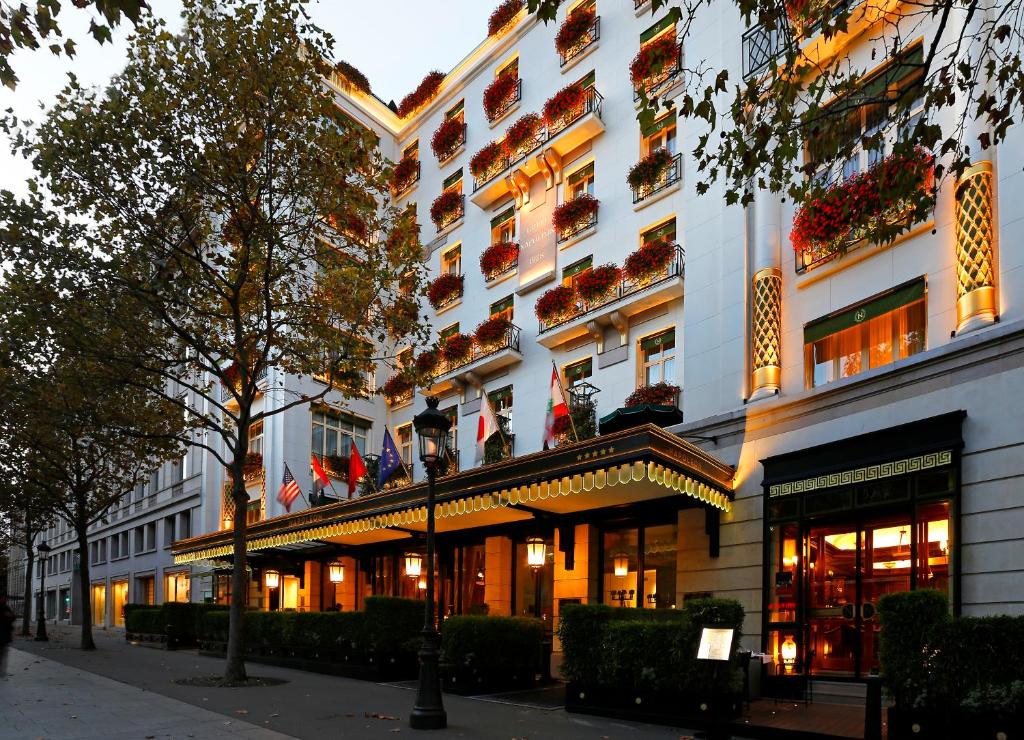
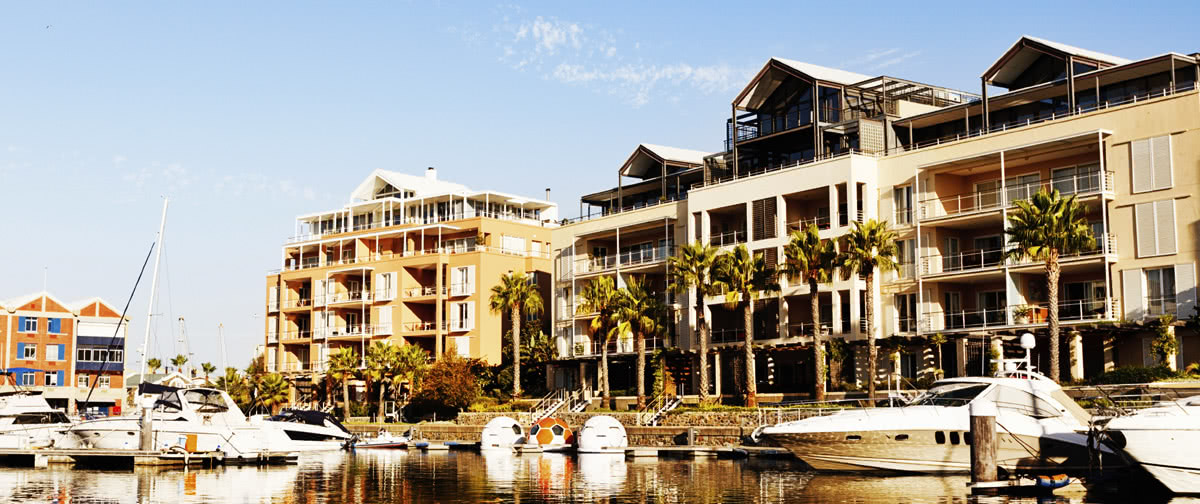
