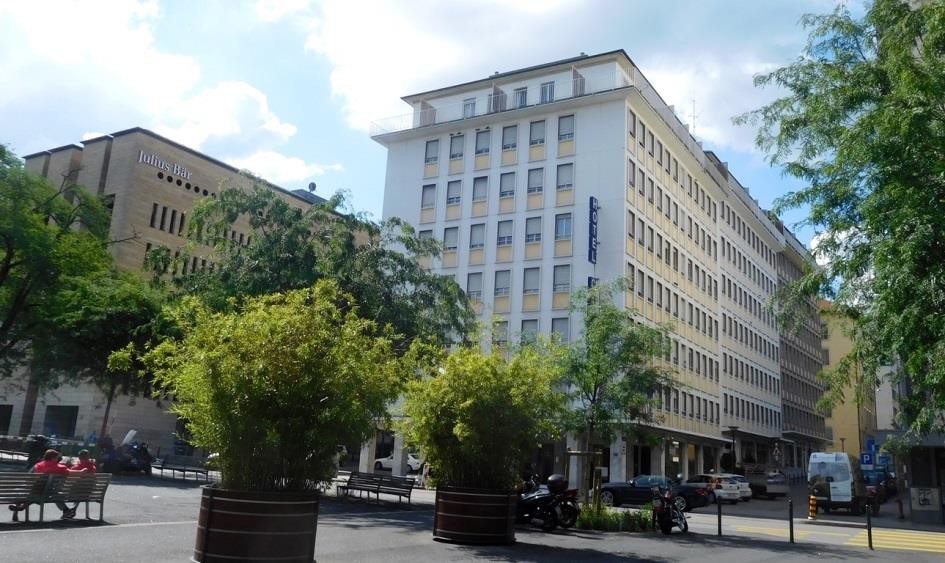
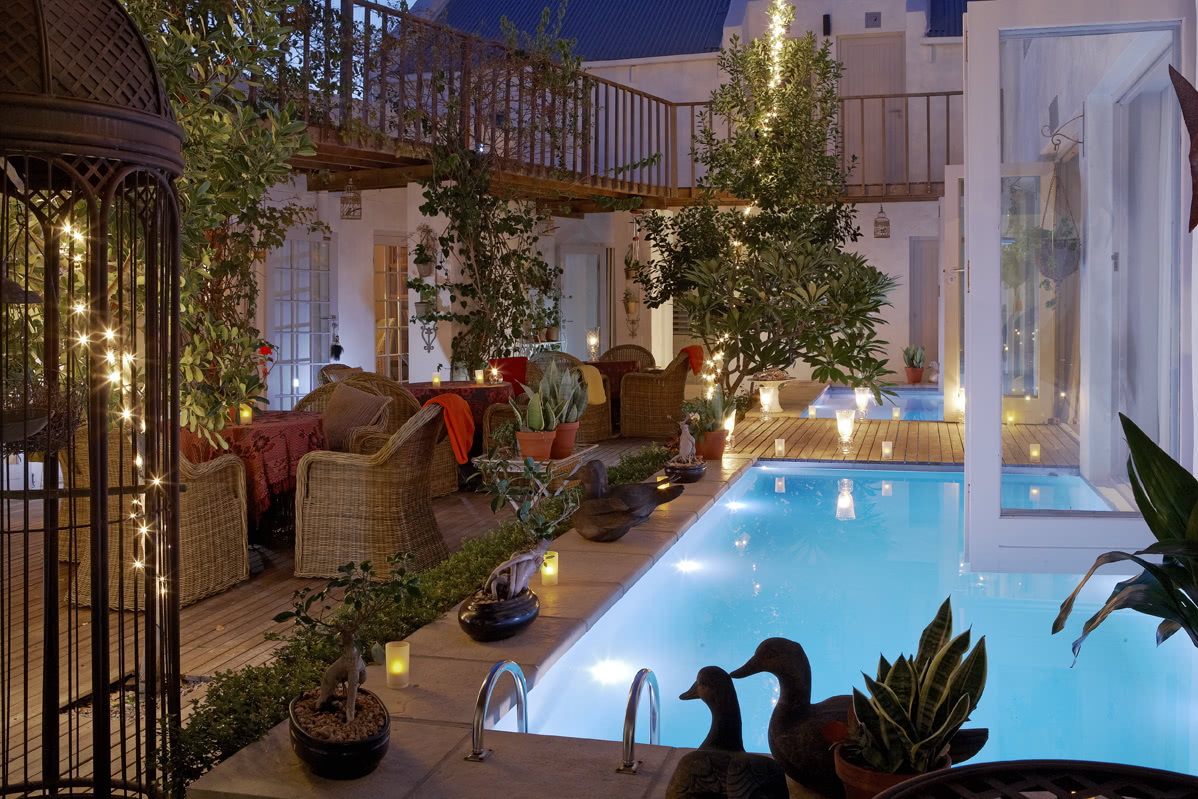
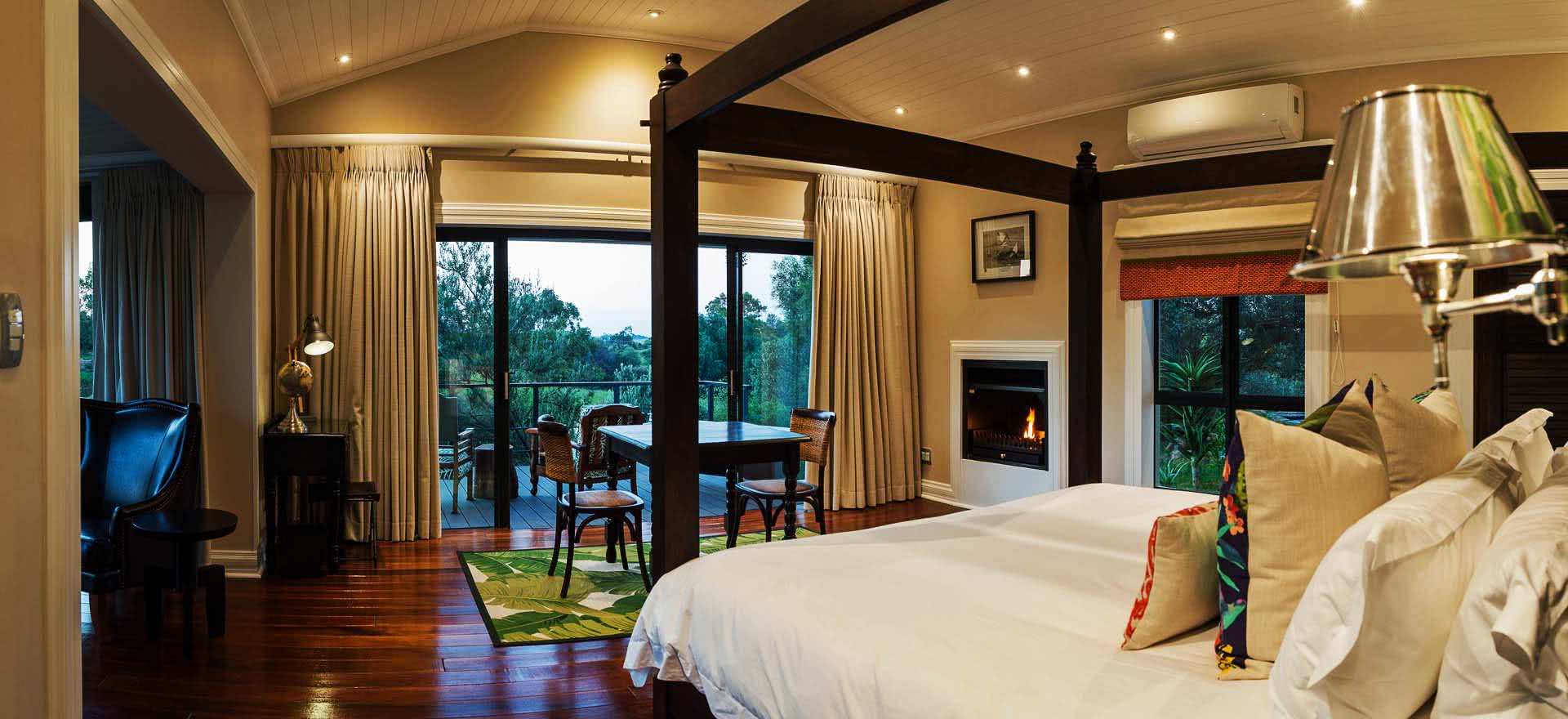
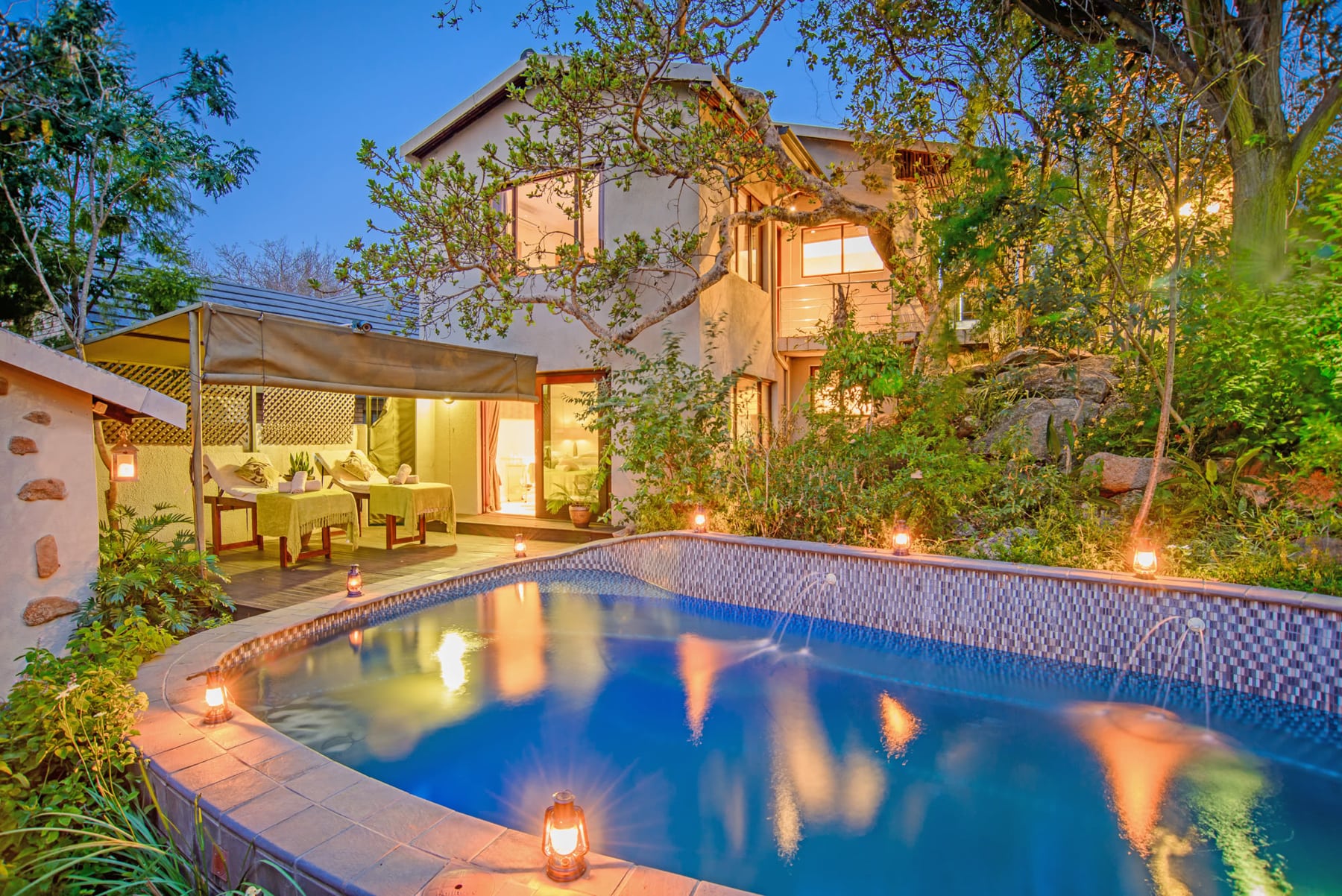
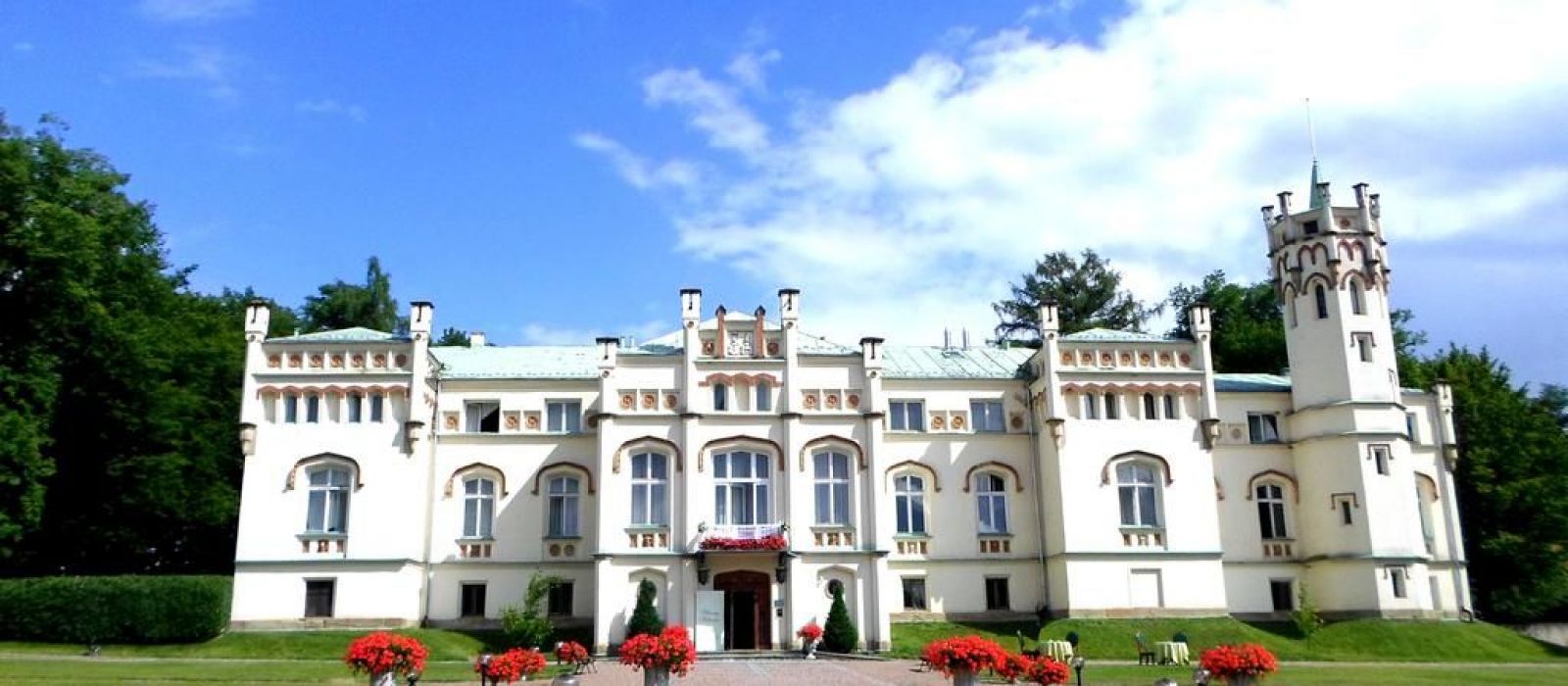
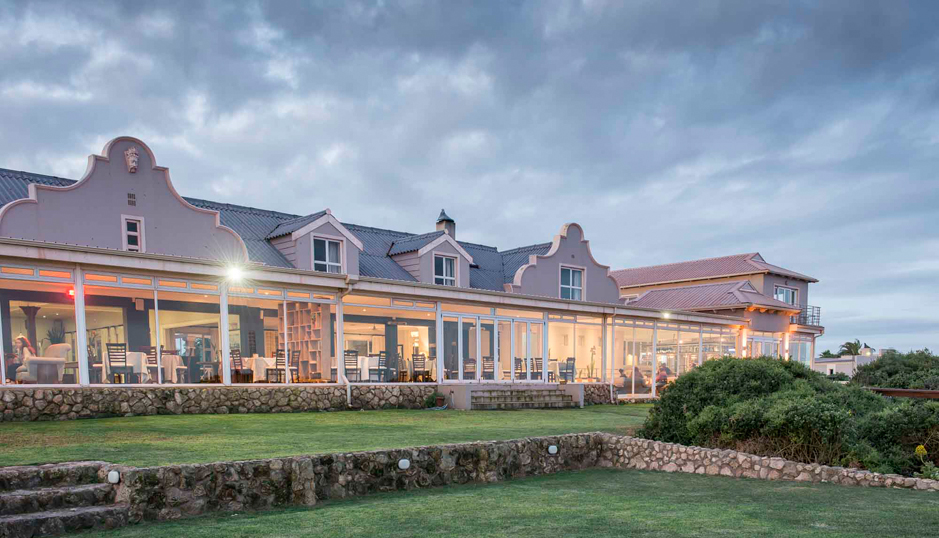
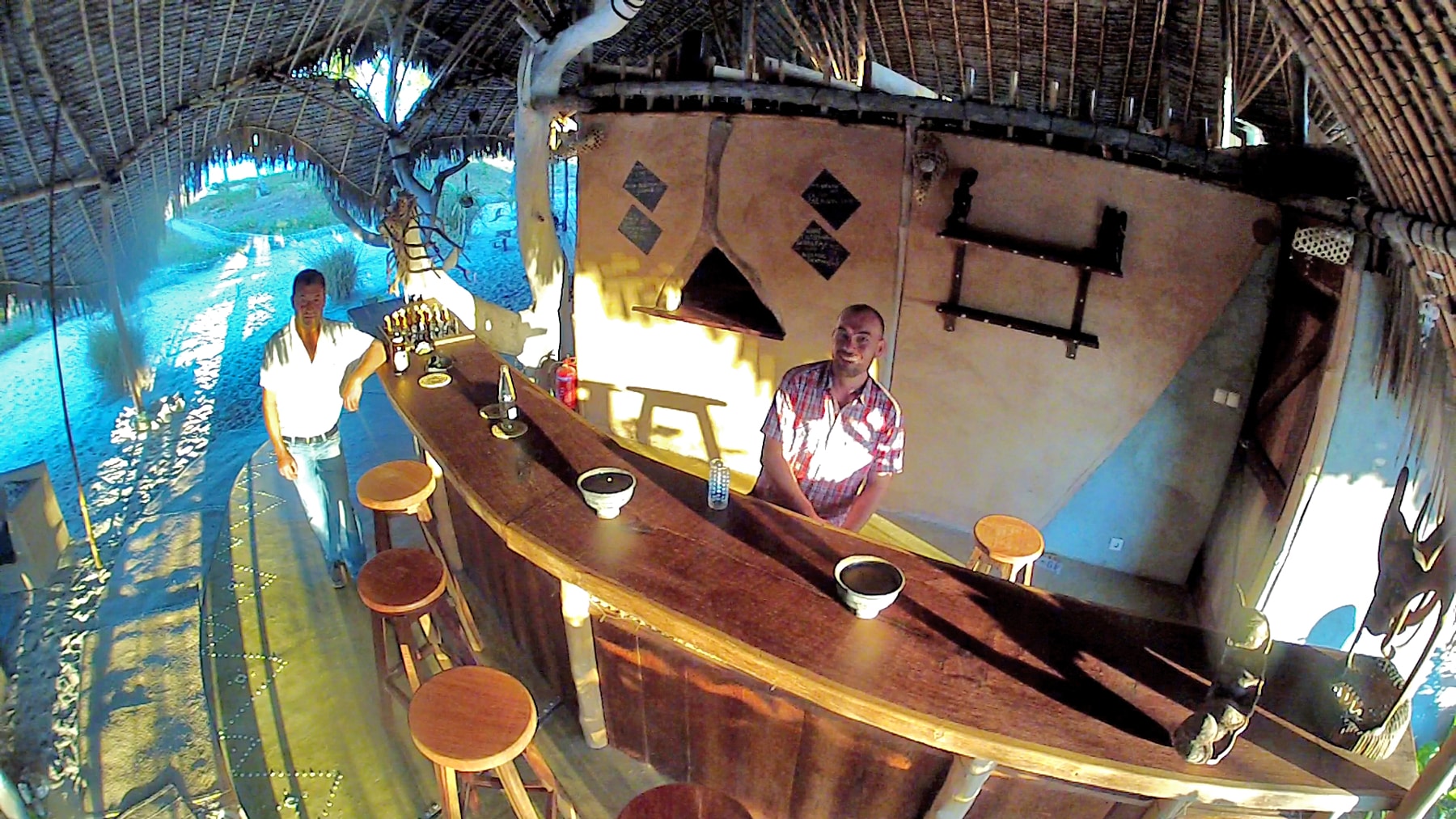
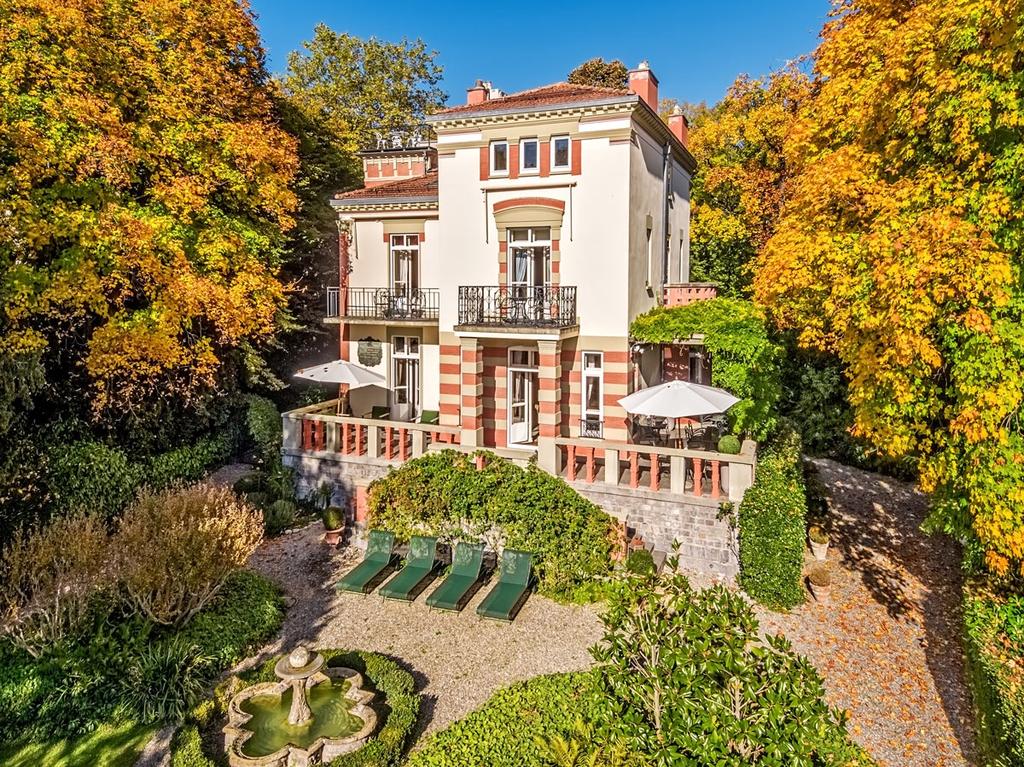
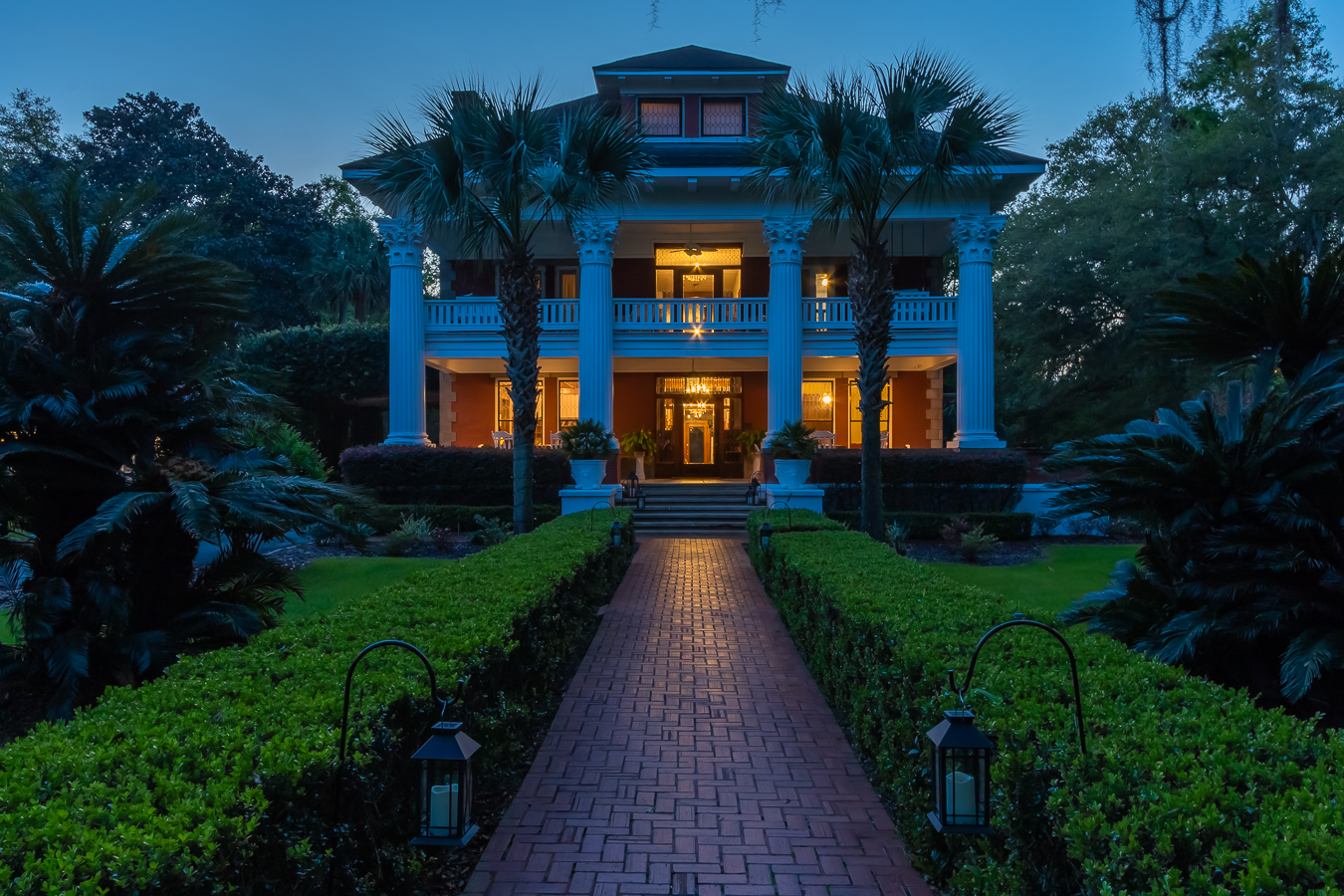
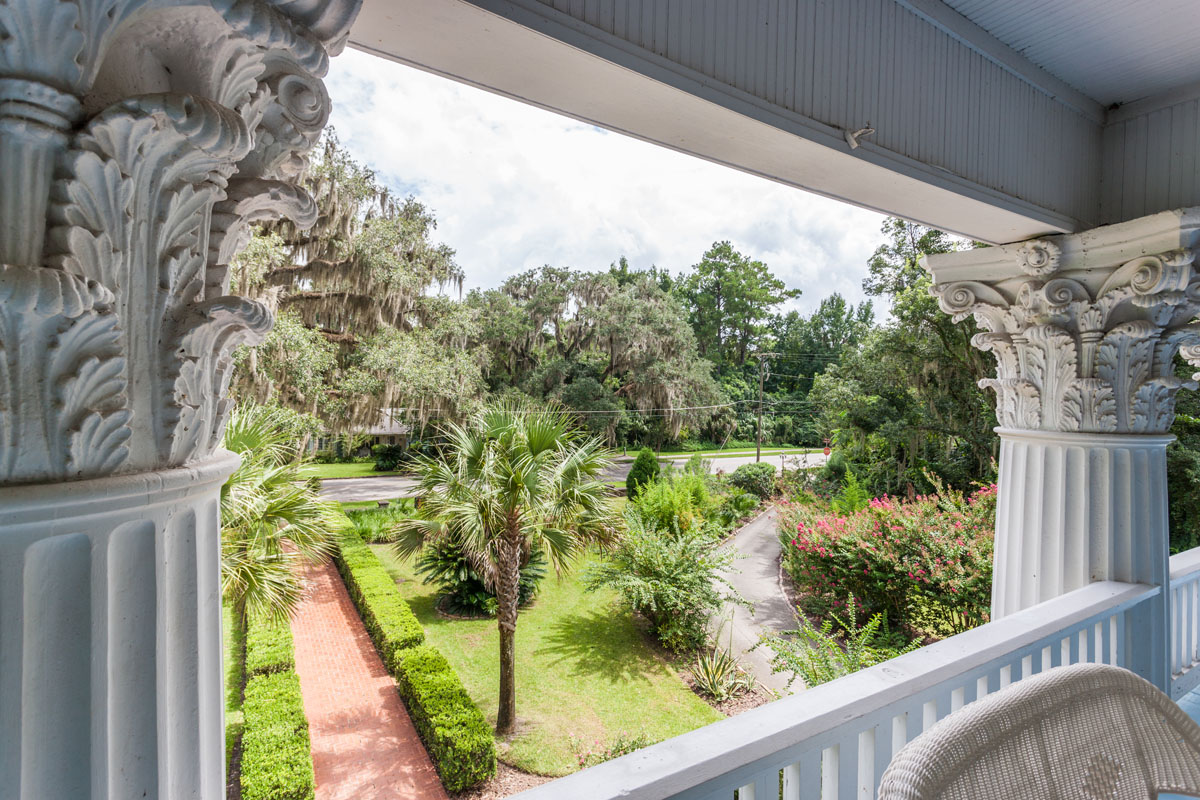
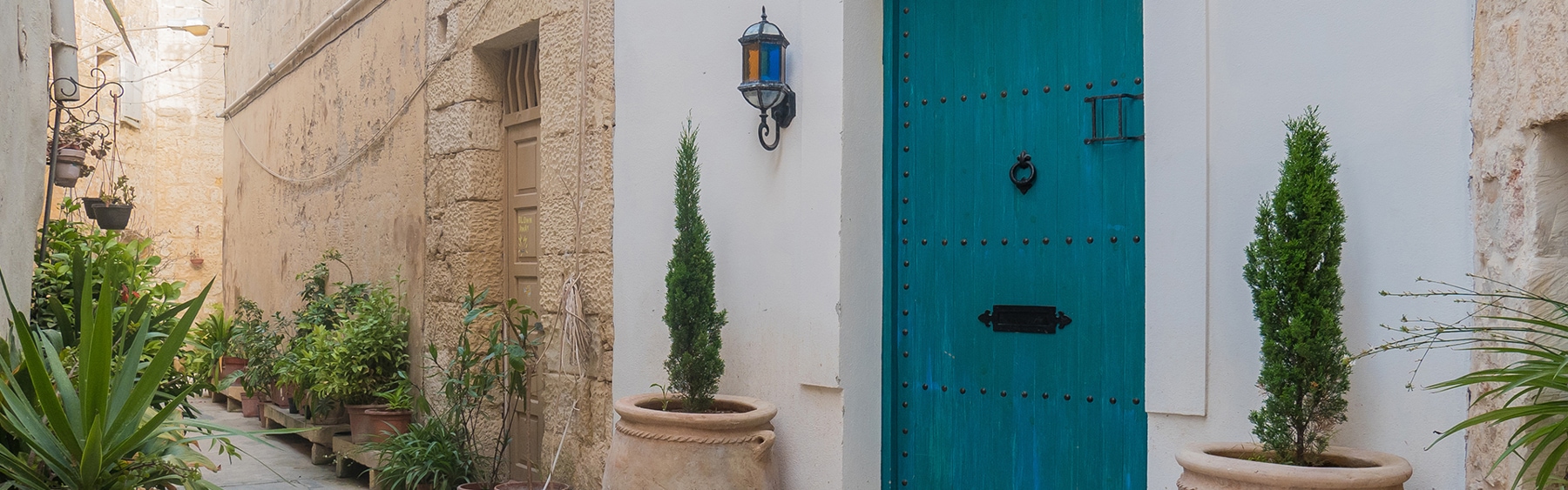
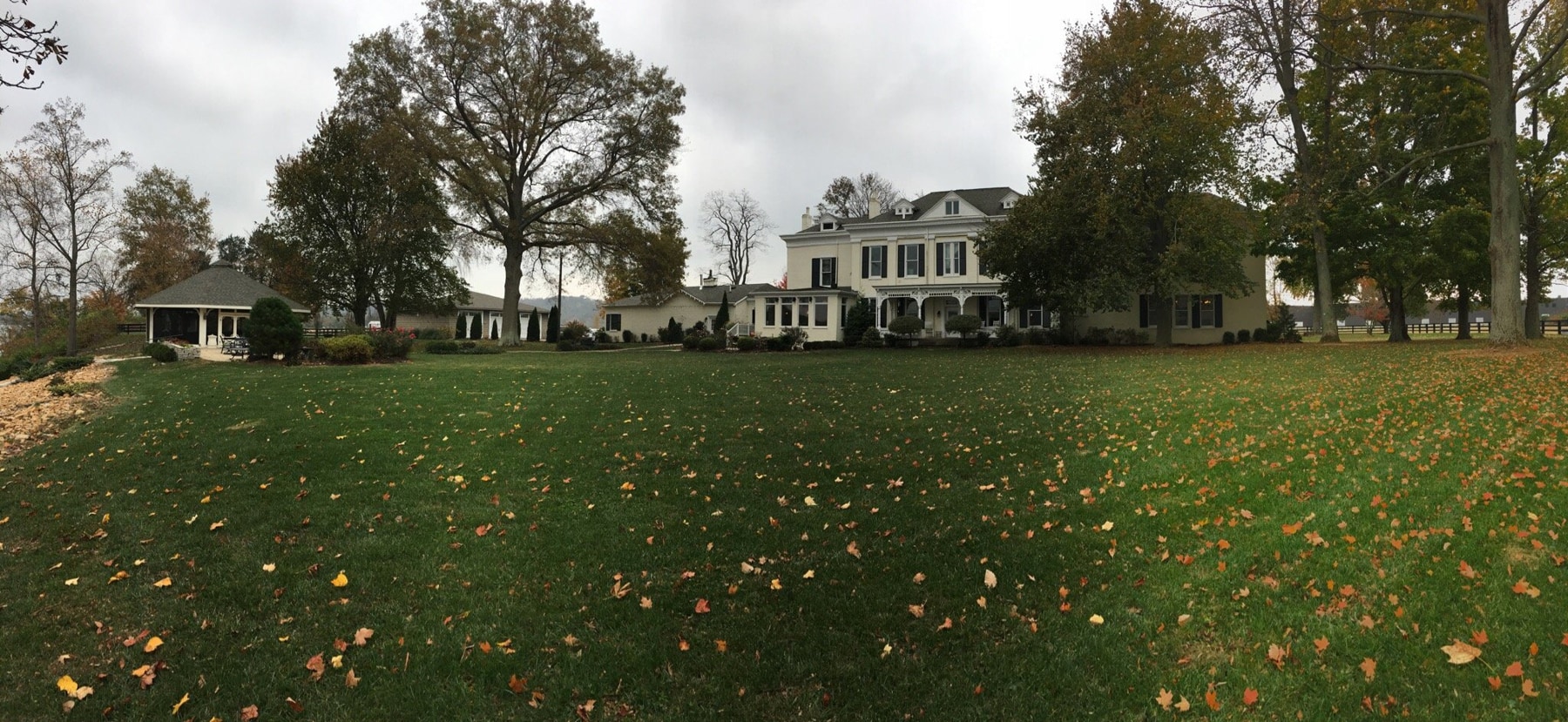
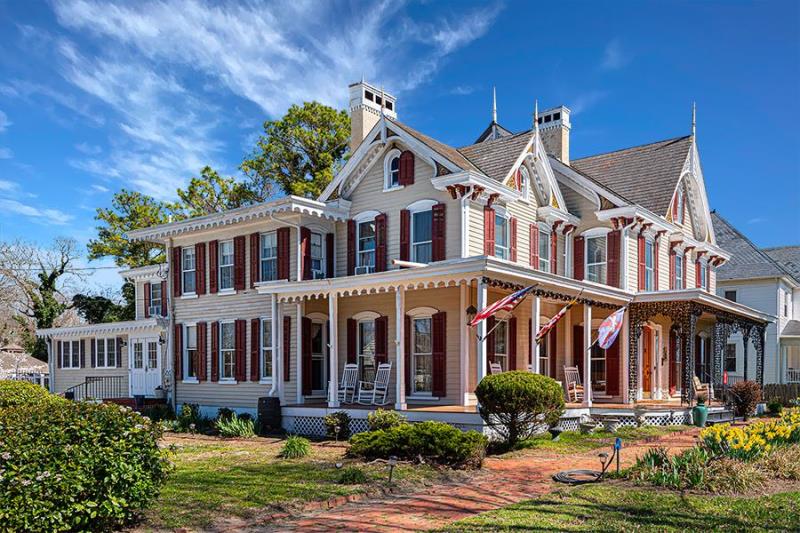
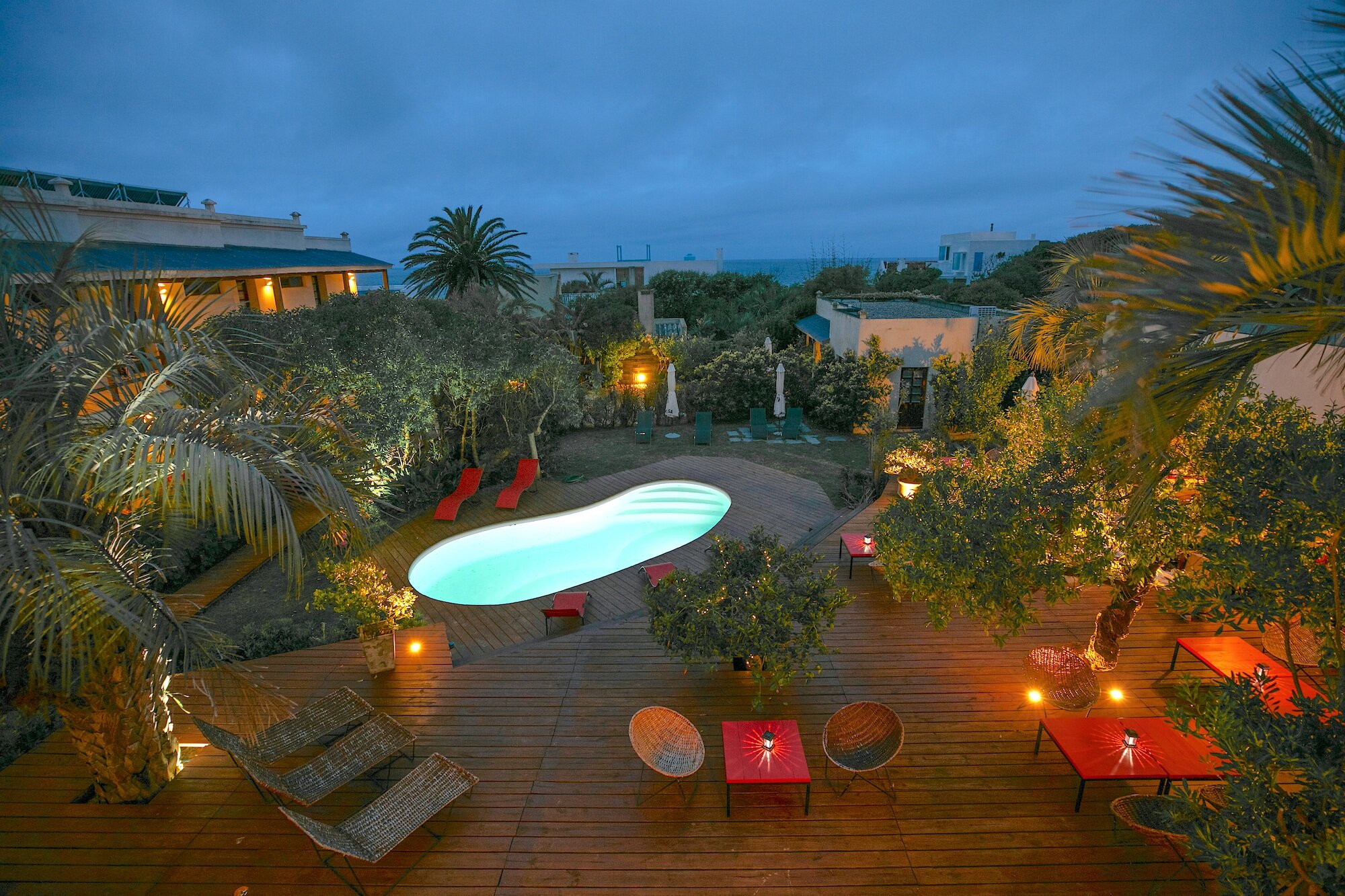
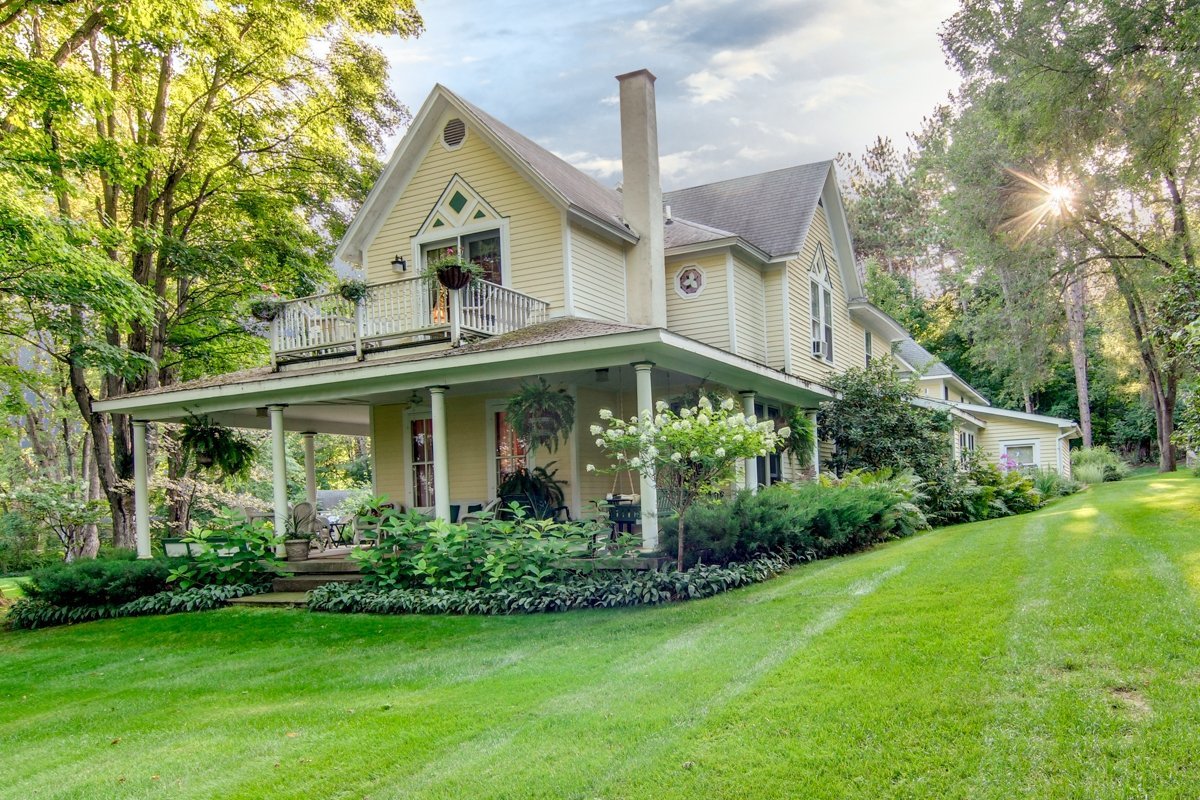
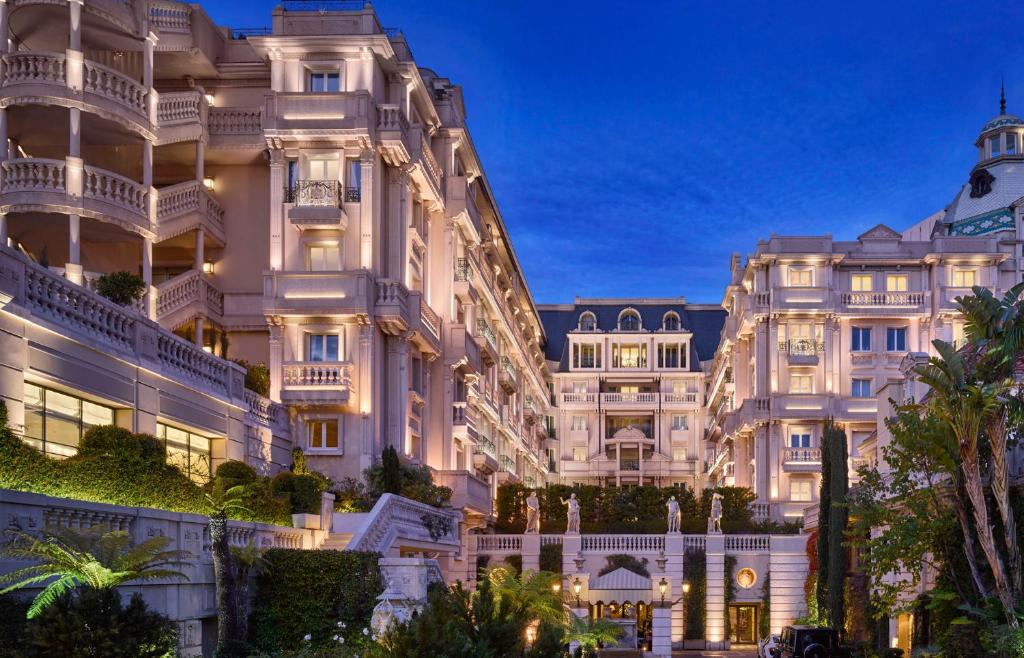







































































Kimberley, Northern Cape, South Africa
Agent: Cliff Jacobs - Managing Principal Estate Agent & CEO (Nat.Dpl.Hotel Man (UJ). M.P.R.E.)
Agent Cellphone: +27 (0) 84 413 1071 / +27 (0) 61 716 6951
Agent Office Number: +27 (0) 84 413 1071
Agent Email Address: cliff@exquisitehotelconsultants.com
Type: Heritage Boutique Hotel
Bedrooms: 50
Bathrooms: 50
Parking: 50
Yield: Not Disclosed
TGCSA Rating:

Kimberley
Kimberley is the capital and largest city of the Northern Cape Province of South Africa. It is located approximately 110 km east of the confluence of the Vaal and Orange Rivers. The city has considerable historical significance due to its diamond mining past and the siege during the Second Anglo-Boer war. British businessmen Cecil Rhodes and Barney Barnato made their fortunes in Kimberley, and Rhodes established the De Beers diamond company in the early days of the mining town.
On 2 September 1882, Kimberley was the first city in the Southern Hemisphere and the second in the world after Philadelphia, Pennsylvania in the United States to integrate electric street lights into its infrastructure. The first Stock Exchange in Africa was built in Kimberley, as early as 1881. The first Afrikaans high school in Kimberley is known as Diamantveld high school and the first Afrikaans primary school is Diamantveld laerskool.
History
Discovery of diamonds
In 1866, Erasmus Jacobs found a small brilliant pebble on the banks of the Orange River, on the farm De Kalk leased from local Griquas, near Hopetown, which was his father's farm. He showed the pebble to his father, who then sold it. The pebble was purchased from Jacobs' father by Schalk van Niekerk, who later sold it on again. It proved to be a 21.25-carat (4.3 g) diamond and became known as the Eureka. Three years later, in 1869, an 83.5-carat (16.7 g) diamond, which became known as the Star of South Africa, was found nearby. This diamond was sold by van Niekerk for £11,200 and later resold in the London market for £25,000.
