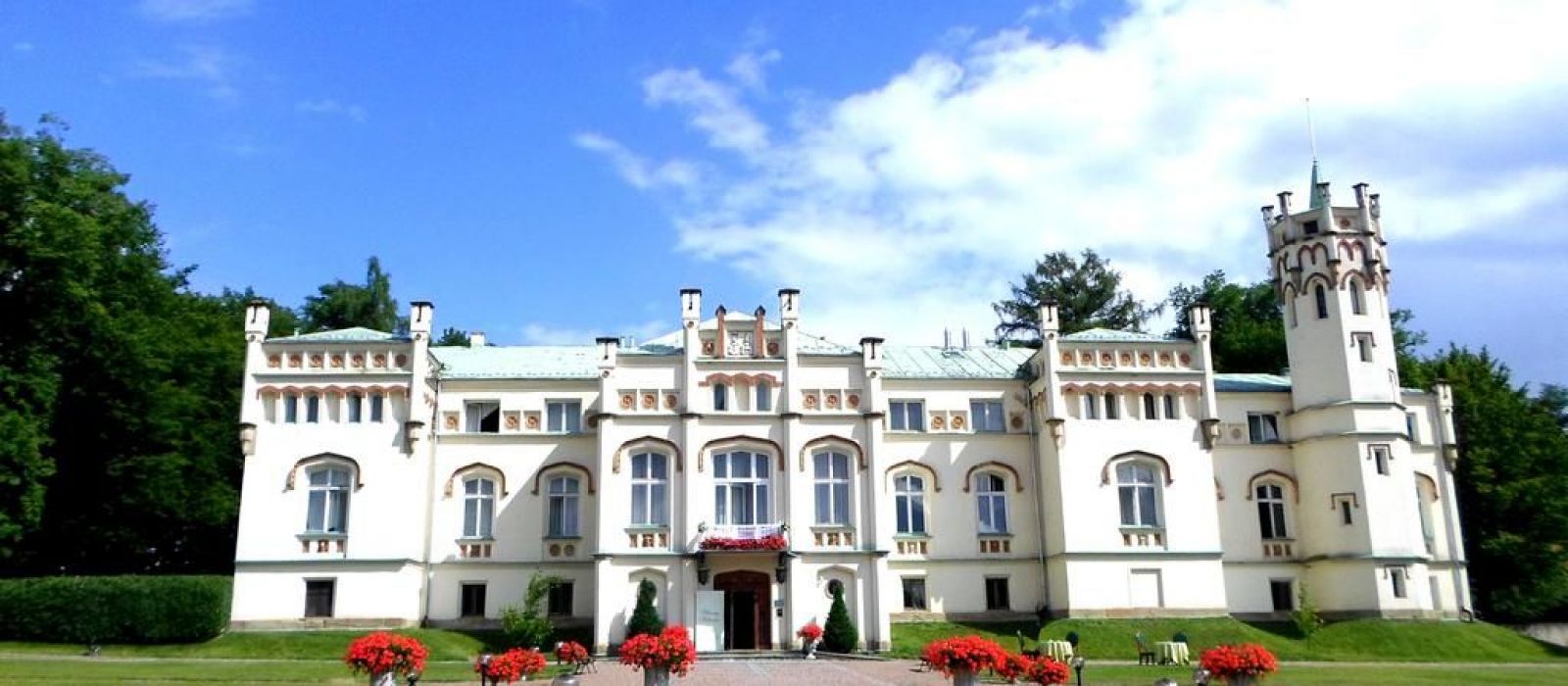
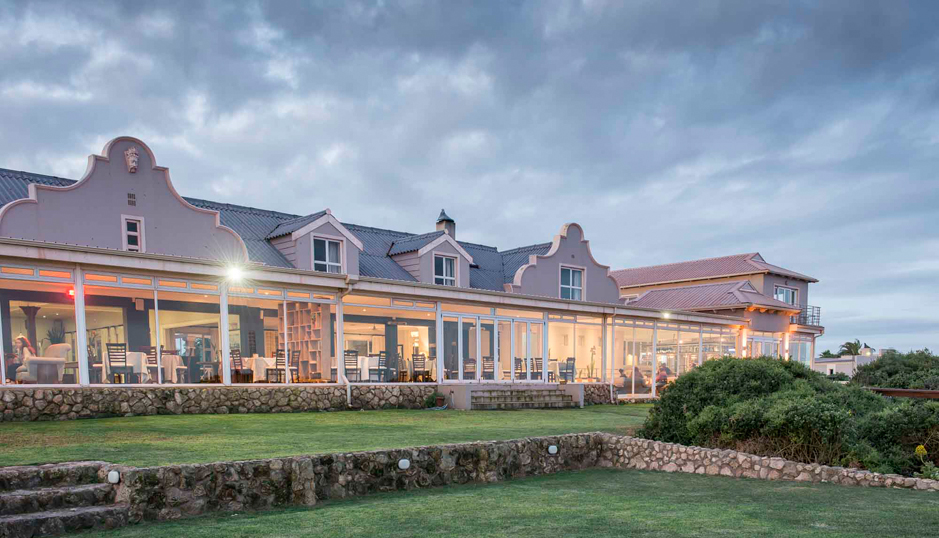
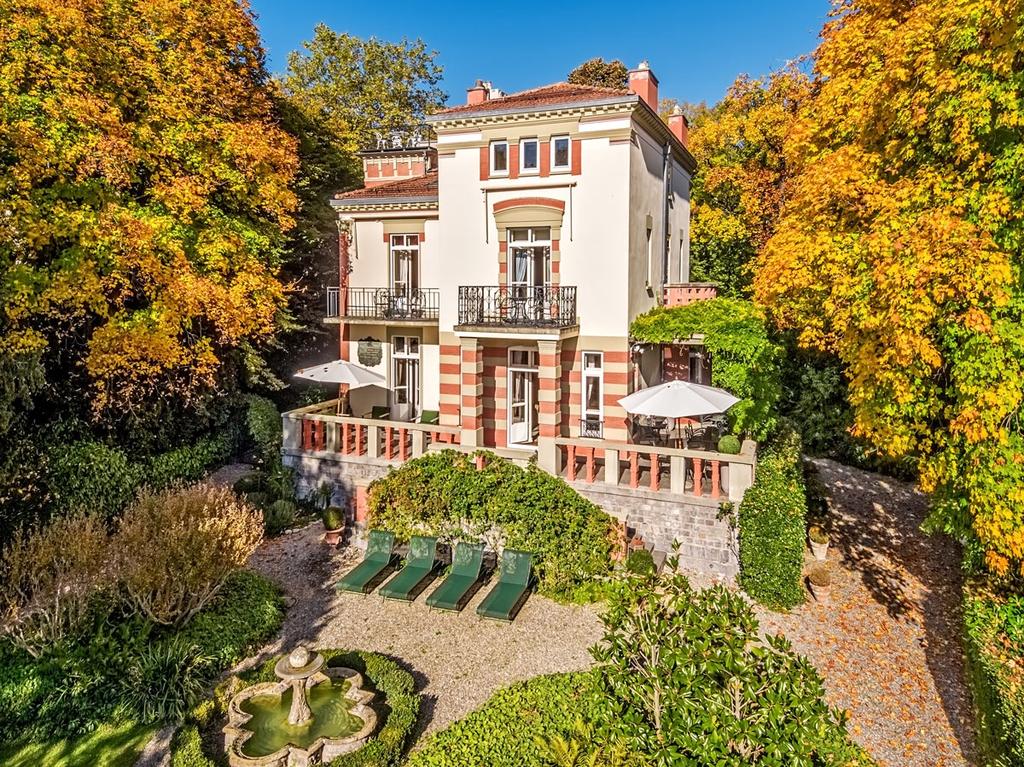
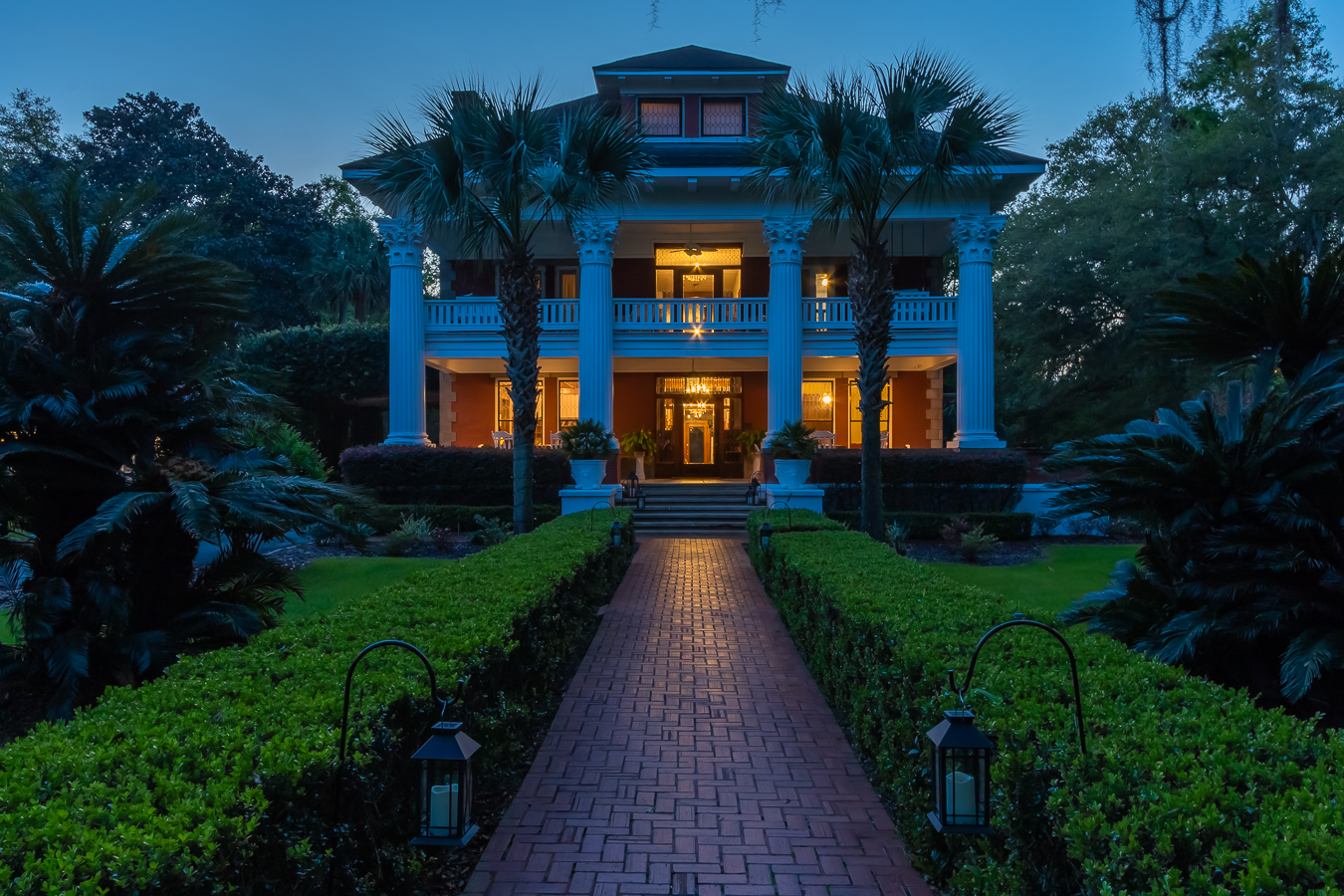
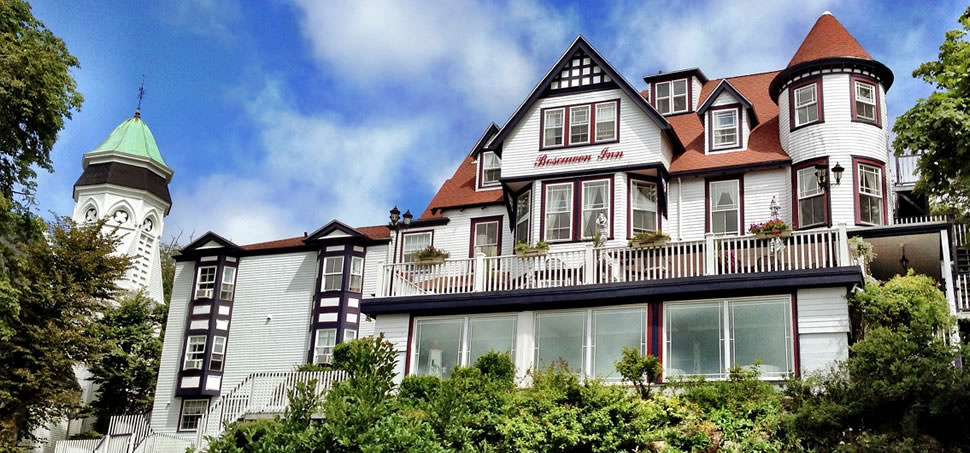