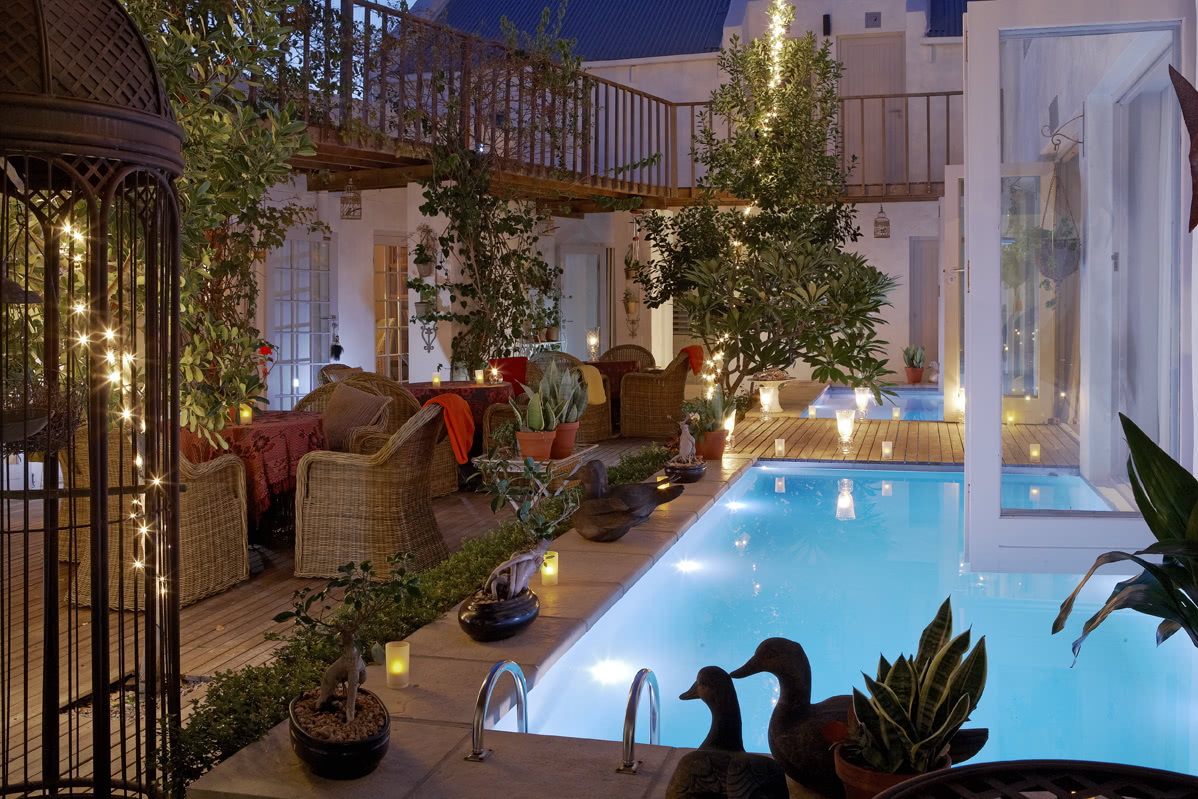
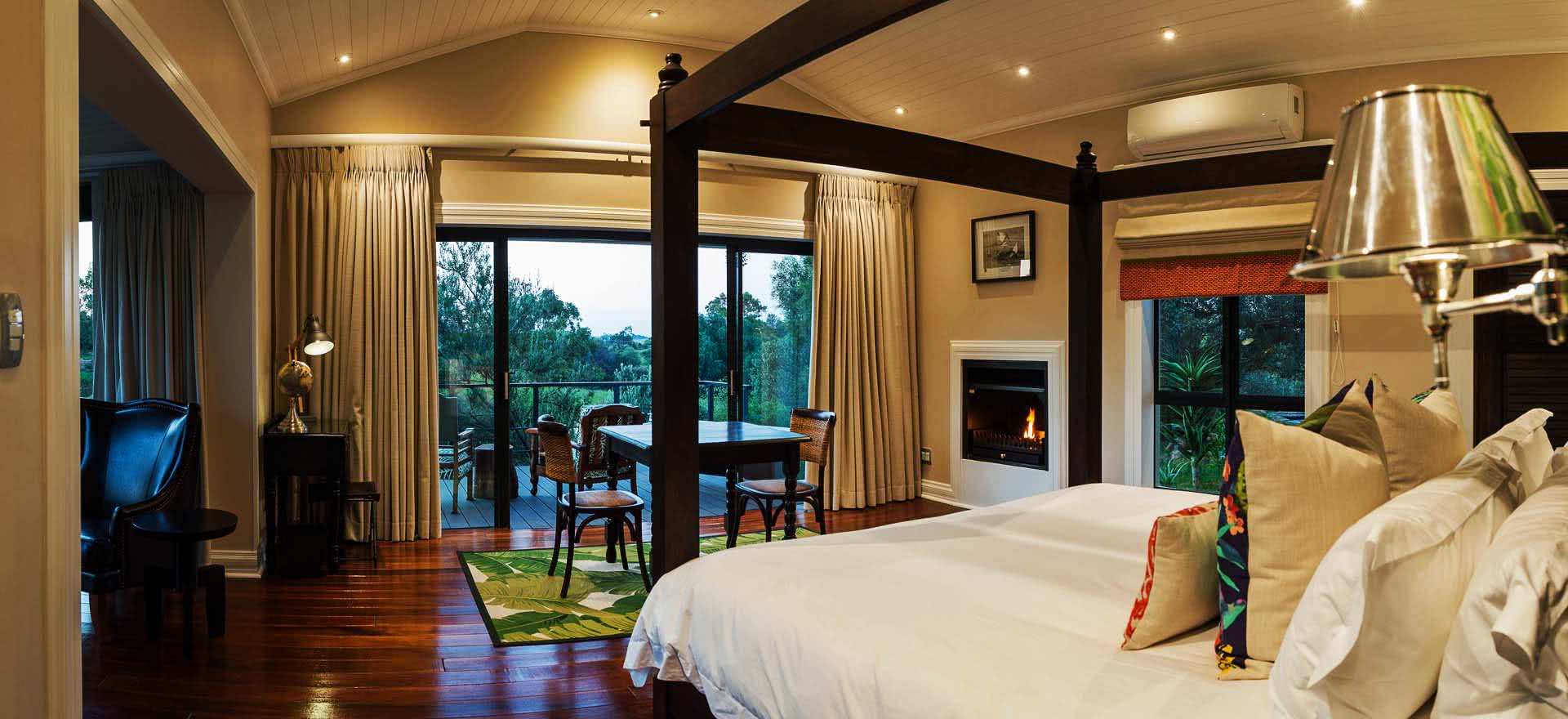