Henry Richard Giddy recounted how Esau Damoense (or Damon), the cook for prospector Fleetwood Rawstorne's "Red Cap Party", found diamonds in 1871 on Colesberg Kopje after he was sent there to dig as punishment. Rawstorne took the news to the nearby diggings of the De Beer brothers – his arrival there sparking off the famous "New Rush" which, as historian Brian Roberts puts it, was practically a stampede. Within a month, 800 claims were cut into the hillock, which was worked frenetically by two to three thousand men. As the land was lowered, so the hillock became a mine – in time, the world-renowned Kimberley Mine.
The Cape Colony, Transvaal, Orange Free State, and the Griqua leader Nicolaas Waterboer all laid claim to the diamond fields. The Free State Boers in particular wanted the area, as it lay inside the natural borders created by Orange and Vaal Rivers. Following the mediation that was overseen by the Governor of Natal, the Keate Award went in favour of Waterboer, who placed himself under British protection. Consequently, the territory known as Griqualand West was proclaimed on 27 October 1871.
Naming the place: from Vooruitzigt to New Rush to Kimberley
Colonial Commissioners arrived in New Rush on 17 November 1871 to exercise authority over the territory on behalf of the Cape Governor. Digger objections and minor riots led to Governor Barkly's visit to New Rush in September the following year, when he revealed a plan instead to have Griqualand West proclaimed a Crown Colony. Richard Southey would arrive as Lieutenant-Governor of the intended Crown Colony in January 1873. Months passed however without any sign of the proclamation or of the promised new constitution and provision for representative government. The delay was in London where Secretary of State for the Colonies, John Wodehouse, 1st Earl of Kimberley, insisted that before electoral divisions could be defined, the places had to receive "decent and intelligible names. His Lordship declined to be in any way connected with such a vulgarism as New Rush and as for the Dutch name, Vooruitzigt … he could neither spell nor pronounce it." The matter was passed to Southey who gave it to his Colonial Secretary J.B. Currey. Roberts writes that "when it came to renaming New Rush, [Currey] proved himself a worthy diplomat. He made quite sure that Lord Kimberley would be able both to spell and pronounce the name of the main electoral division by, as he says, calling it 'after His Lordship'." New Rush became Kimberley, by Proclamation dated 5 July 1873. Digger sentiment was expressed in an editorial in the Diamond Field newspaper when it stated "we went to sleep in New Rush and waked up in Kimberley, and so our dream was gone."
Following agreement by the British government on compensation to the Orange Free State for its competing land claims, Griqualand West was annexed to the Cape Colony in 1877. The Cape Prime Minister John Molteno initially had serious doubts about annexing the heavily indebted region, but, after striking a deal with the Home Government and receiving assurances that the local population would be consulted in the process, he passed the Griqualand West Annexation Act on 27 July 1877.