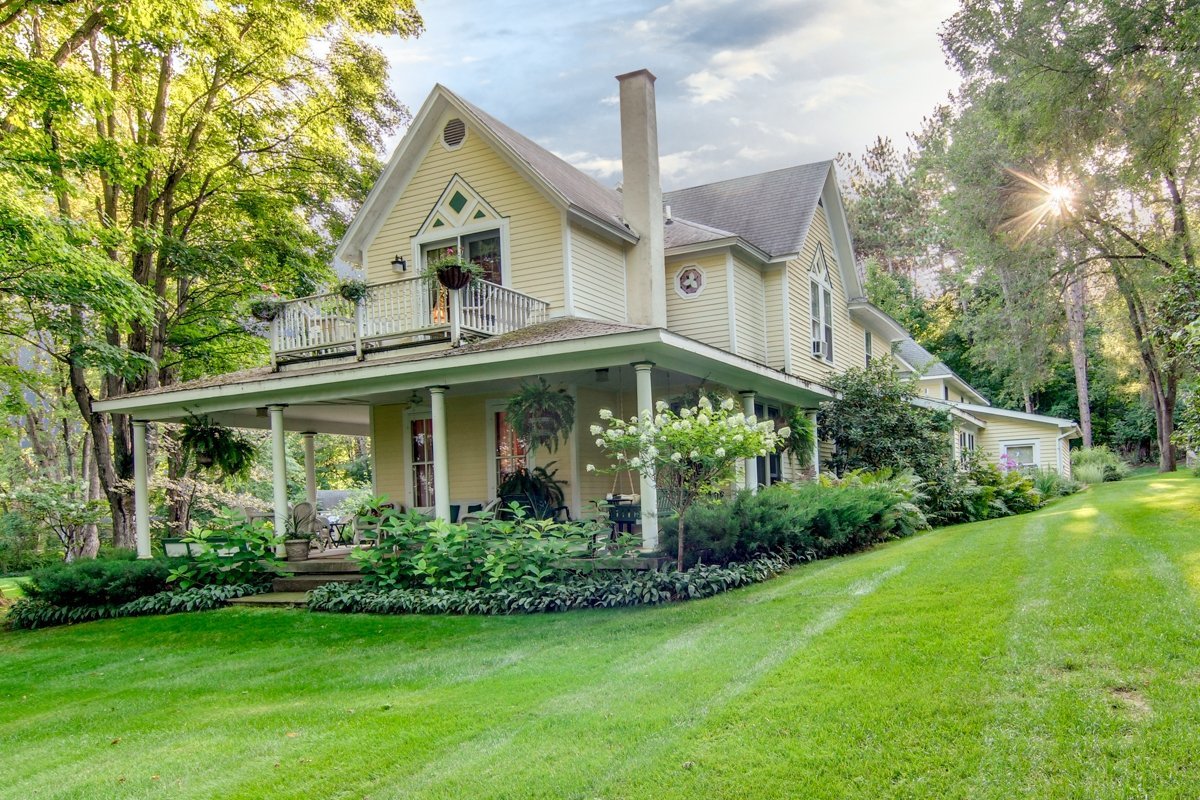







































































 Hotel, Conferncing & Wedding Venue
Hotel, Conferncing & Wedding Venue
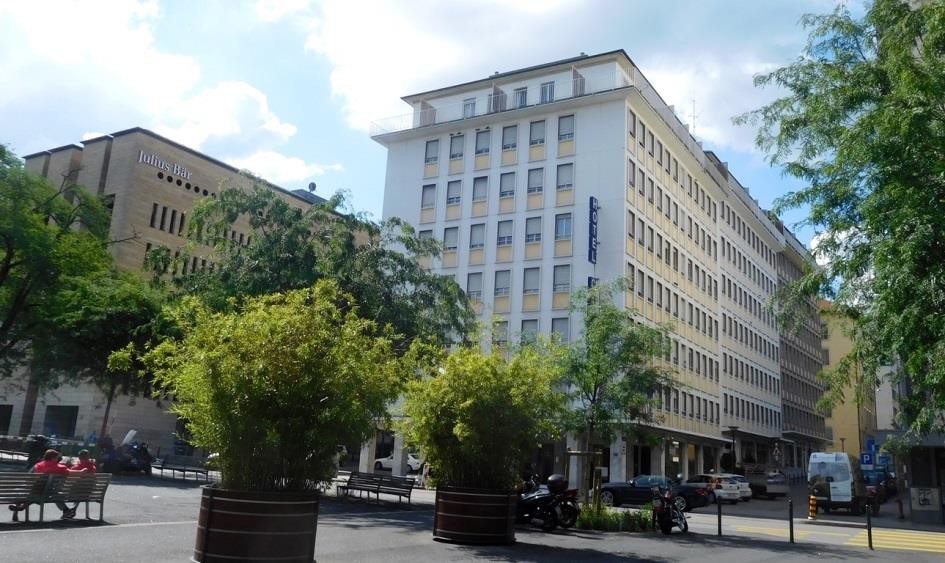