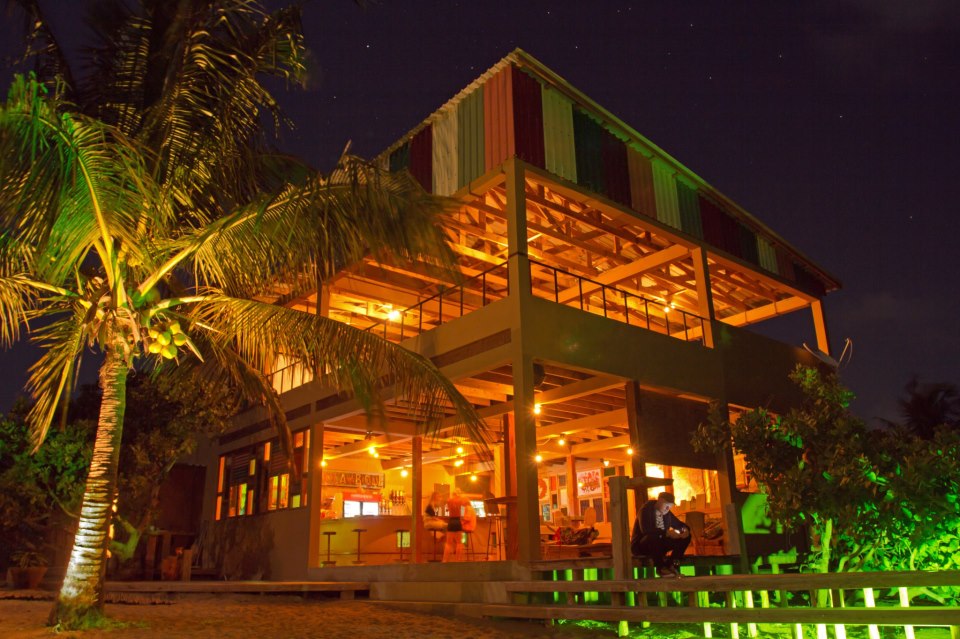
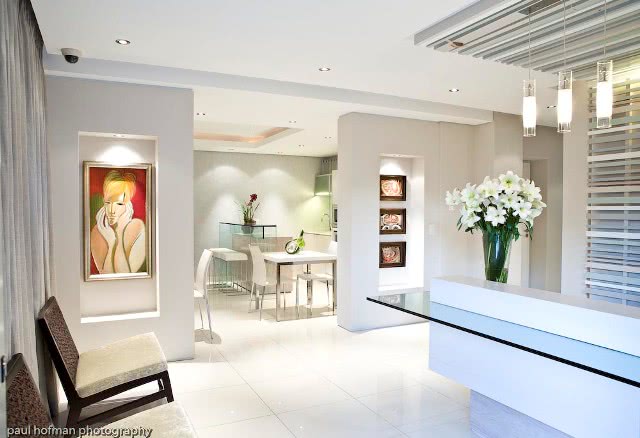