Big Hole and other mines
As miners arrived in their thousands the hill disappeared and subsequently became known as the Big Hole (or Kimberley se Gat in Afrikaans) or, more formally, Kimberley Mine. From mid-July 1871 to 1914, 50,000 miners dug the hole with picks and shovels, yielding 2,722 kg of diamonds. The Big Hole has a surface of 17 hectares (42 acres) and is 463 metres wide. It was excavated to a depth of 240 m, but then partially infilled with debris reducing its depth to about 215 m; since then it has accumulated water to a depth of 40 m leaving 175 m visible. Beneath the surface, the Kimberley Mine underneath the Big Hole was mined to a depth of 1097 metres. A popular local myth claims that it is the largest hand-dug hole on the world, however, Jagersfontein Mine appears to hold that record.The Big Hole is the principal feature of a May 2004 submission which placed "Kimberley Mines and associated early industries" on UNESCO's World Heritage Tentative Lists.
By 1873 Kimberley was the second largest town in South Africa, having an approximate population of 40,000.
Role and influence of De Beers
A sign next to the Big Hole, reading "If all the diamonds recovered from the Kimberley Mine could be gathered together they would fill three cocopans such as these"
The various smaller mining companies were amalgamated by Cecil Rhodes and Charles Rudd into De Beers, and The Kimberley under Barney Barnato. In 1888, the two companies merged to form De Beers Consolidated Mines, which once had a monopoly over the world's diamond market.
Very quickly, Kimberley became the largest city in the area, partly due to a massive African migration to the area from all over the continent. The immigrants were accepted with open arms because the De Beers company was in search of cheap labour to help run the mines. Another group drawn to the city for money was prostitutes, from a wide variety of ethnicities who could be found in bars and saloons. It was praised as a city of limitless opportunity.
Five big holes were dug into the earth following the kimberlite pipes, which are named after the town. Kimberlite is a diamond-bearing blue ground that sits below a yellow colored soil. The largest, The Kimberley mine or "Big Hole" covering 170,000 square metres (42 acres), reached a depth of 240 metres (790 ft) and yielded three tons of diamonds. The mine was closed in 1914, while three of the holes – Dutoitspan, Wesselton and Bultfontein – closed down in 2005.
Second Boer War