Stutterheim, Eastern Cape, South Africa
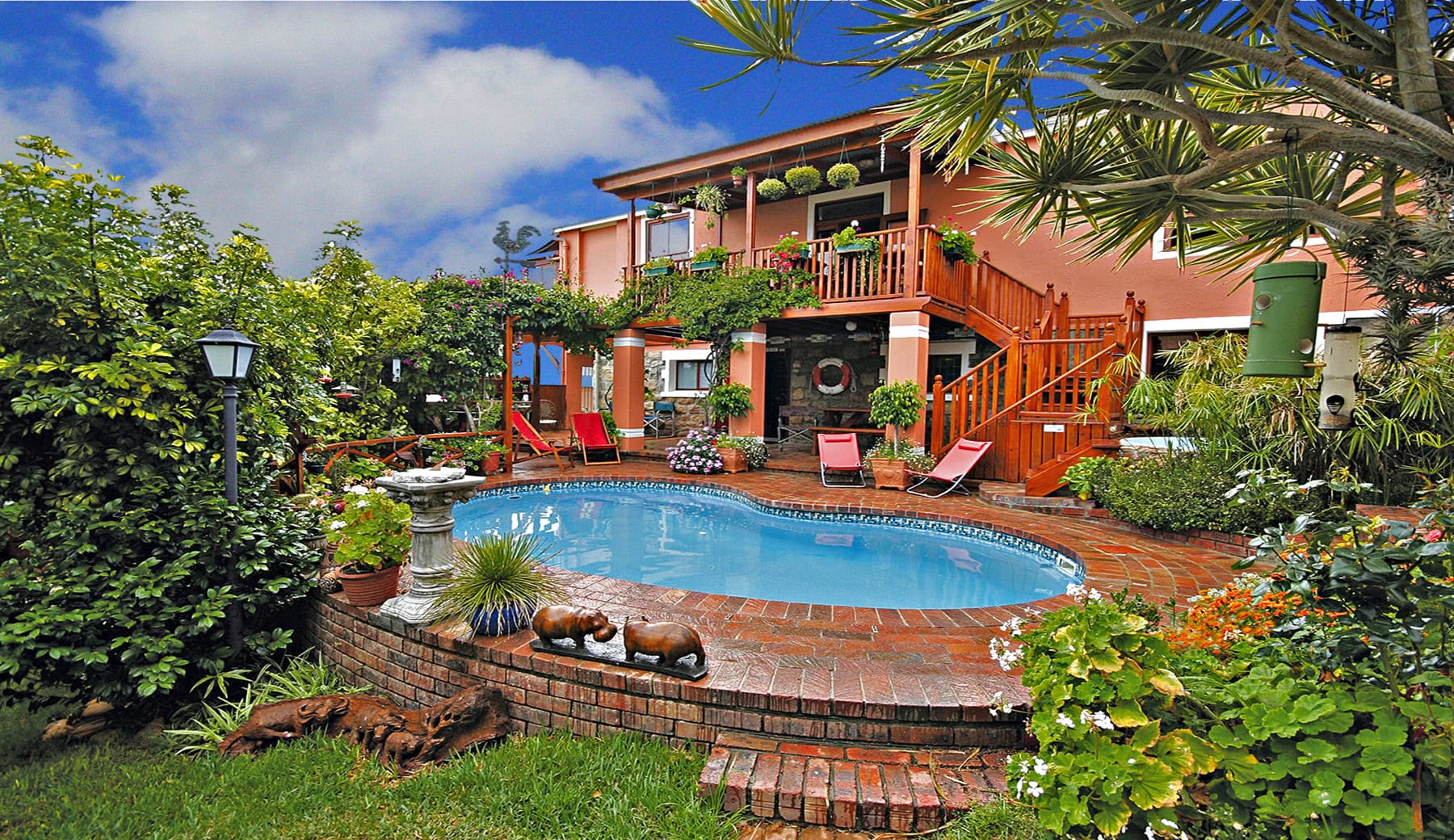
About us
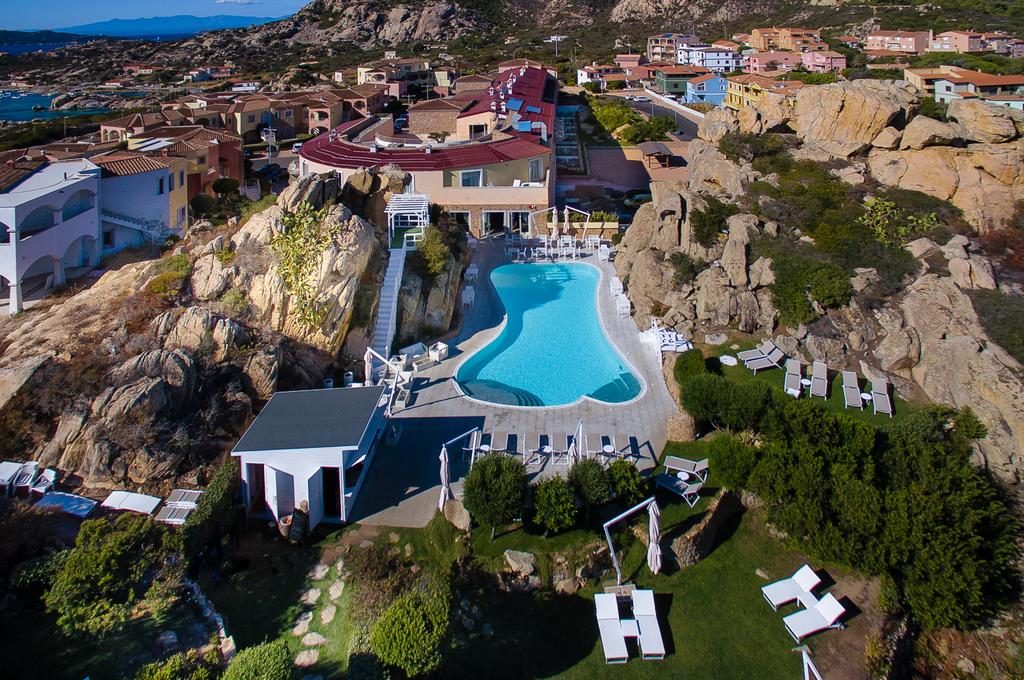
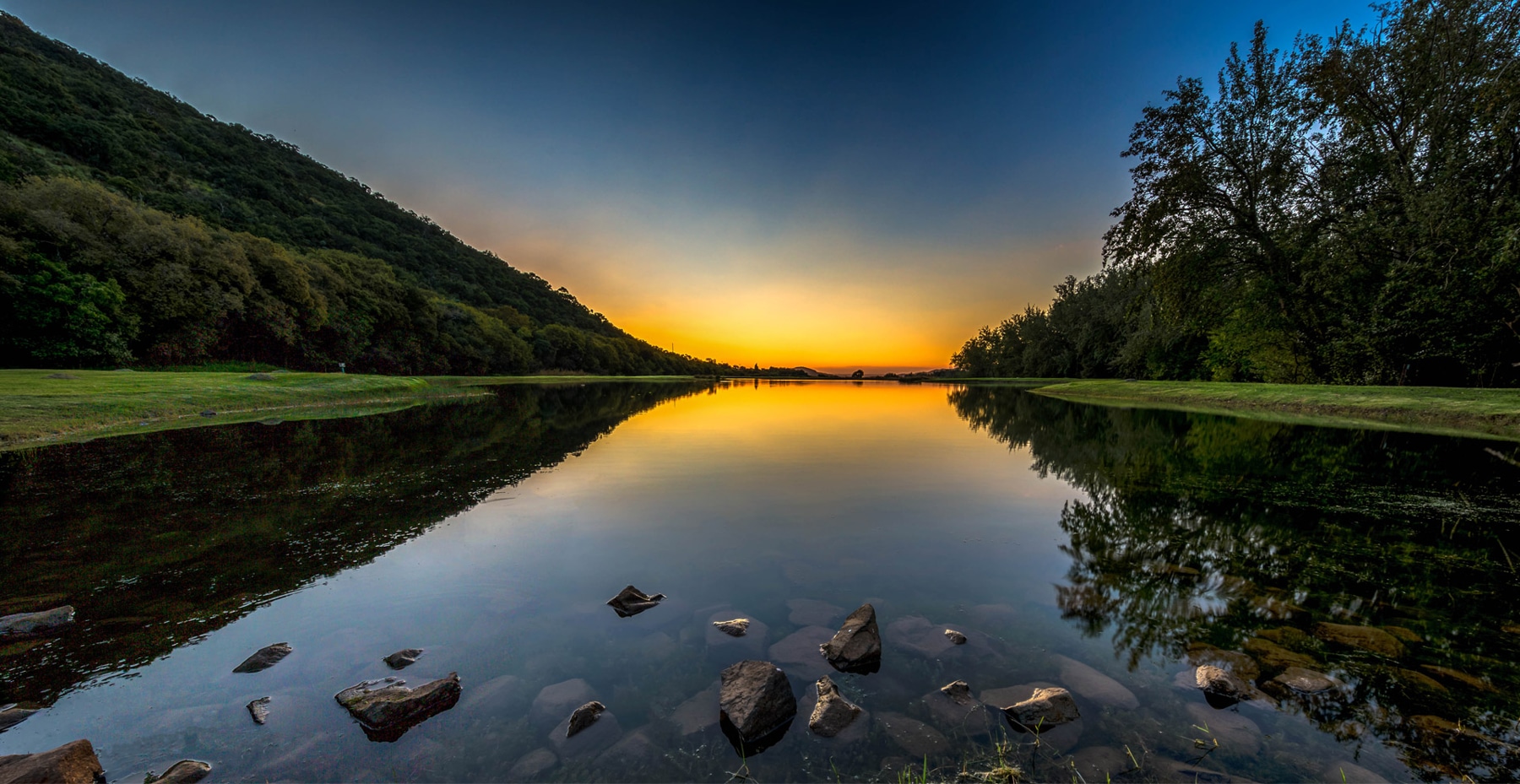
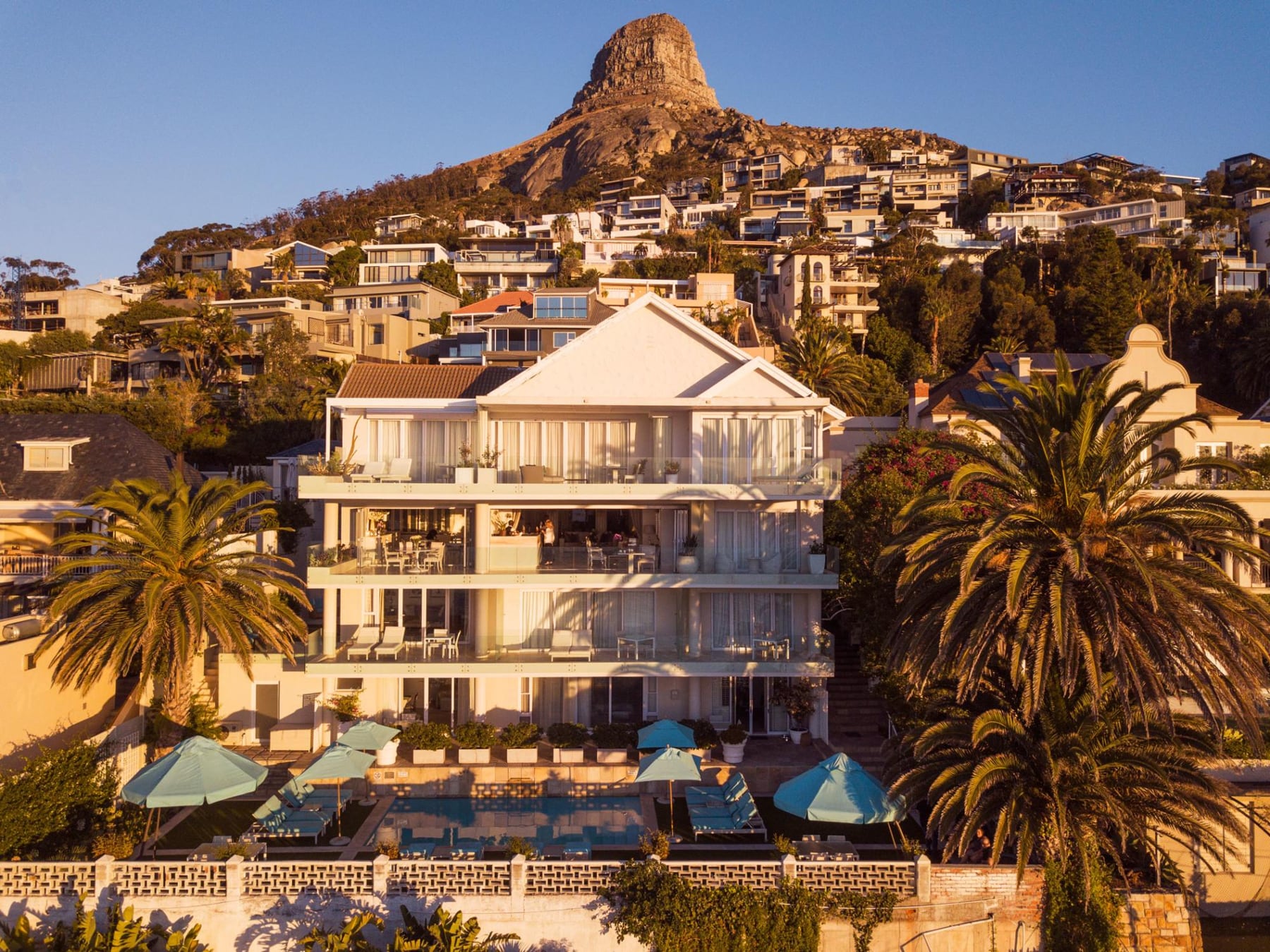