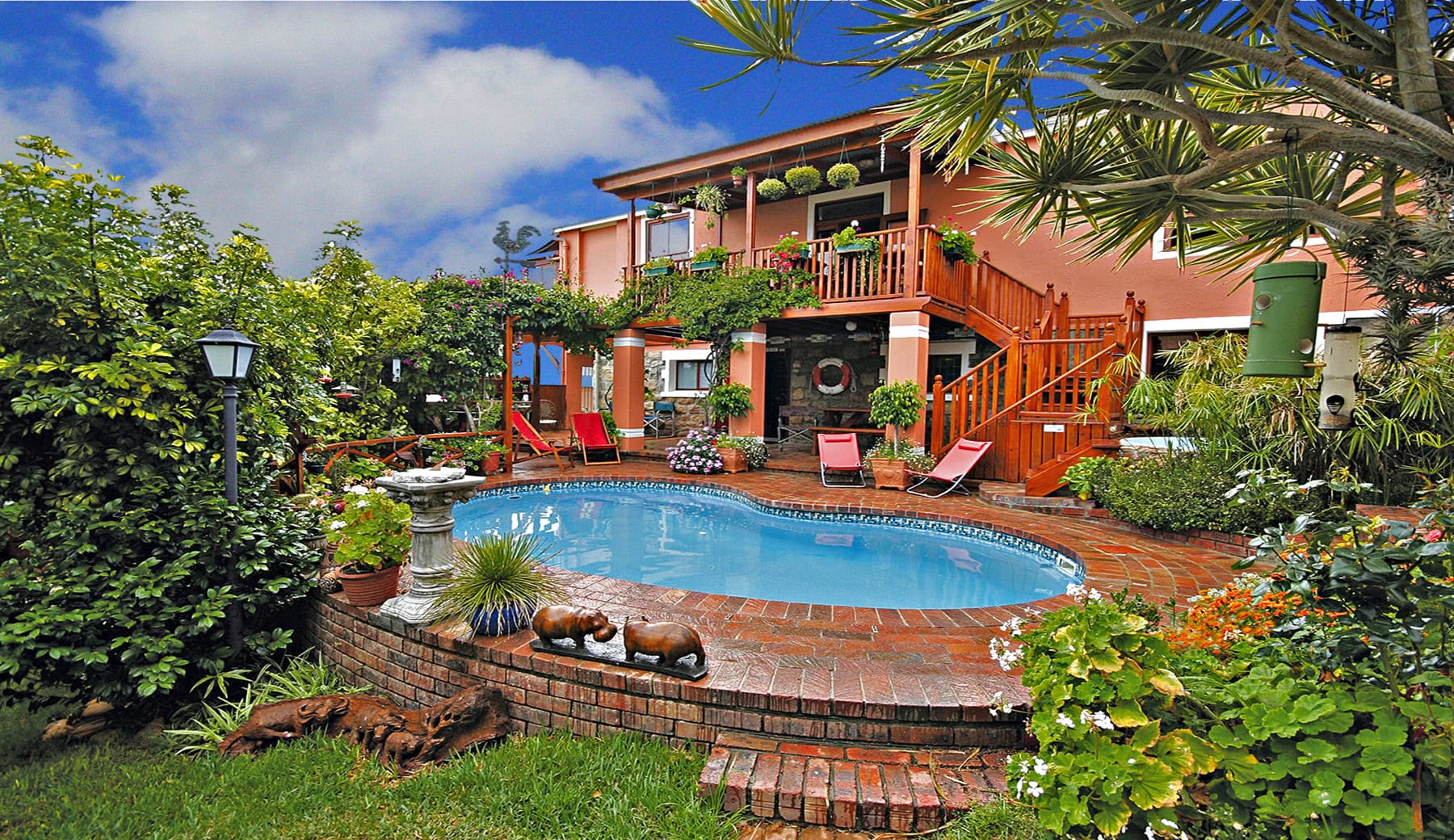
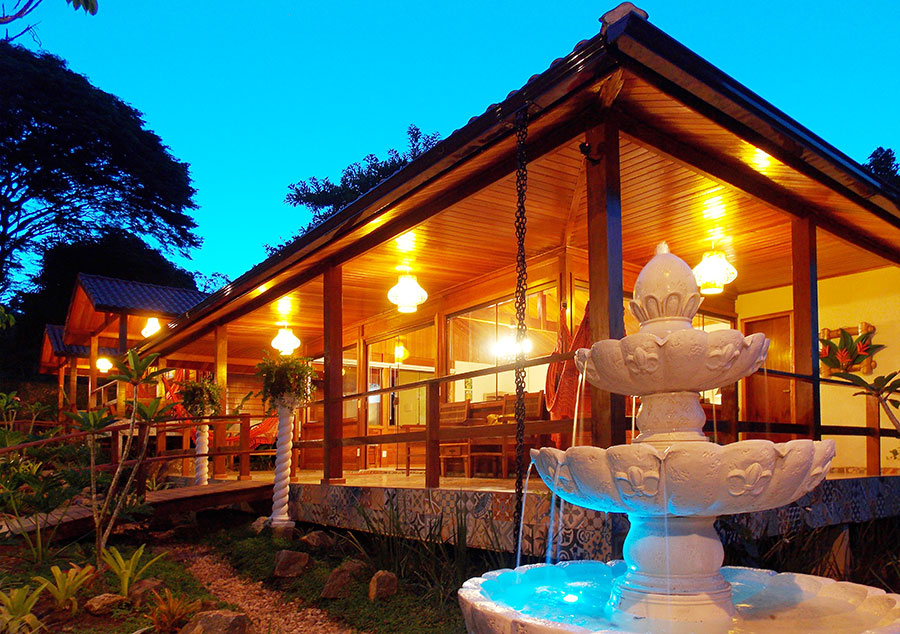