On 14 October 1899, Kimberley was besieged at the beginning of the Second Boer War. The British forces trying to relieve the siege suffered heavy losses. The siege was only lifted on 15 February 1900, but the war continued until May 1902. By that time, the British had built a concentration camp at Kimberley to house Boer women and children.
Under Apartheid
Although a considerable degree of urban segregation already existed, one of the most significant impacts of Apartheid on the city of Kimberley was the implementation of the Group Areas Act. Communities were divided according to legislated racial categories, namely European (White), Native (Black), Coloured and Indian – now legally separated by the Prohibition of Mixed Marriages Act. Individual families could be split up to three ways (based on such notorious measures as the 'pencil test') and mixed communities were either completely relocated (as in Malay Camp – although those clearances began before Apartheid as such) or were selectively cleared (as in Greenpoint which became a 'Coloured' Group Area, its erstwhile African and other residents being removed to other parts of town). Residential segregation was thus enforced in a process that saw the creation of new townships at the northern and north-eastern edges of the expanding city. Institutions that were hard hit by the Group Areas Act, Bantu Education and other Acts included churches (such as the Bean Street Methodist Church) and schools (some, such as William Pescod and Perseverance School, moved while the Gore Browne (Native) Training School was closed down). Other legislation restricted the movement of Africans and some public places became 'Europeans Only' preserves in terms of the Reservation of Separate Amenities Act. The Native Laws Amendment Act sought to cleave church communities along racial lines – a law rejected on behalf of all Anglicans in South Africa by Archbishop Clayton in 1957 (in terms of which this aspect of apartheid was never completely implemented in churches such as Kimberley's St Cyprian's Cathedral).
Post-Apartheid
The Northern Cape Province became a political fact in 1994, with Kimberley as its capital. Some quasi-provincial infrastructure was in place from the 1940s, but in the post-1994 period, Kimberley underwent considerable development as administrative departments were set up and housed for the governance of the new province. A Northern Cape Legislature was designed and situated to bridge the formerly divided city. The Kimberley City Council of the renamed Sol Plaatje Local Municipality (see below) was enlarged. A new coat of arms and Motto for the city were ushered in.
With the abolition of apartheid previously 'whites only' institutions such as schools became accessible to all, as did suburbs previously segregated by the Group Areas Act. In practice, this process has been one of upward mobility by those who could afford the more costly options, while by far the majority of Black people remain in the townships where poverty levels are high.