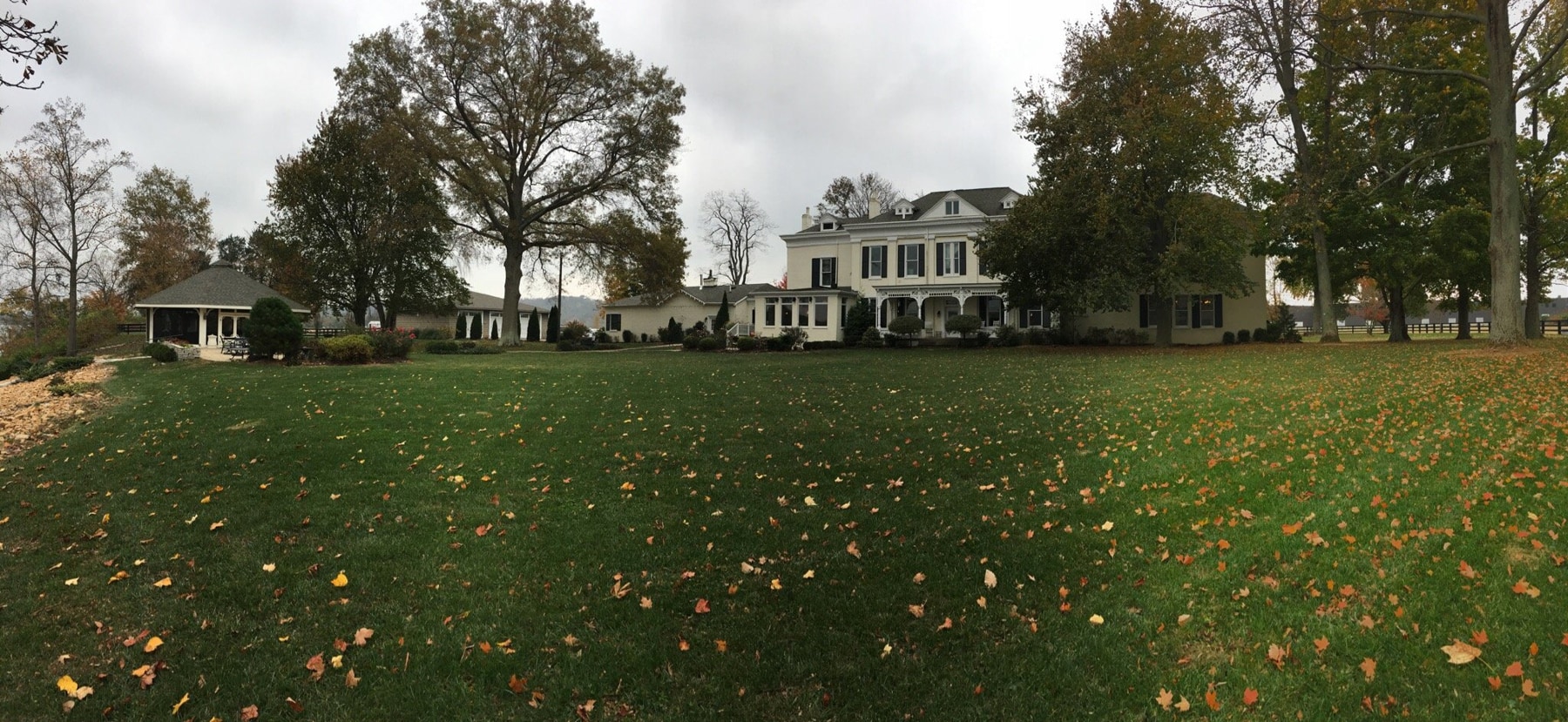
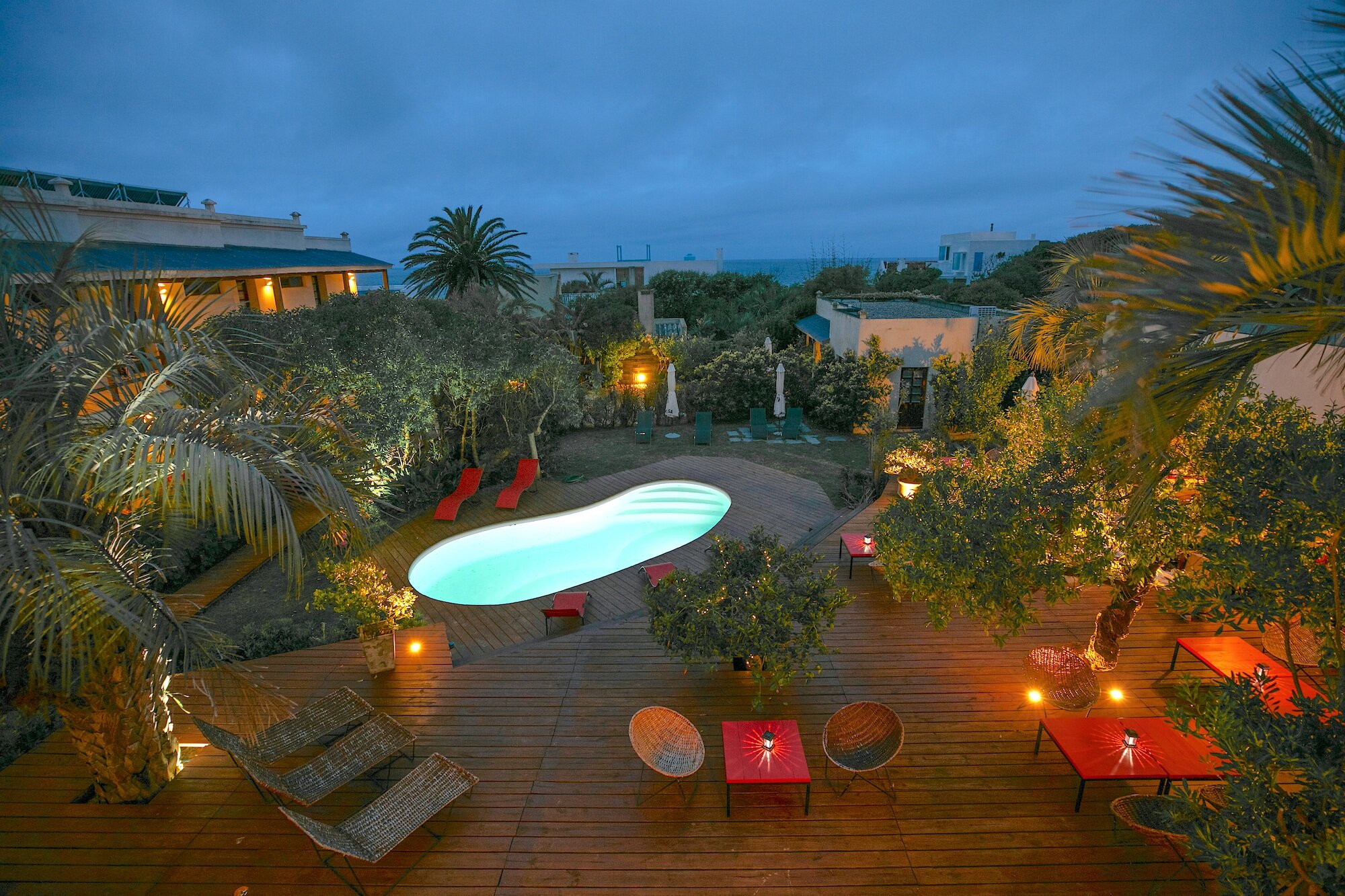
Our hotel is situated at the base of the forested Amatola Mountains and enjoys sweeping views of the mountain and indigenous forest.