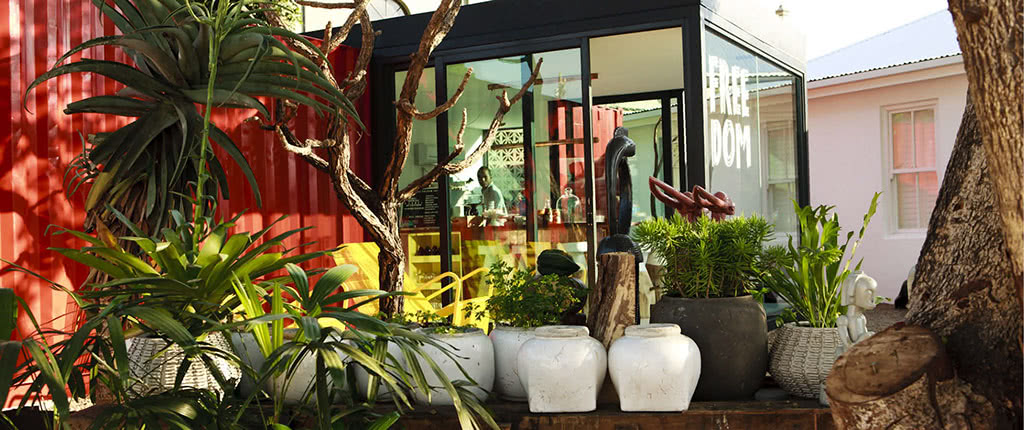
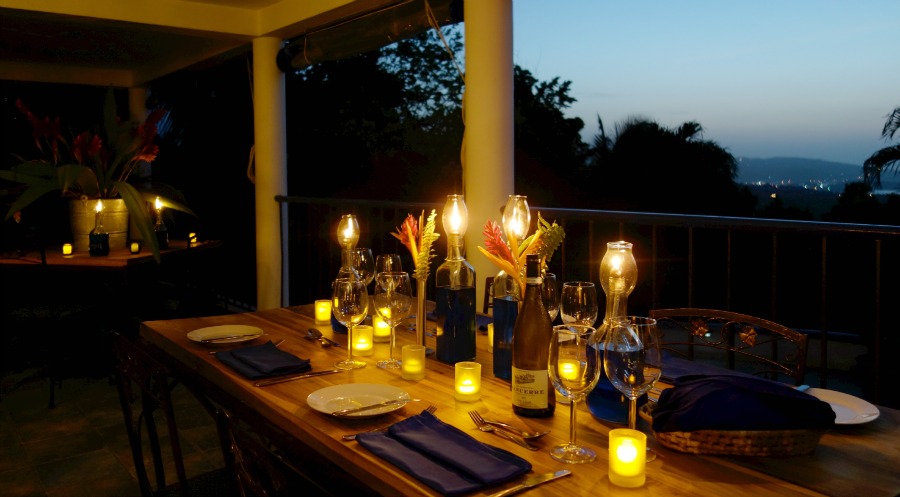
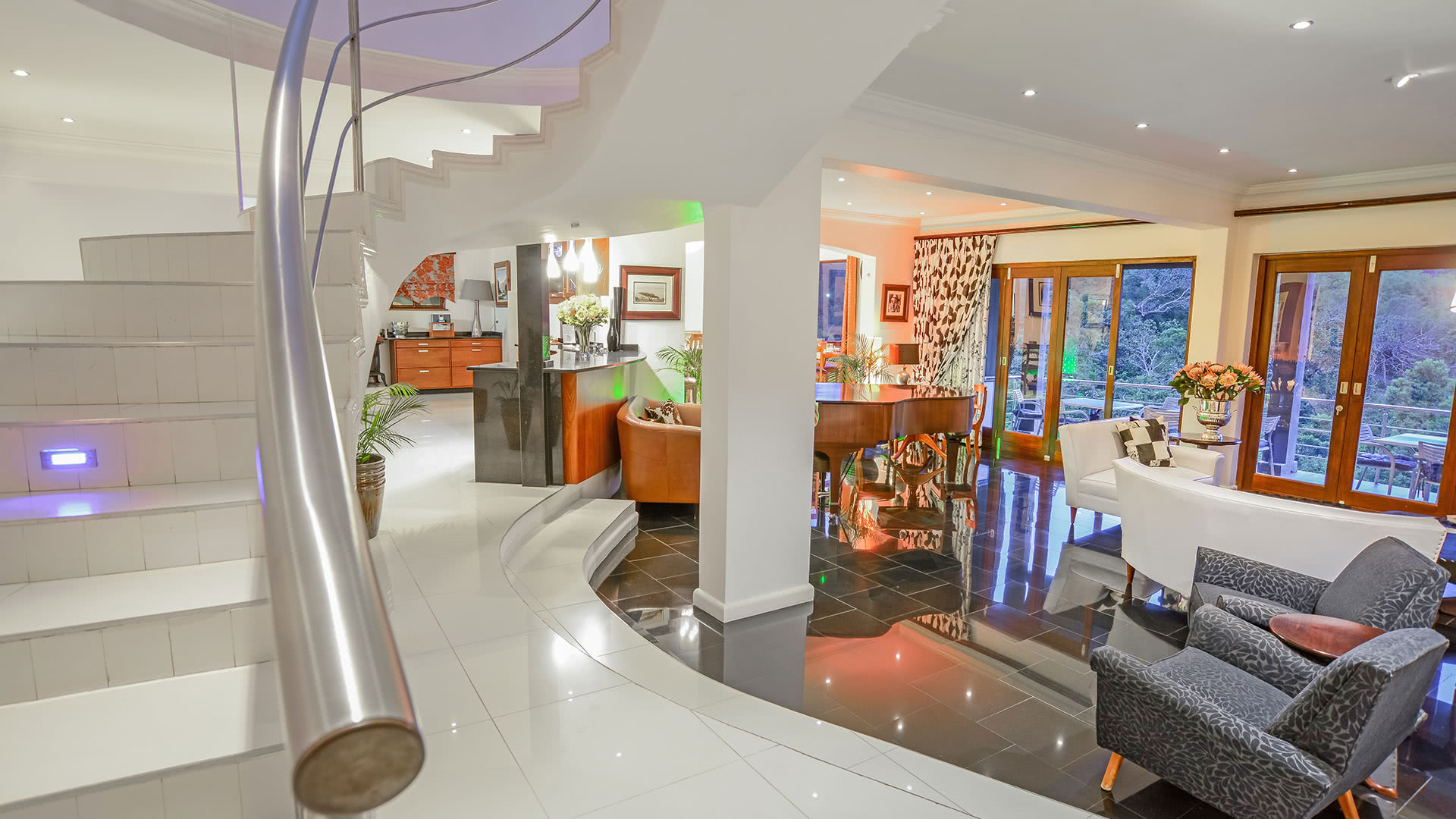