Major township residential developments, with 'RDP housing', were implemented – not without criticism concerning quality. There has been an increase in Kimberley's population, urbanization being spurred on in part by the abolition of the Influx Control Act.
Also added to the city is the settlement of Platfontein created when the ! Xun and Khwe community formerly of Schmidtsdrift and originally from Angola/Namibia acquired the land in 1996. Most of the community had moved to the new township by the end of 2003.
In 1998 the Kimberley Comprehensive Urban Plan estimated that Kimberley had 210,800 people representing 46,207 households living in the city.
By 2008 estimates were in the region of 250,000 inhabitants.
Economy
Kimberley was the initial hub of industrialisation in South Africa in the late nineteenth century, which transformed the country's agrarian economy into one more dependent on its mineral wealth. A key feature of the new economic arrangement was migrant labour, with the demand for African labour in the mines of Kimberley (and later on the goldfields) drawing workers in growing numbers from throughout the subcontinent. The labour compound system developed in Kimberley from the 1880s was later replicated on the gold mines and elsewhere.
The city housed South Africa's first stock exchange, the Kimberley Royal Stock Exchange, which opened on 2 February 1881.
On 2 September 1882, Kimberley became the first town in the Southern Hemisphere to install electric street lighting.
The rising importance of Kimberley led to one of the earliest South African and International Exhibitions to be staged in Kimberley in 1892. It was opened by Sir Henry Loch, the then Governor of the Cape of Good Hope on 8 September. It presented exhibits of art, an exhibition of paintings from the royal collection of Queen Victoria and mining machinery and implements amongst other items. The exhibition aroused considerable interest at international level, which resulted in a competition for display space.
South Africa's first school of mines was opened here in 1896 and later relocated to Johannesburg, becoming the core of the University of the Witwatersrand. A Pretoria campus later became the University of Pretoria. In fact, the first two years were attended at colleges elsewhere, in Cape Town, Grahamstown or Stellenbosch, the third year in Kimberley and the fourth year in Johannesburg. Buildings were constructed against a total cost of 9,000 pounds with De Beers contributing on a pound for pound.
Tourism
The city projects itself as a significant tourist destination, the 'City that Sparkles', boasting a diversity of museums and visitor attractions. It is also a gateway to other Northern Cape destinations including the Mokala National Park, nature reserves and numerous game farms or hunting lodges, as well as historic sites of the region.
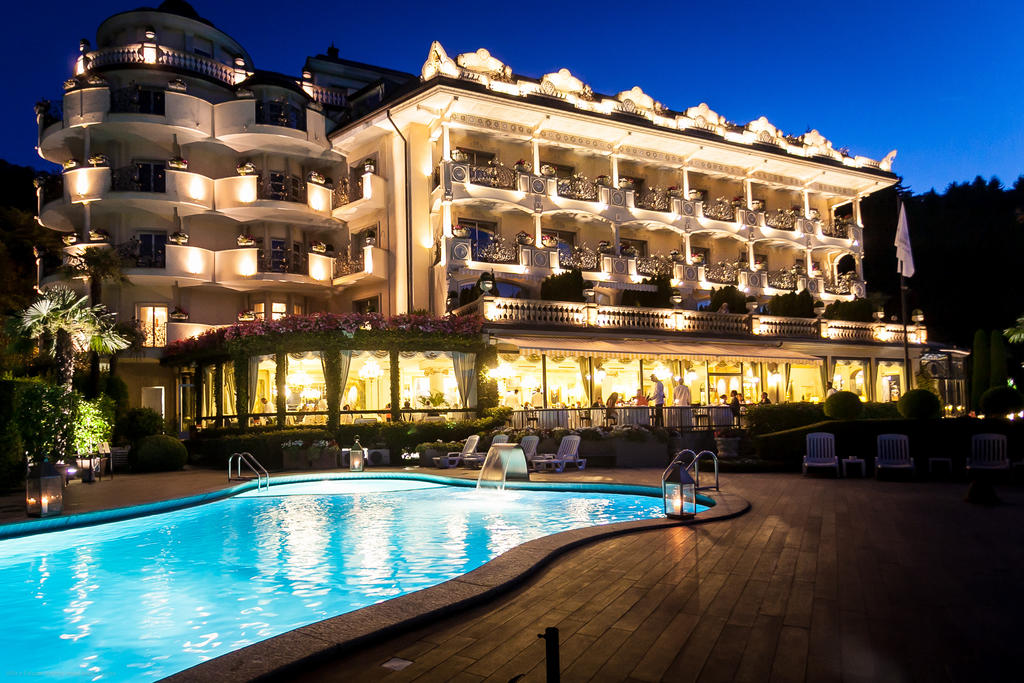
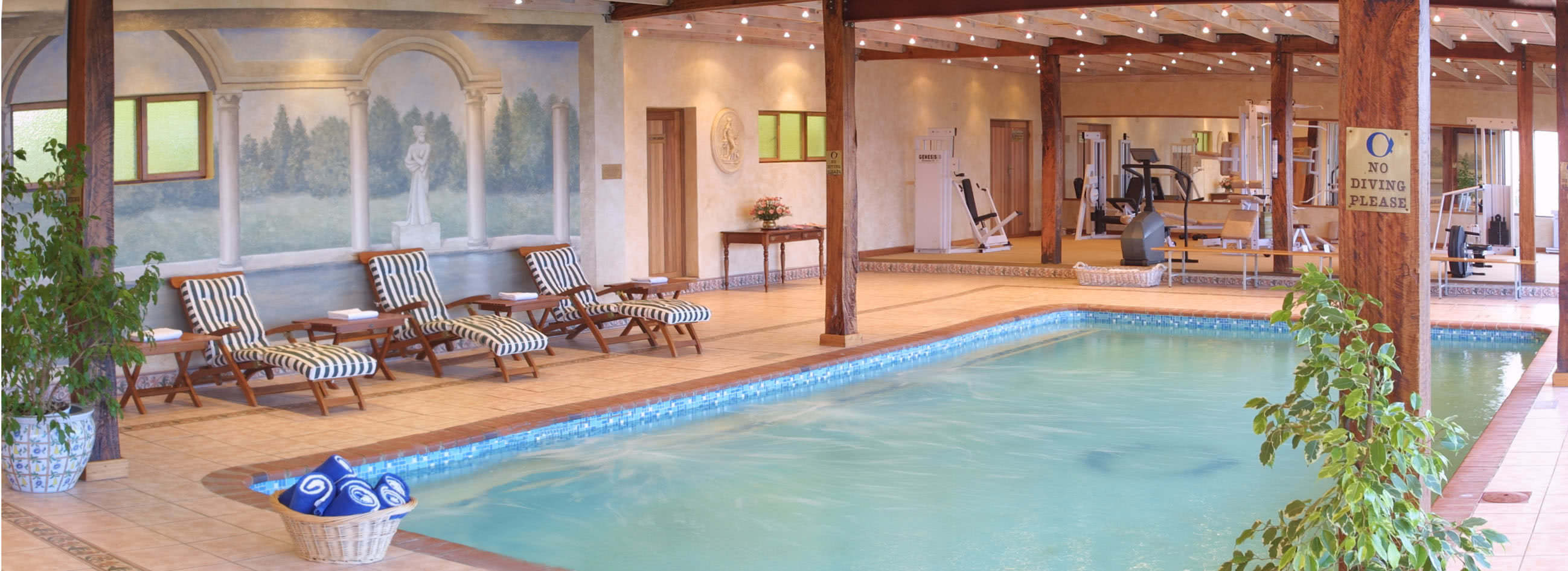
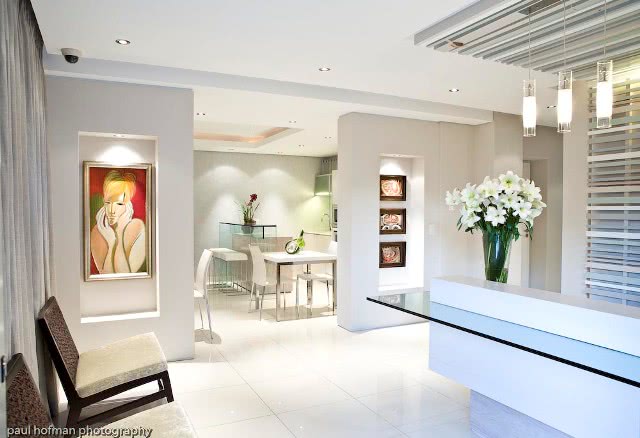
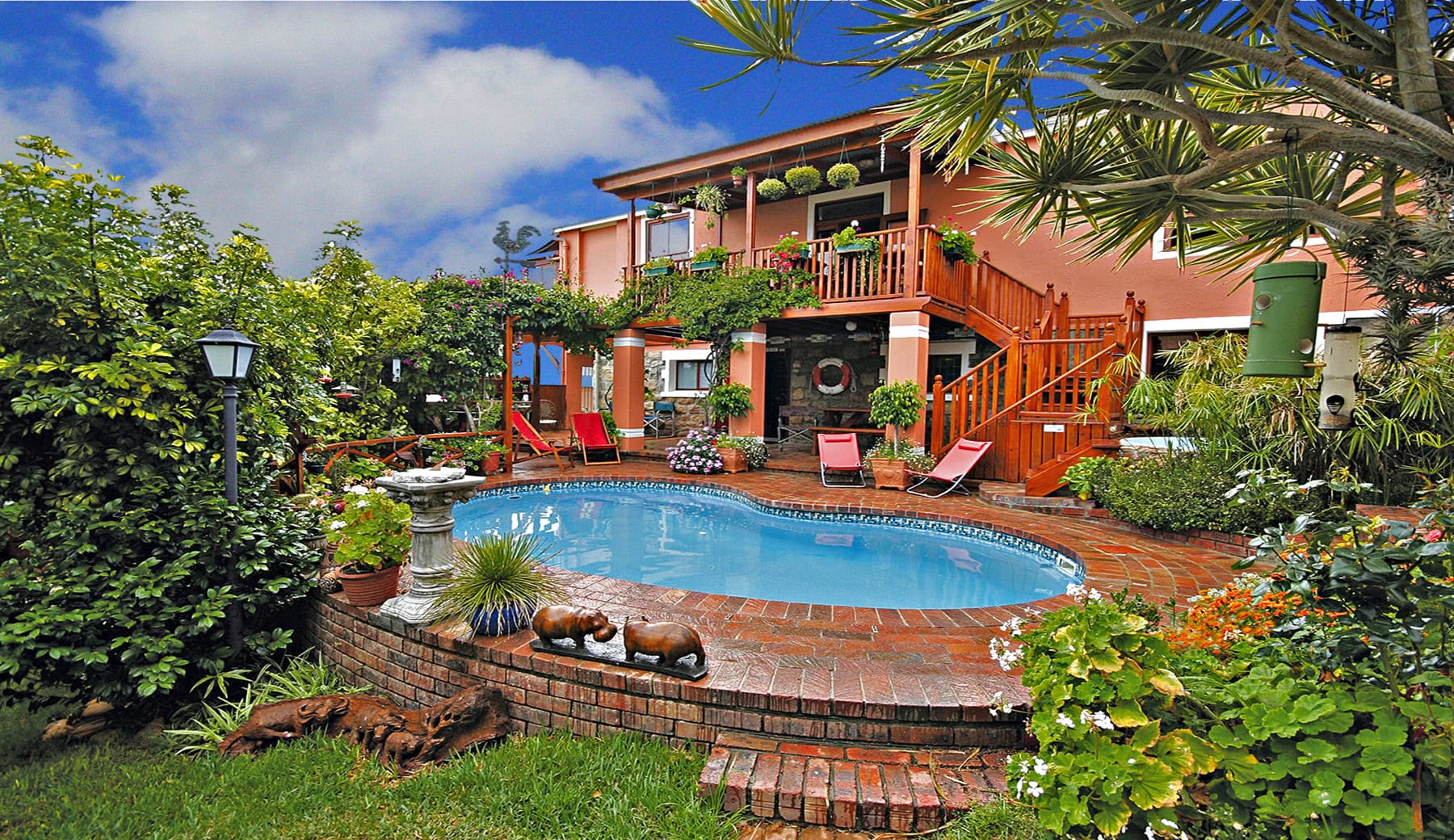
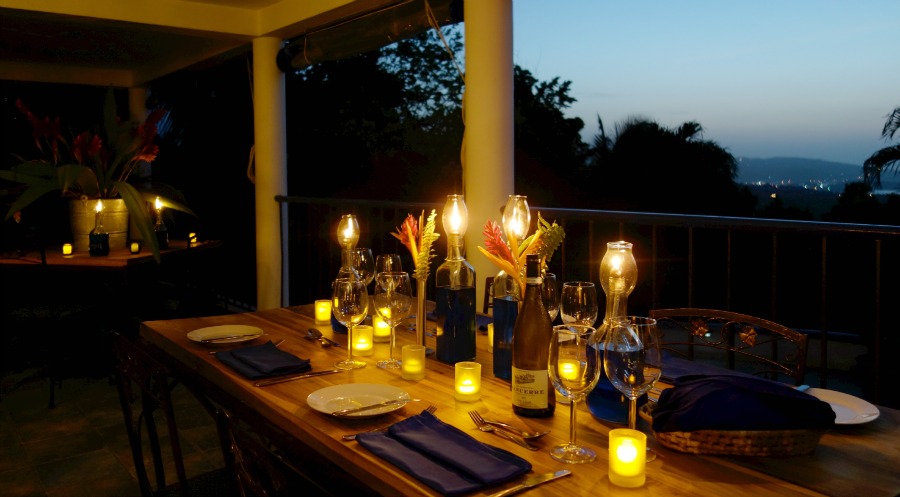
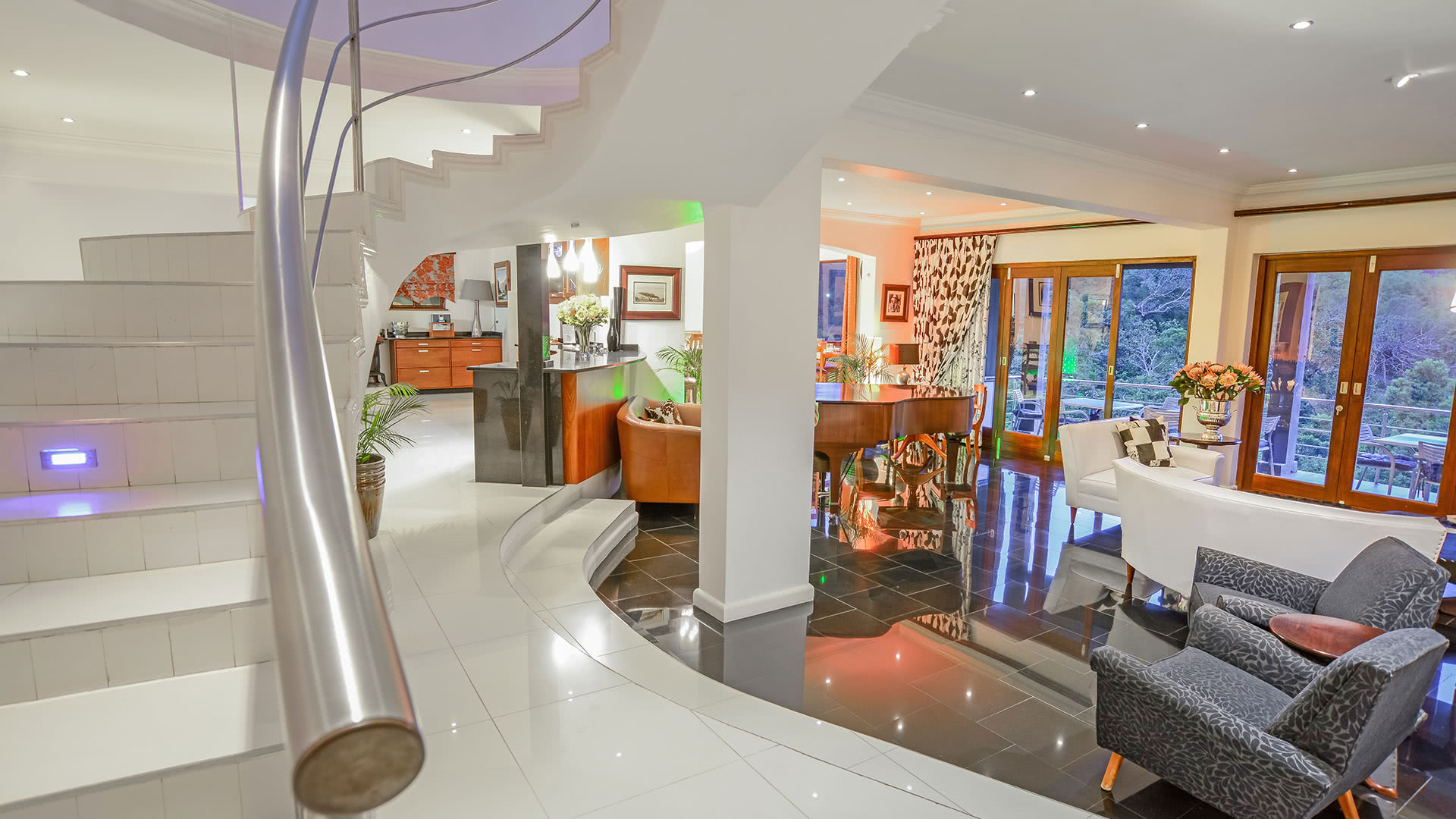
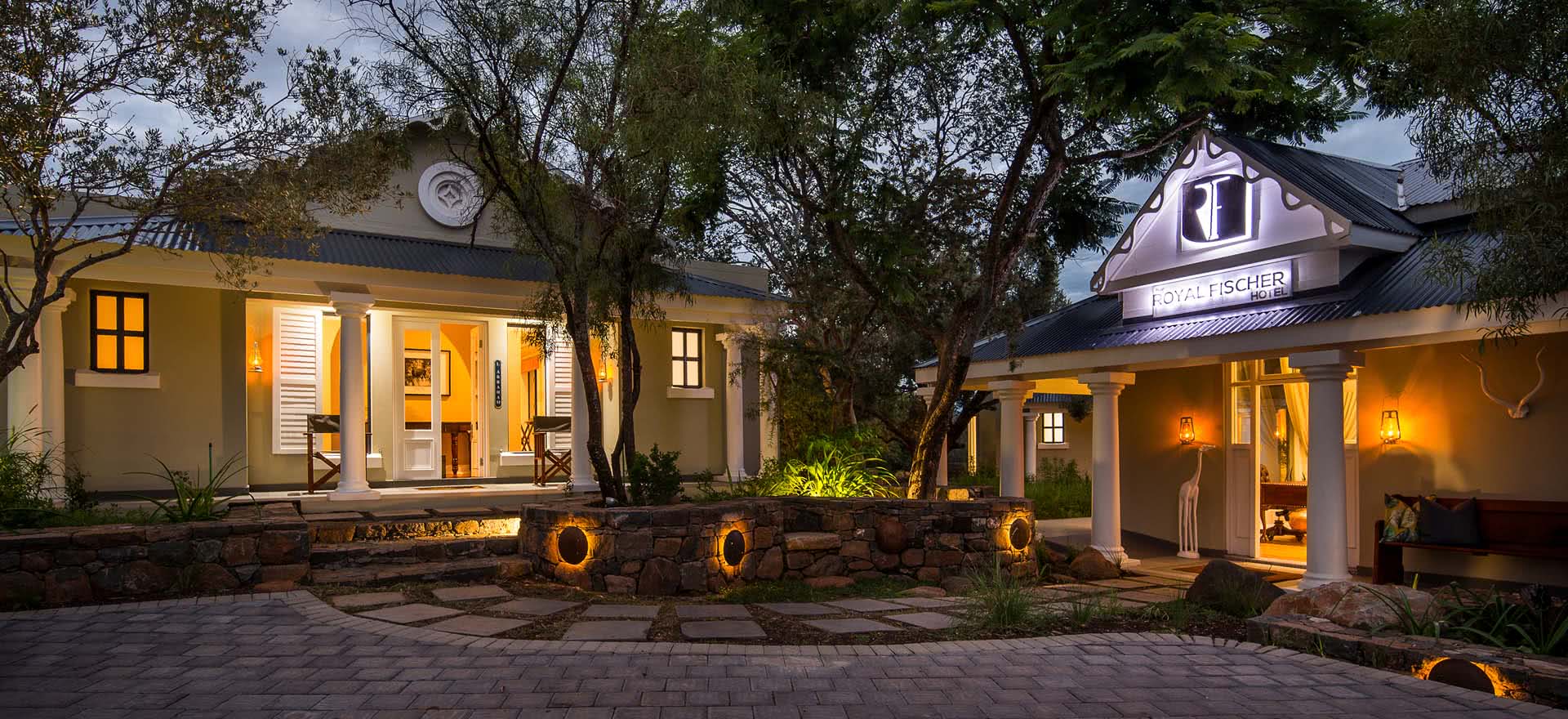
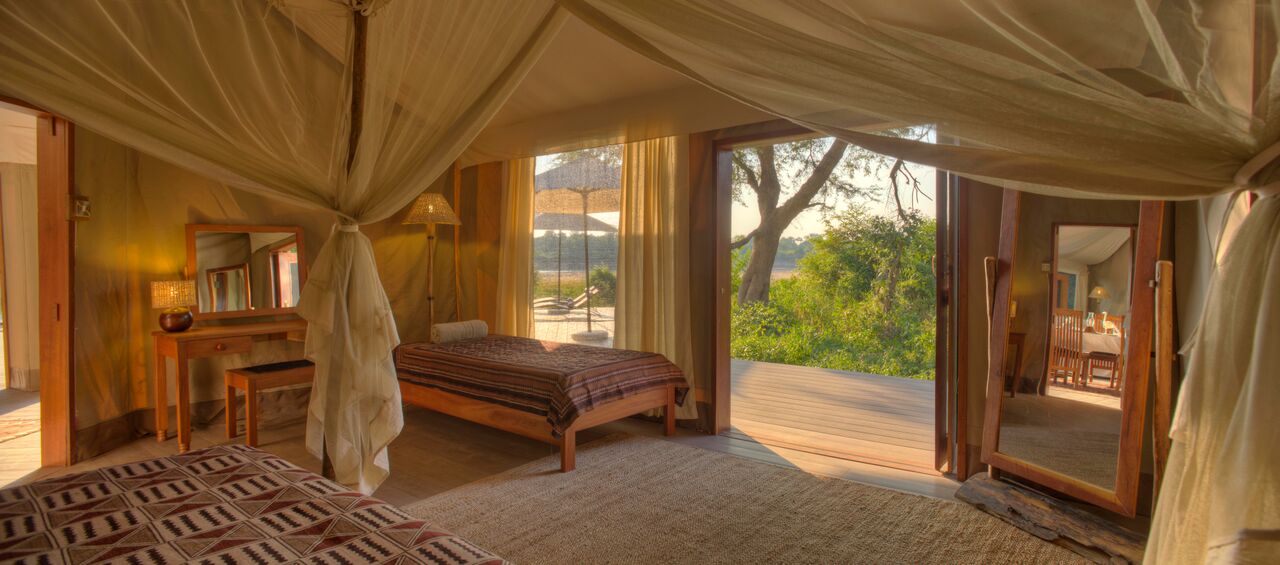
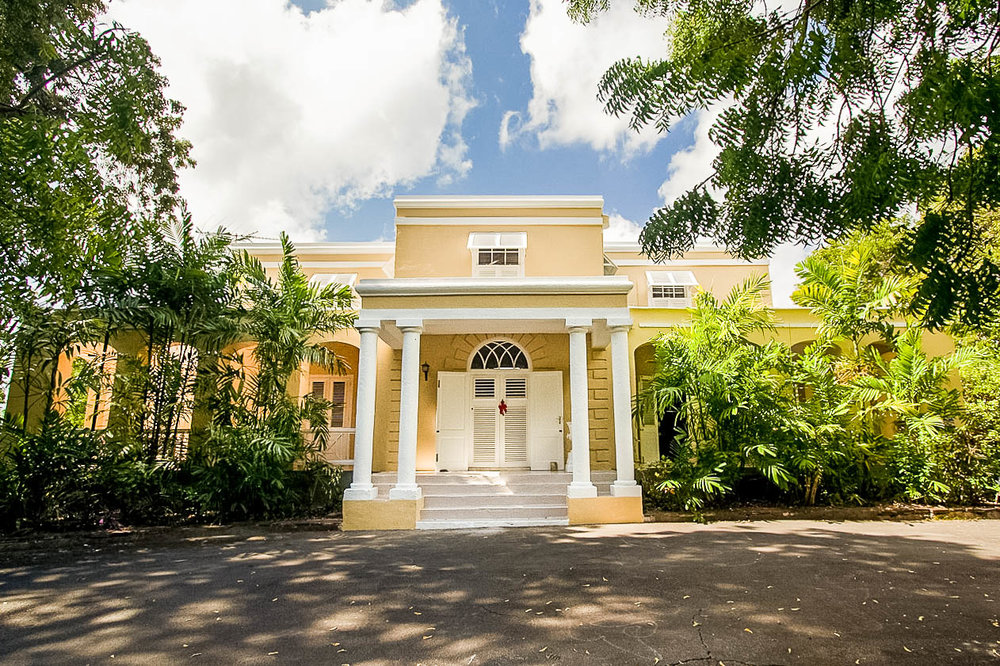
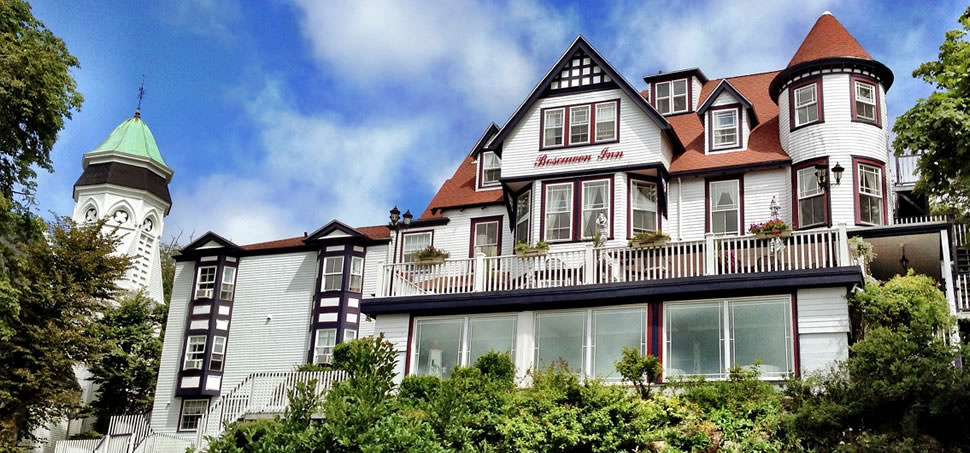
About The Hotel
The Hotel is one of Kimberley’s oldest and most enchanting hotels and has lived through the diamond heydays.