The geographical location of the hotel in the province of the Eastern Cape is conveniently close to East London, Bhisho and King Williams Town. It is also a well-placed stop-over for travellers on the N2 from Durban or the N6 from Johannesburg.
Our Hotel is never without water or electricity.
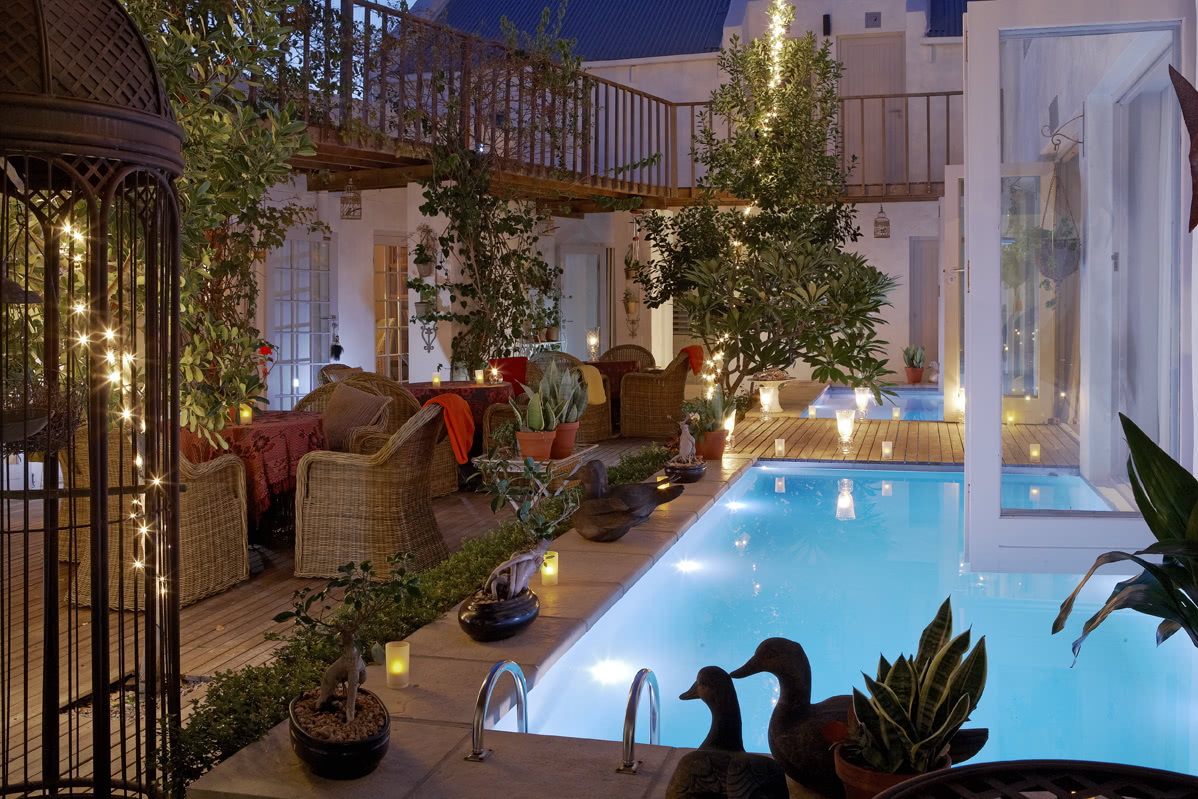
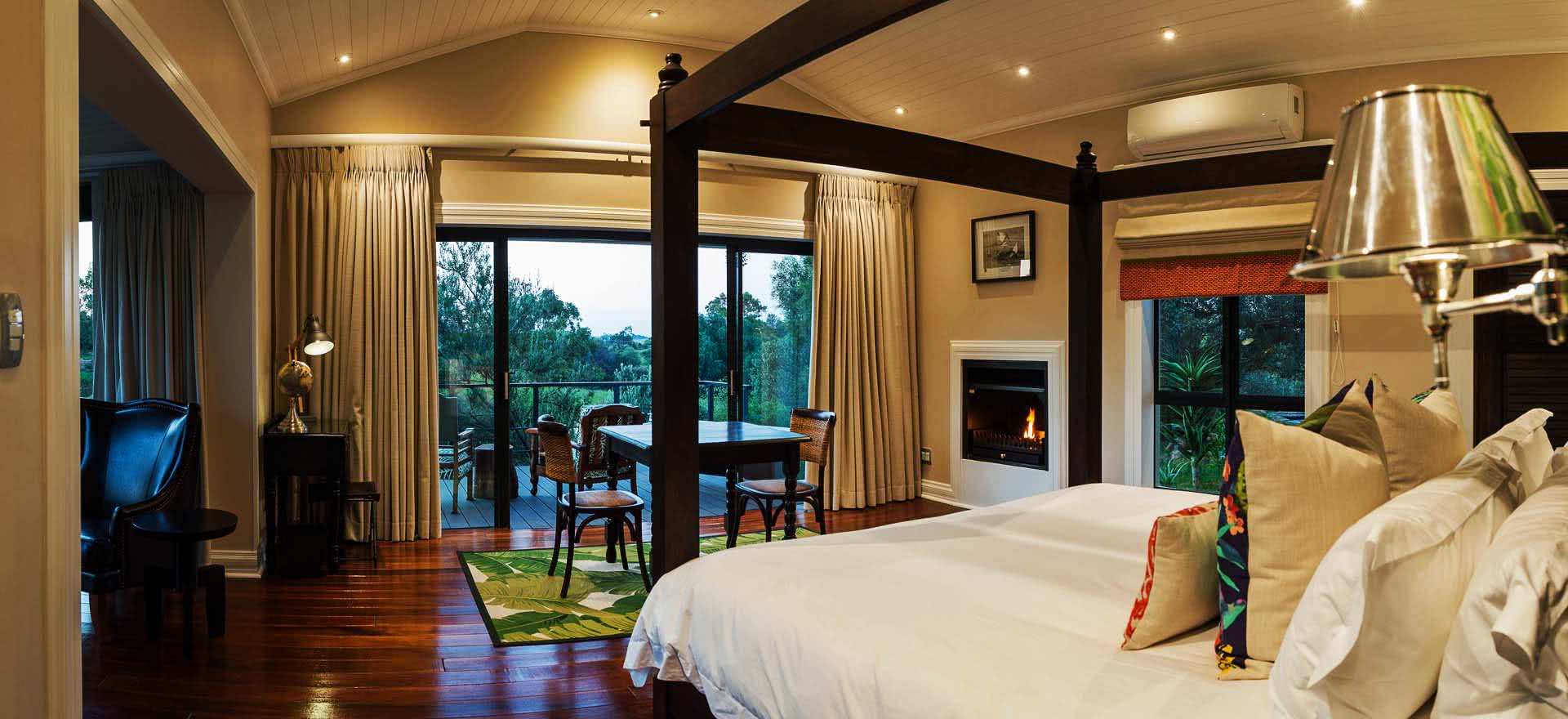
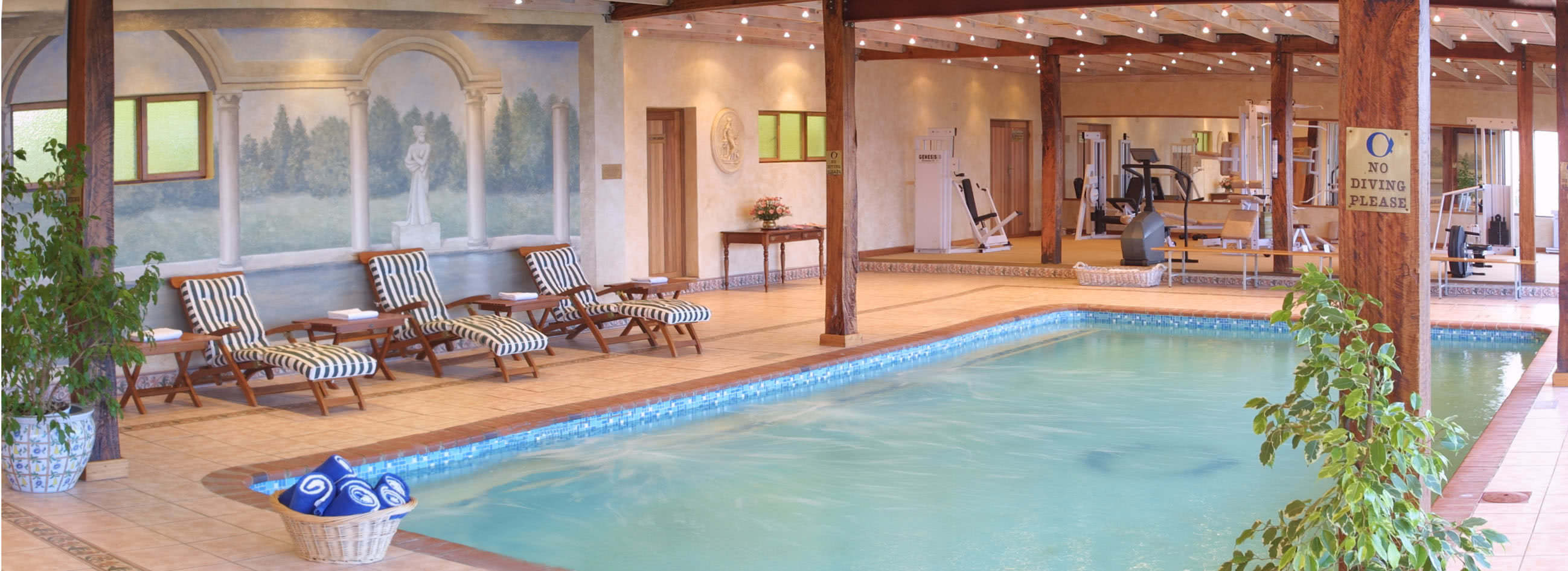