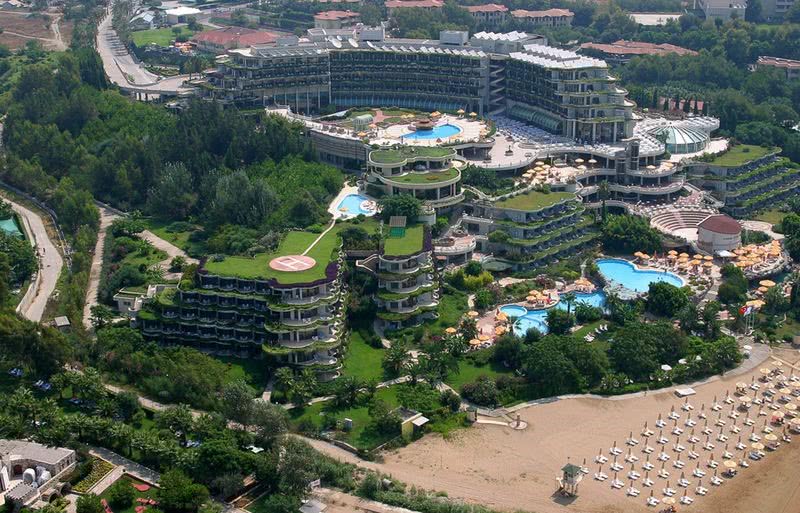
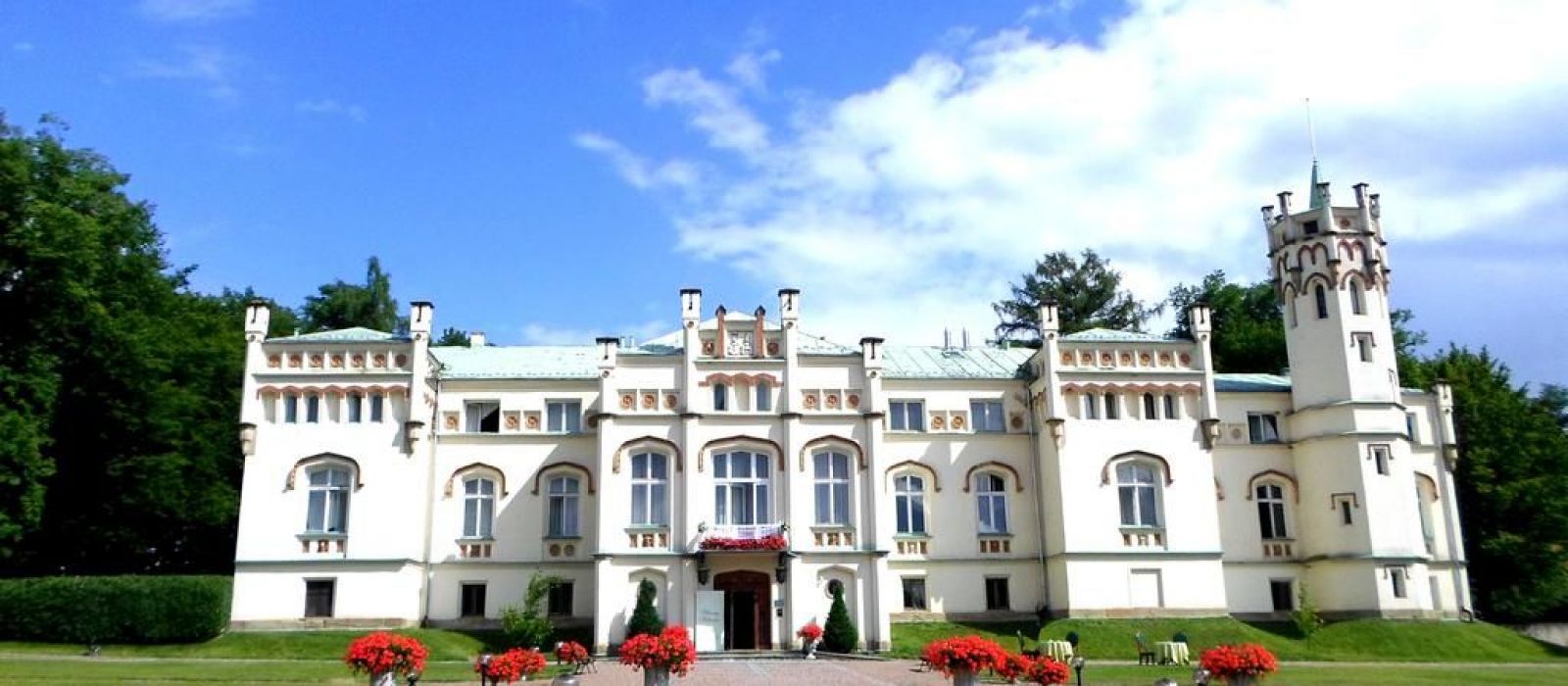