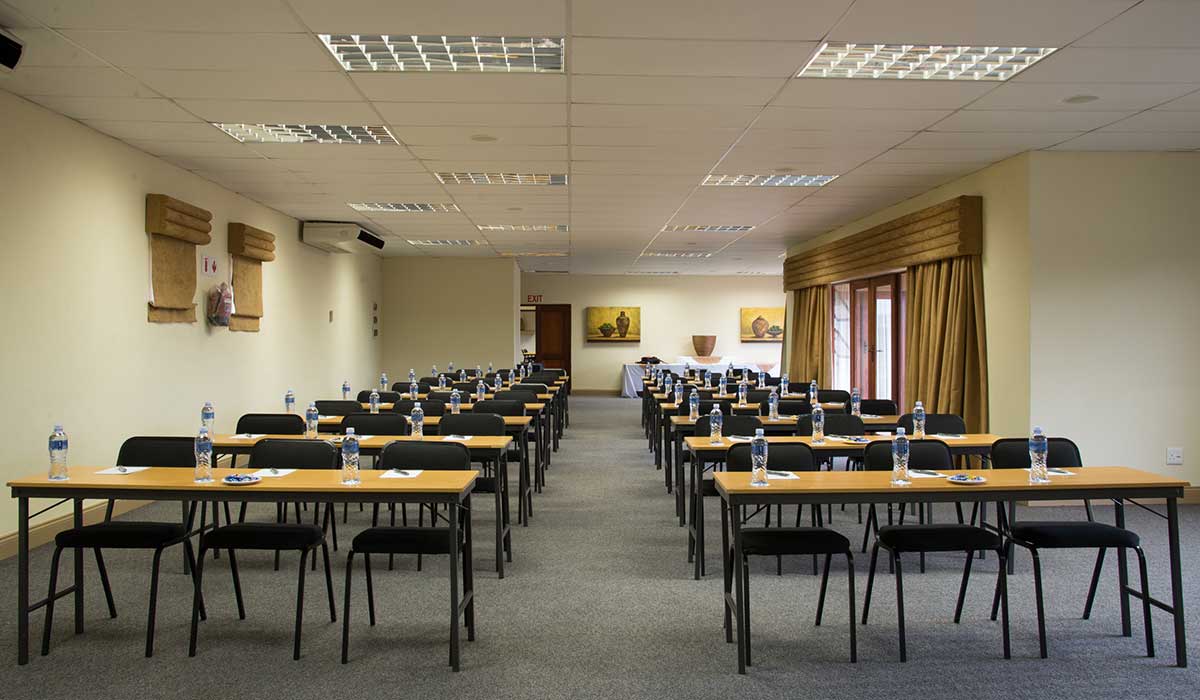
The hotel has established itself as a prime venue for conferences, workshops, and events and offers 14 different conference venues.
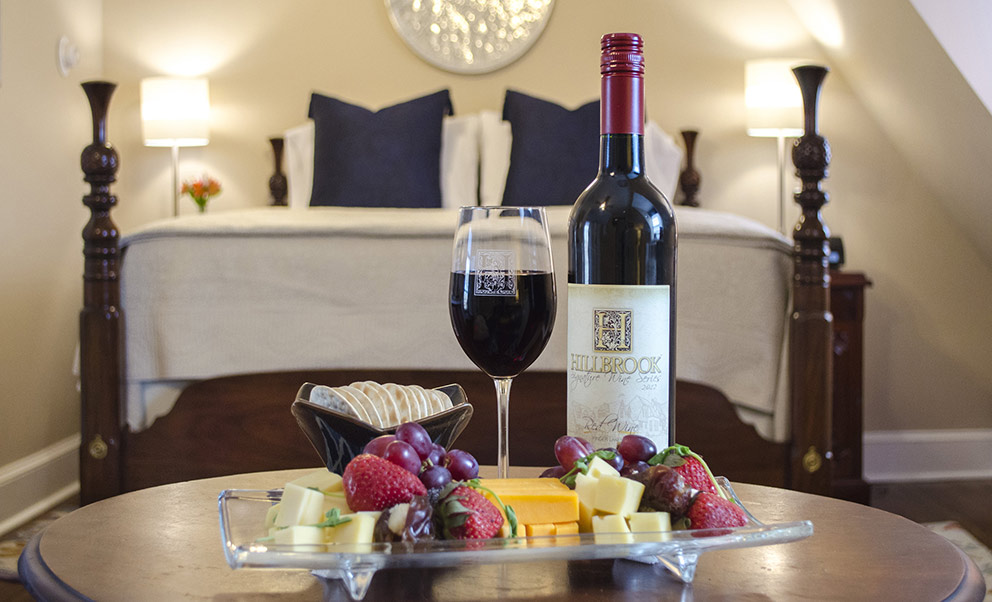
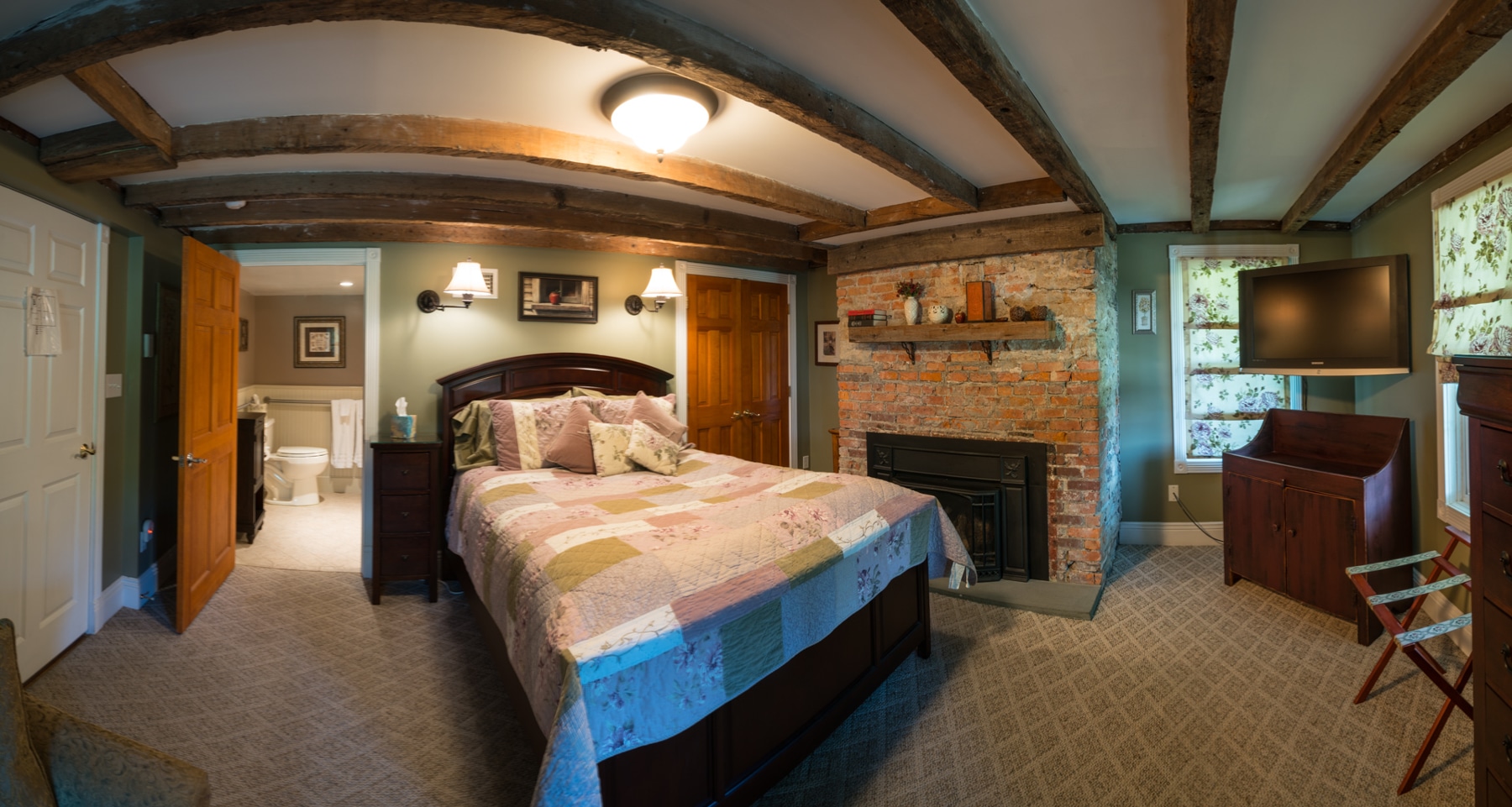
Rooms
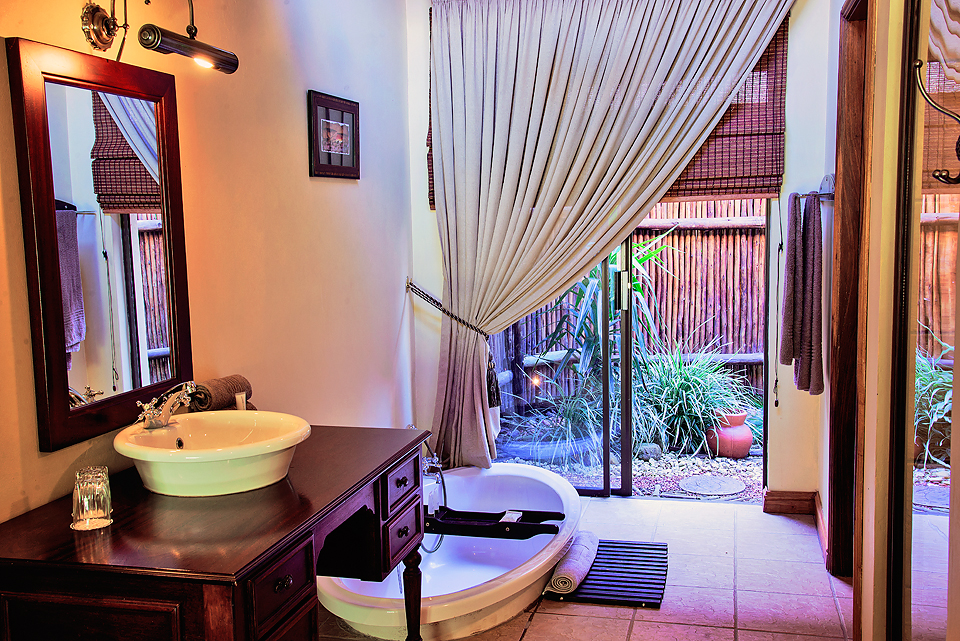
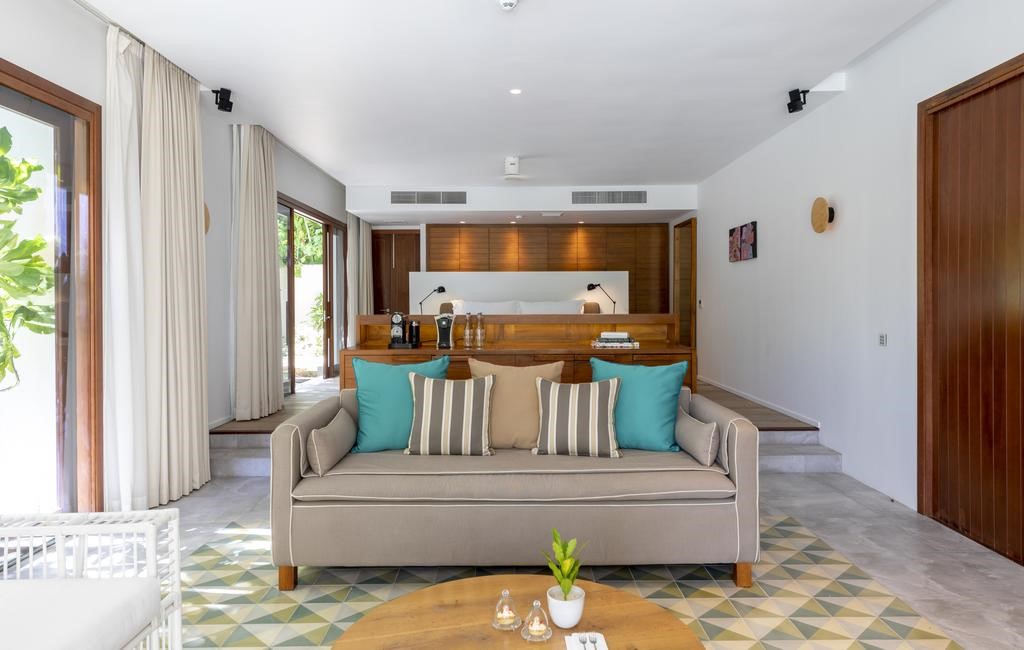
The hotel has 50 spacious bedrooms and suites that can accommodate up to 119 guests.
All rooms are equipped with air-conditioners, TV, Radio, tea & coffee facilities and an en-suite bathroom with either bath and/or shower.