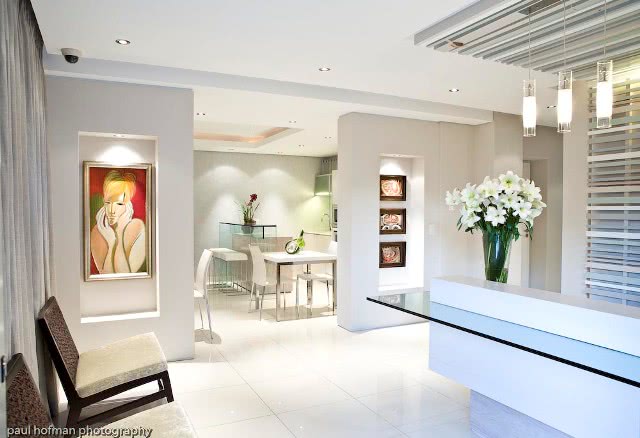
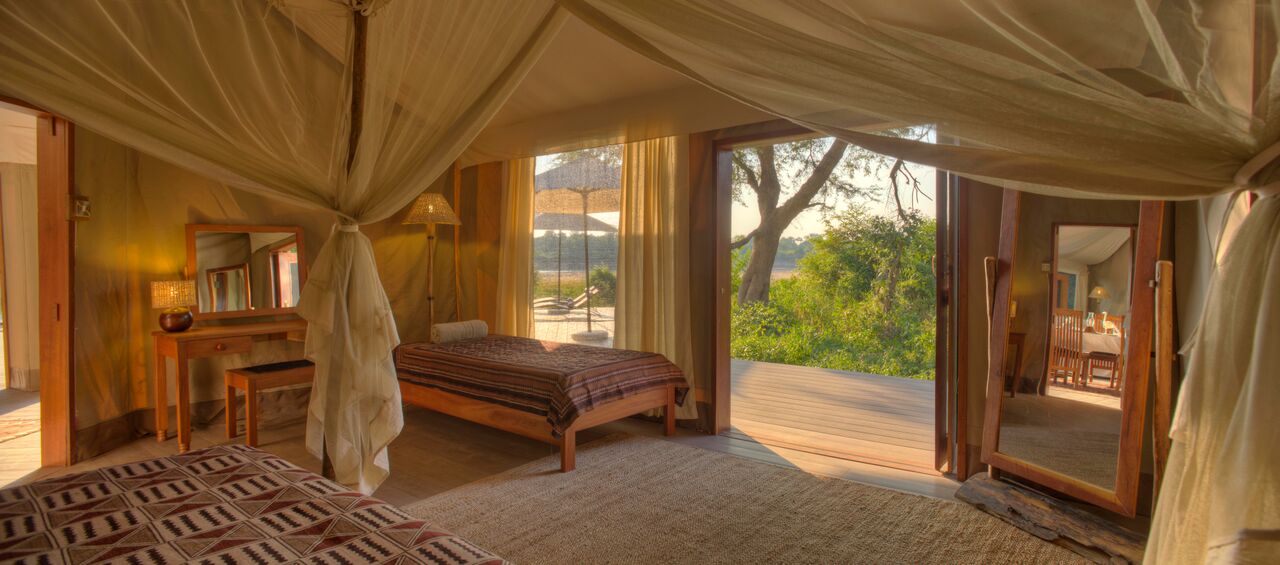
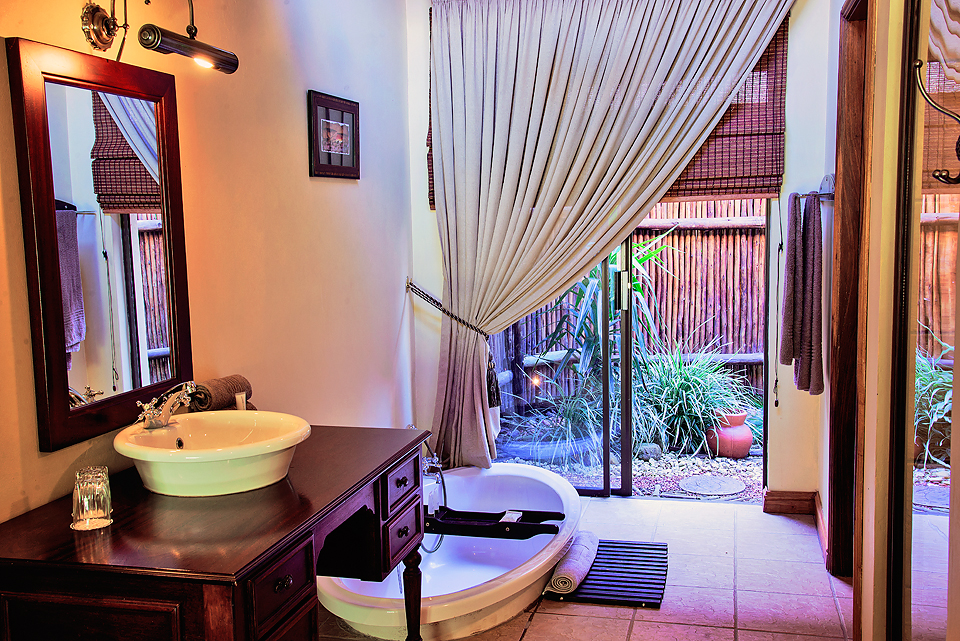
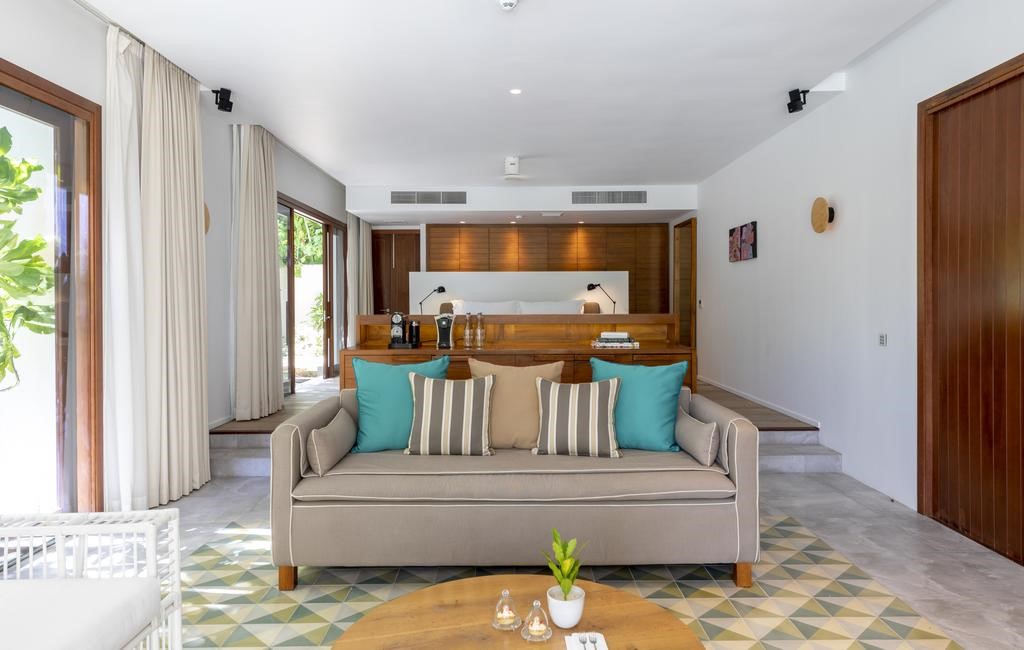
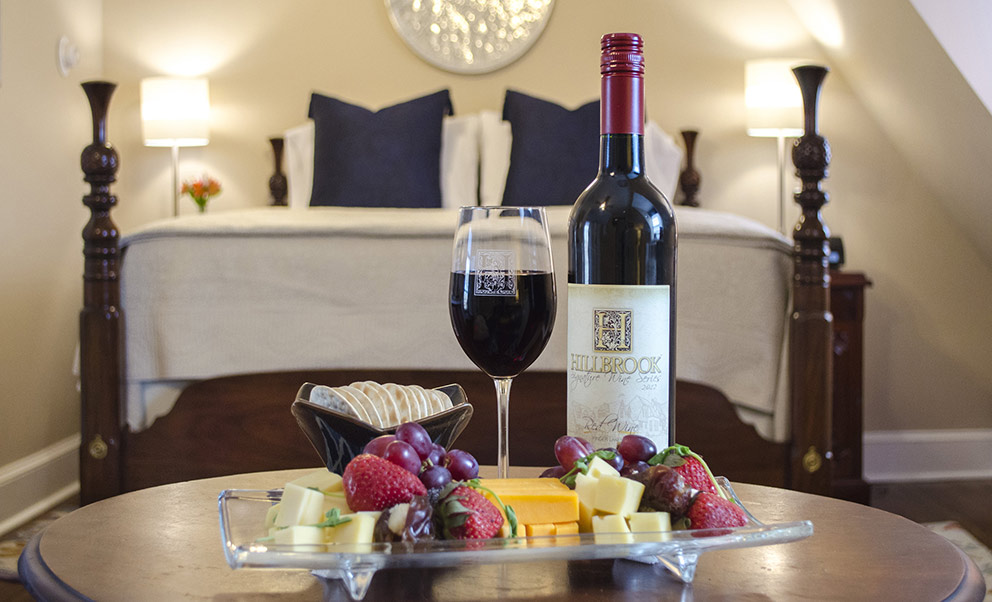
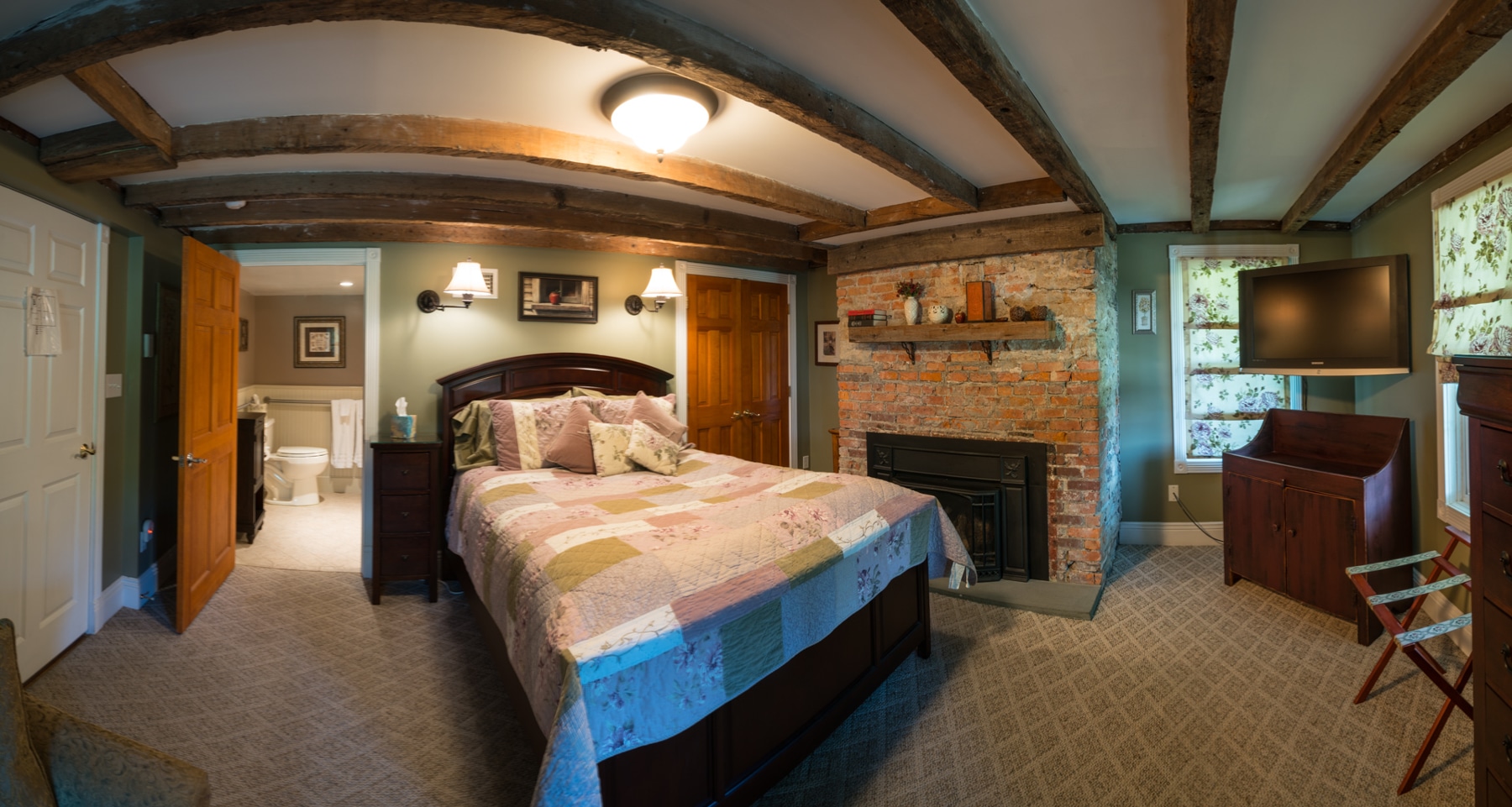
Rooms and Suites
Standard Rooms
The standard rooms are en-suite with a separate bath and shower.
The standard rooms are equipped with tea and coffee-making facilities, TVs, electric blankets and wall heaters.
Suites
The suites are spacious with ther own private entrances, outdoor seating areas in a garden setting. Each of these suites are equipped with a sleeper couch or extra bed. Ideal for parents with young children.
The suites are equipped with tea and coffee-making facilities, TVs, electric blankets and wall heaters.