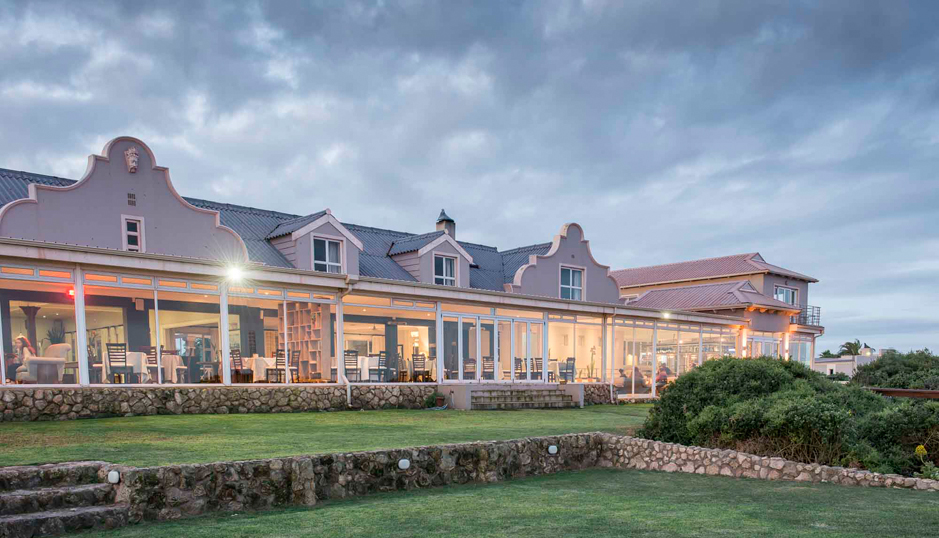
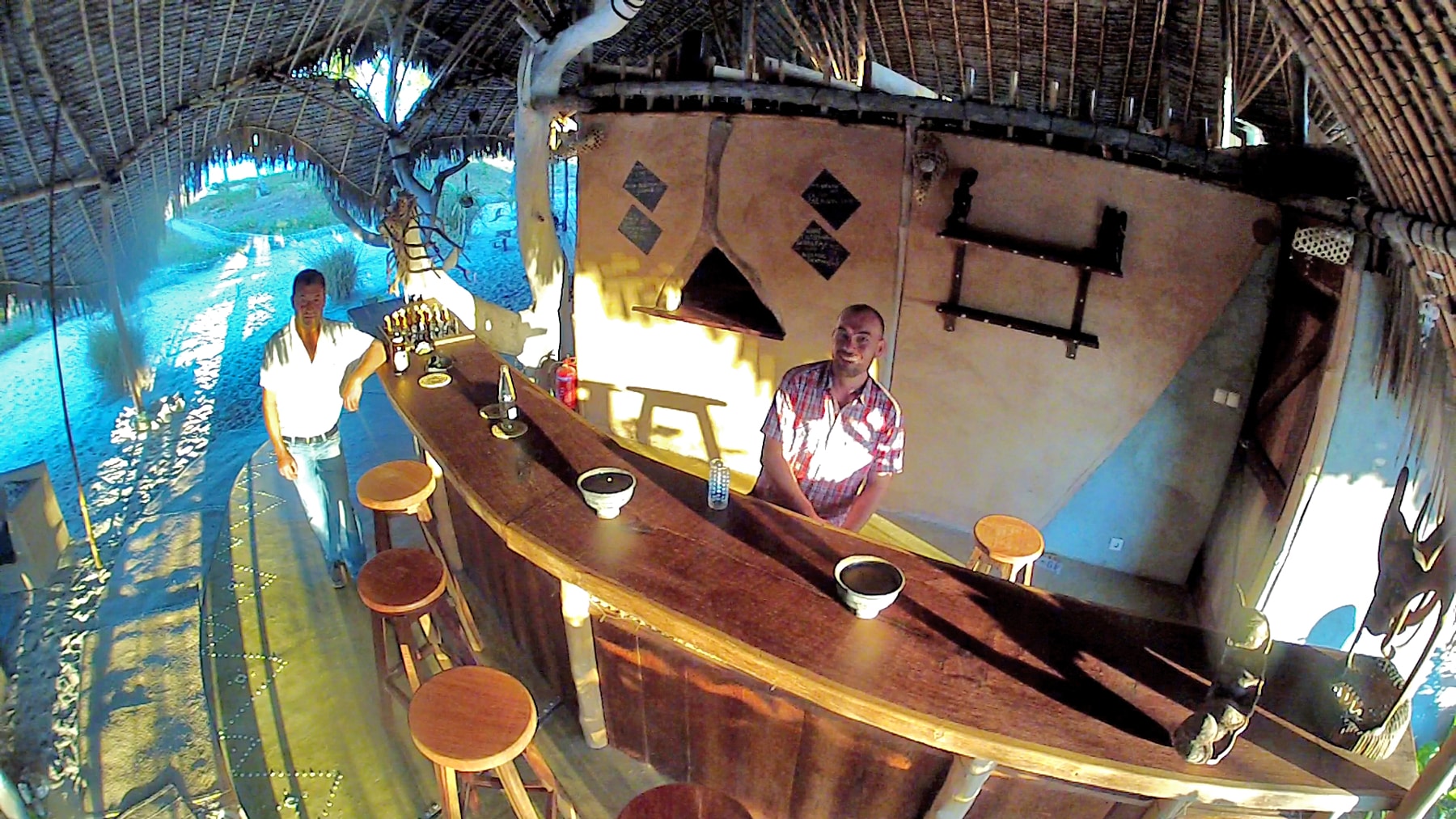