Room types
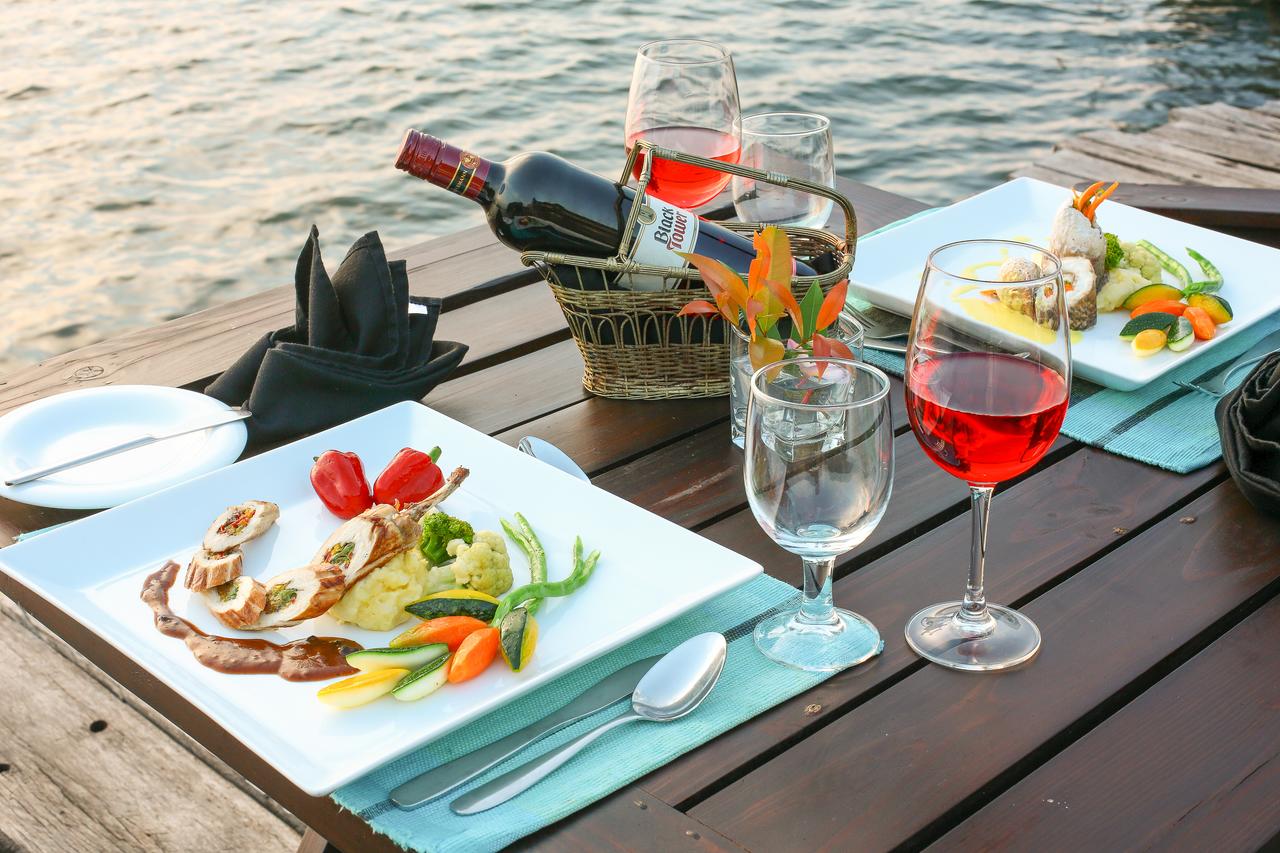
Dining
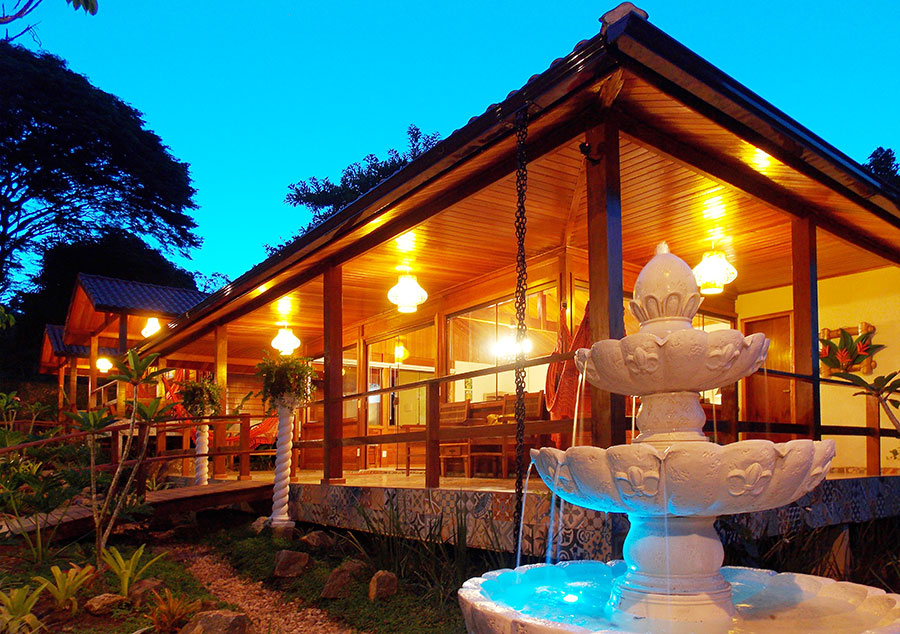
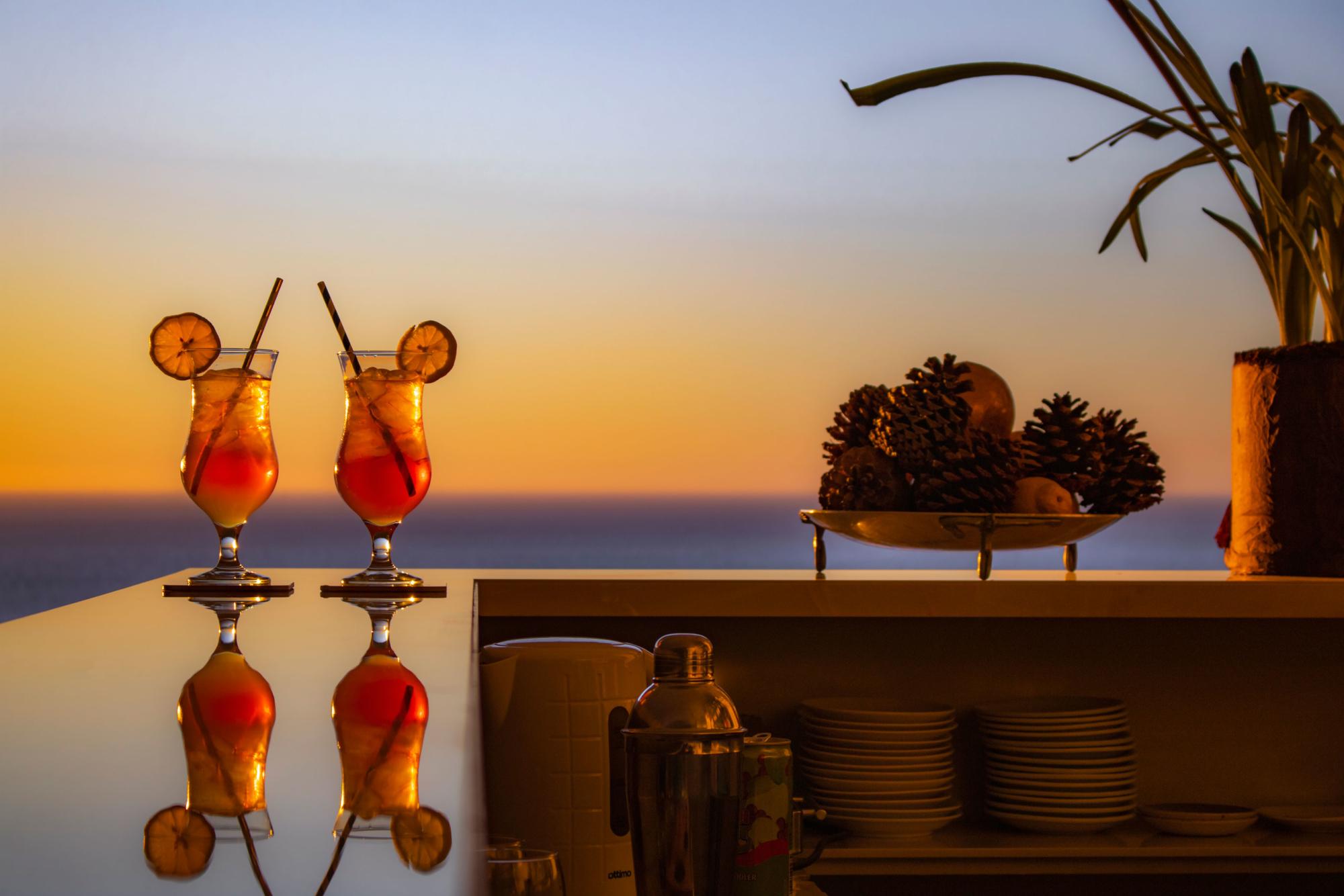
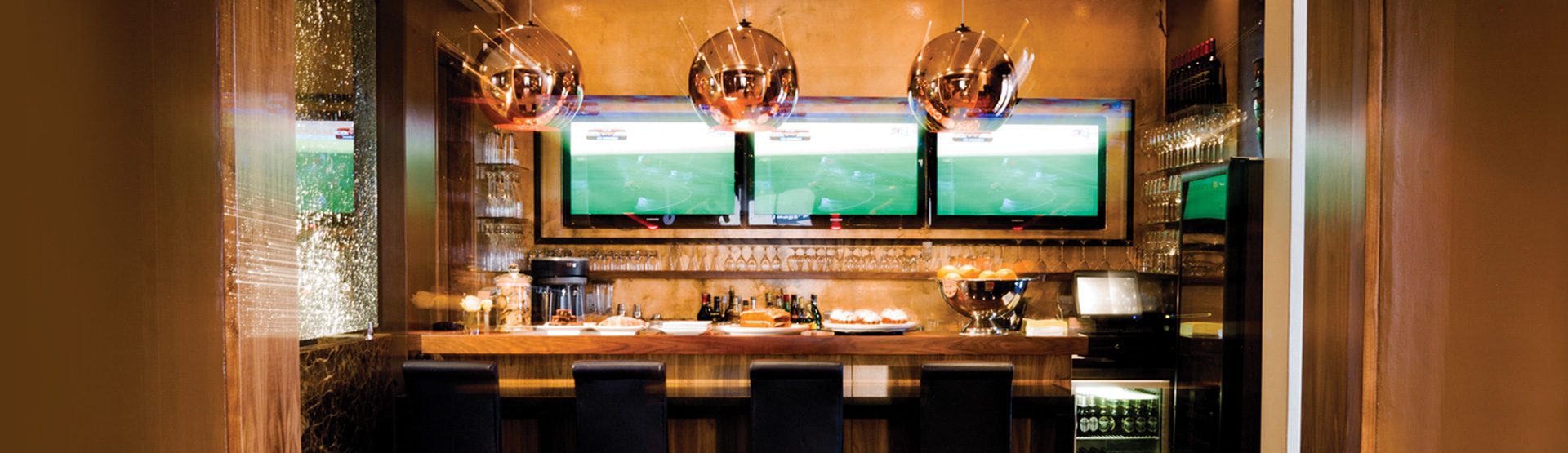
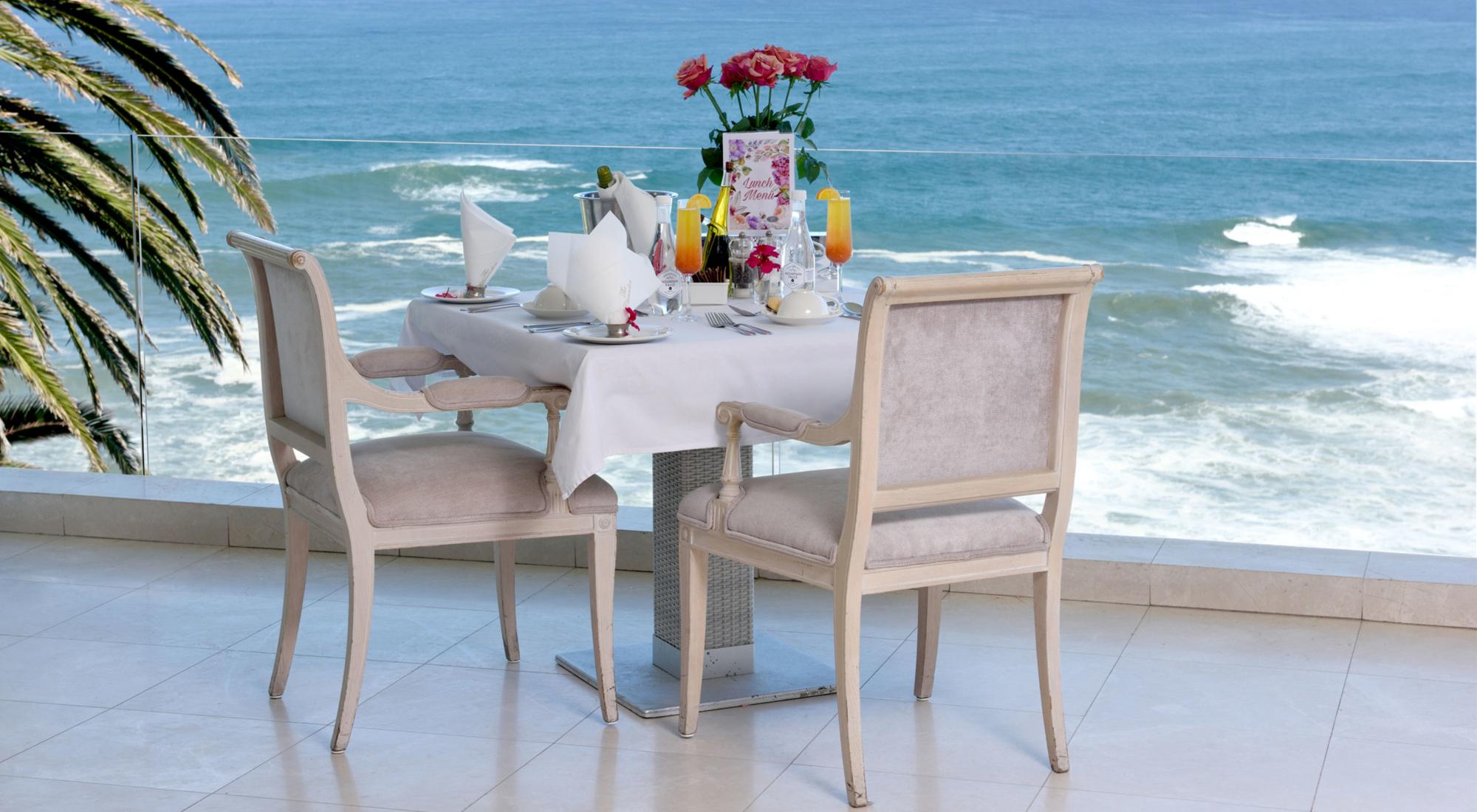
The upmarket Tiffany’s Restaurant and the old-style Tiffany’s Bar cater for all your dining and entertainment requirements. For meetings, conferences or events enjoy the service of the Conference Centre.
Facilities and Services
Places of Interest in & around Kimberley













































Cliff Jacobs (Nat Dpl Hotel Man (UJ). MPRE. GA Level 5 TEFL) Managing Principal / CEO Exquisite Hotel Consultants (Pty) Ltd Mobile: +27 (0) 67 587 2532 (voice calls) Mobile: +27 (0) 84 413 1071 (WhatsApp voice calls and chats only) / +27 (0) 61 716 6951 (WhatsApp voice calls and chats only) Email: cliff@exquisitehotelconsultants.com Web: https://www.exquisitehotelconsultants.com © All rights reserved Terms and Conditions apply Scroll down to view our Hospitality Properties and Businesses for sale or lease or lease-to-buy or partnership arrangement or management agreement arrangement.