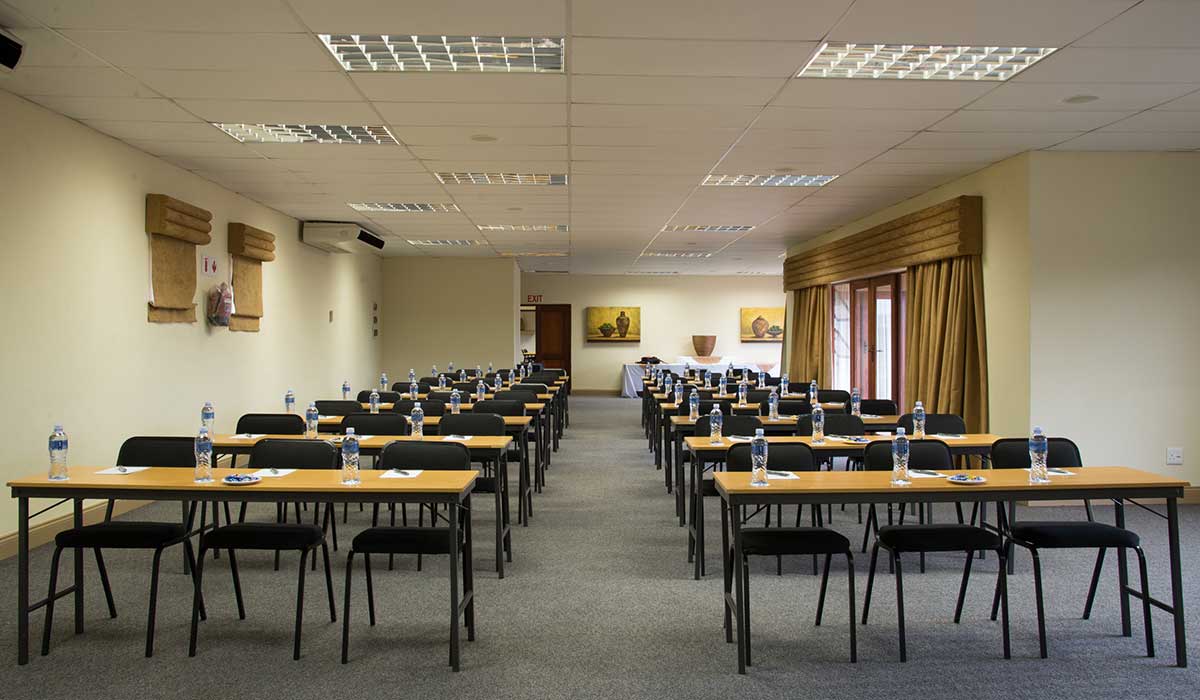
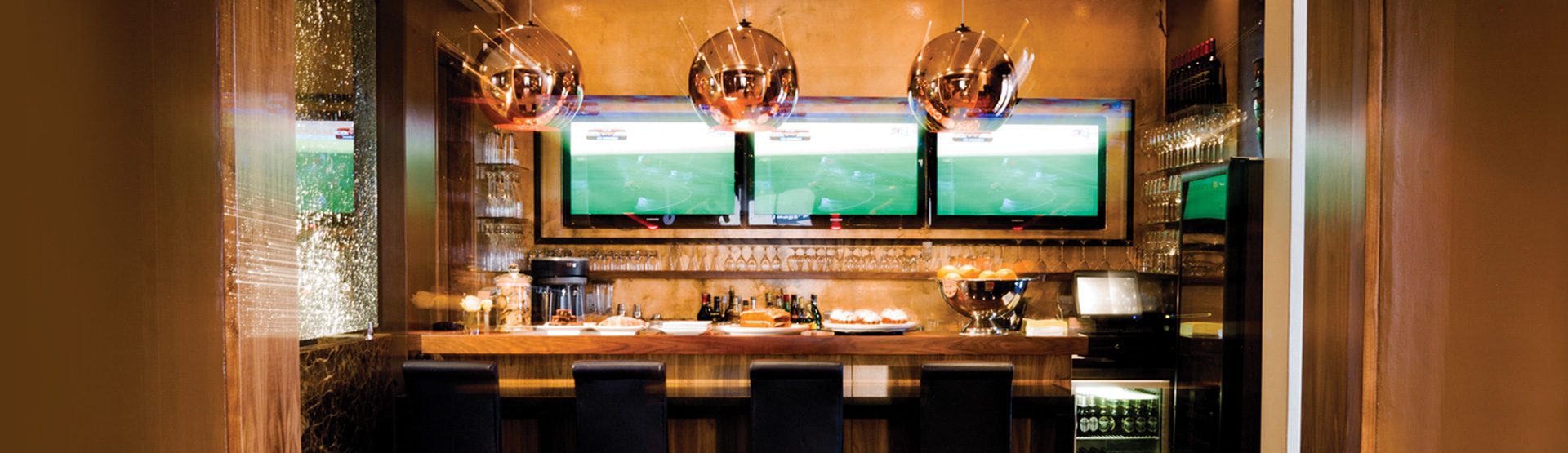
Conference Centre
All three venues are specifically designed and built for conferencing purposes with high-quality fixtures, ideal for conferences, training seminars, presentations, product launches, and meetings. Conferencing facilities include:
Cliff Jacobs (Nat Dpl Hotel Man (UJ). MPRE. GA Level 5 TEFL) Managing Principal / CEO Exquisite Hotel Consultants (Pty) Ltd Mobile: +27 (0) 84 413 1071 / +27 (0) 61 716 6951 Email: cliff@exquisitehotelconsultants.com Web: https://www.exquisitehotelconsultants.com © All rights reserved Terms and Conditions apply Scroll down to view our Hospitality Properties and Businesses for sale or lease or lease-to-buy or partnership arrangement or management agreement arrangement.



 Name: BondExcel
Name: BondExcel Mortgage Origination
We interface with all of the major banks in South Africa to ensure that you get the right home loan solution at the best possible rate.
Looking forward to assist you with your home loan application!
 Name: Businessentials For Hospitality
Name: Businessentials For Hospitality Hospitality Consulting, Accounting, Bookkeeping and Payroll Services
 Name: Capital Efficiency Group
Name: Capital Efficiency Group Corporate Finance, Tax & Accounting and Treasury Services.
Attorneys, Notaries and Conveyancers
 Name: D E I R D R E R E N N I E R S Interior Design
Name: D E I R D R E R E N N I E R S Interior Design Interior Design
 Name: De Leeuw Valuers Cape Town
Name: De Leeuw Valuers Cape Town Property Valuation Services
 Name: E C Mobility
Name: E C Mobility International property, law and immigration
 Name: Edward Tokolo Kasete
Name: Edward Tokolo Kasete Real Estate Specialist - Our Associate in Namibia
We offer an international platform of specialist hospitality property and/or business brokering services by listing and marketing for sale or lease or by investment partner arrangement or management agreement arrangement of a variety of hospitality products (i.e. hotels, resorts, boutique hotels, guest houses, guest lodges, B&Bs, game resorts, wine farms, yachts, cruise liners, etc) through our association with EC Mobility (in Portugal and Spain), BON Hotels (Africa), Giovanni Conti (Italy, North and East Africa, Sri Lanka), Nuno Boquinhas (Portugal, Azores, Madeira, Mozambique), Property 24, Seeff Property Services, Harcourts, Realnet, RE/MAX, Dogon Property Group, Rawson Estates, among many other prominent commercial estate agencies throughout Southern Africa - and now we are entering other African Countries on the East and West Coasts of Africa and moving further abroad! To date, Exquisite Hotel Consultants has a presence in over 80 countries - and counting...
Working with the above-mentioned agencies and others provides the largest possible reach nationally and internationally for all prospective buyers and sellers wishing to enter or exit the Hospitality Industry.
Sister websites have been opened in the following countries: United Kingdom: see www.exquisitehotelconsultants.co.uk, and in Germany: see www.exquisitehotelconsultants.de, and in the United States of America: see www.exquisitehotelconsultants.us.
Please note that several of our hospitality properties and/or businesses for sale or lease or through business partnership arrangements or management contracts are officially "Off-Market" - mainly for privacy reasons. Therefore, they are not listed as part of our hospitality properties/businesses for sale or lease stock. Please contact me for further details.
Should you be considering to sell or buy or lease or obtain a partnership arrangement or management agreement arrangement for your hotel, boutique hotel, resort, guest house, B&B, game lodge, game resort, guest farm, yacht or cruise liner etc, I would be most pleased to provide you with further details of our way of working to effectively market and sell your property(ies) and/or business(es).
 Name: Electrolux Professional
Name: Electrolux Professional Food Service, Beverage and Laundry Solutions
Electrolux Professional is a leading global provider of foodservice, beverage and laundry solutions, serving a wide range of customers globally, from restaurants and hotels to healthcare, educational and other service facilities.
 Name: Exquisite Hotel Consultants' Hospitality Training Department
Name: Exquisite Hotel Consultants' Hospitality Training Department Learn to speak Hotel English (one-to-one online course)
Our TEFL trained tutors teach the following functions
The course consists of 21 lessons (4 to 5 one-hour lessons per month).
 Name: FVE Interiors
Name: FVE Interiors Interior Design
 Name: Healing Earth
Name: Healing Earth Hotel Amenities - inspired by Africa
 Name: Hospro
Name: Hospro Hospitality Consultancy and Procurement
 Name: Hotel Revenue Management
Name: Hotel Revenue Management Revenue (yield) Management
Online room inventory Distribution & Rates optimisation
Implementation of Best Available Rate (BAR), in conjunction with point 1 & 2
 Name: Indigo Real Estate Agency
Name: Indigo Real Estate Agency Real Estate Agency - Our Associate in Mozambique
 Name: Lisa Dunn - Tourism Grading Assessor
Name: Lisa Dunn - Tourism Grading Assessor Tourism Grading Assessment
 Name: Ooba (Pty) Ltd
Name: Ooba (Pty) Ltd Mortgage Origination
ooba offers you:
 Name: SK Sambu Tours & Transfers
Name: SK Sambu Tours & Transfers Johannesburg based Tours & Transfers Operator
We look forward to being of service to you.
Kind regards
King Sambu
 Name: Soul Private Collection
Name: Soul Private Collection Hotel Management and Marketing
 Name: The Dumb Butler Hospitality Suppliers
Name: The Dumb Butler Hospitality Suppliers Hotel Linen Suppliers
LUX Award Winners 2021 for The Best Hospitality Suppliers. We are a proudly South African brand established in 2006.
We Supply:
 Name: The High Street Auction Company
Name: The High Street Auction Company
Property Auctioneers
Appreciating Property Value
 Name: Touch Point Retail
Name: Touch Point Retail Smart Interior Design
Cliff Jacobs (Nat Dpl Hotel Man (UJ). MPRE. GA Level 5 TEFL) Managing Principal / CEO Exquisite Hotel Consultants (Pty) Ltd Mobile: +27 (0) 84 413 1071 / +27 (0) 61 716 6951 Email: cliff@exquisitehotelconsultants.com Web: https://www.exquisitehotelconsultants.com © All rights reserved Terms and Conditions apply Scroll down to view our Hospitality Properties and Businesses for sale or lease or lease-to-buy or partnership arrangement or management agreement arrangement.