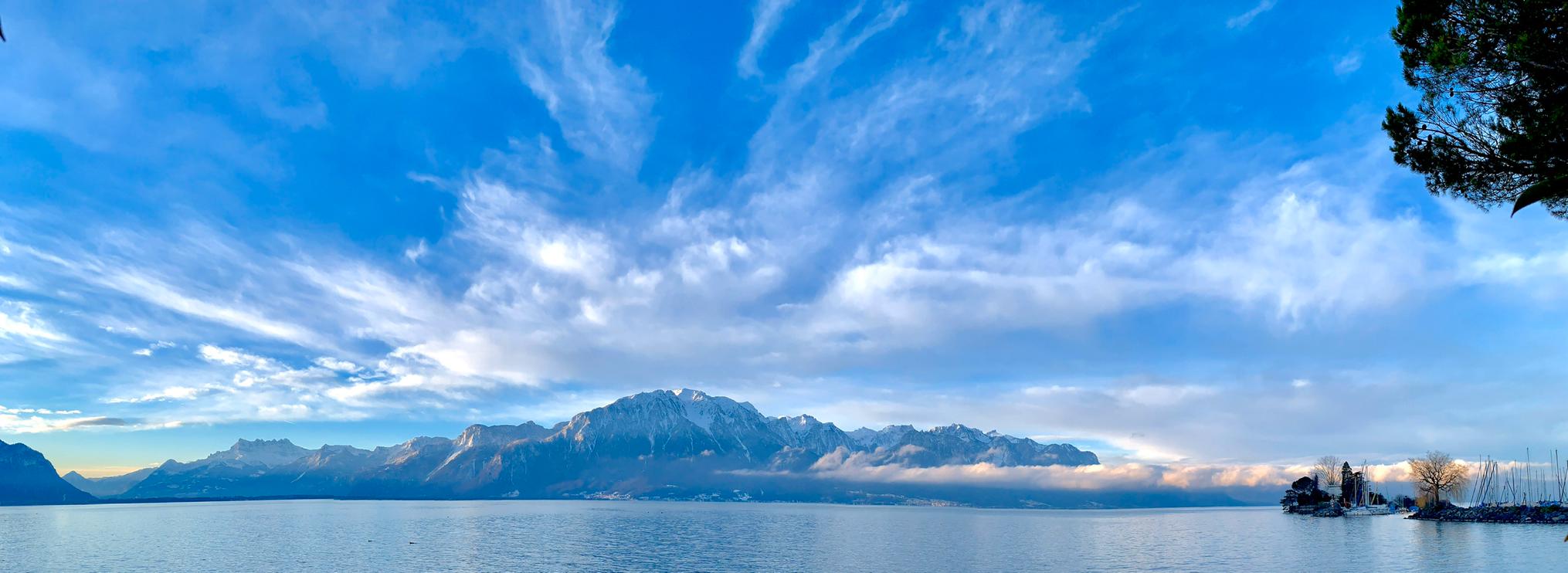
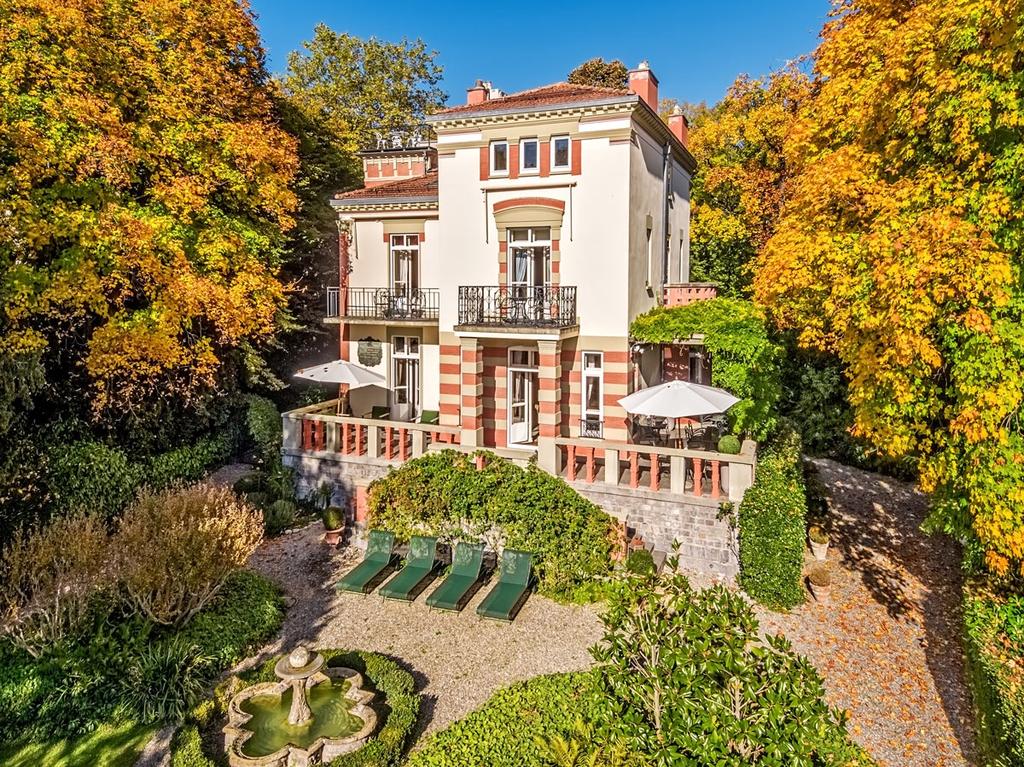
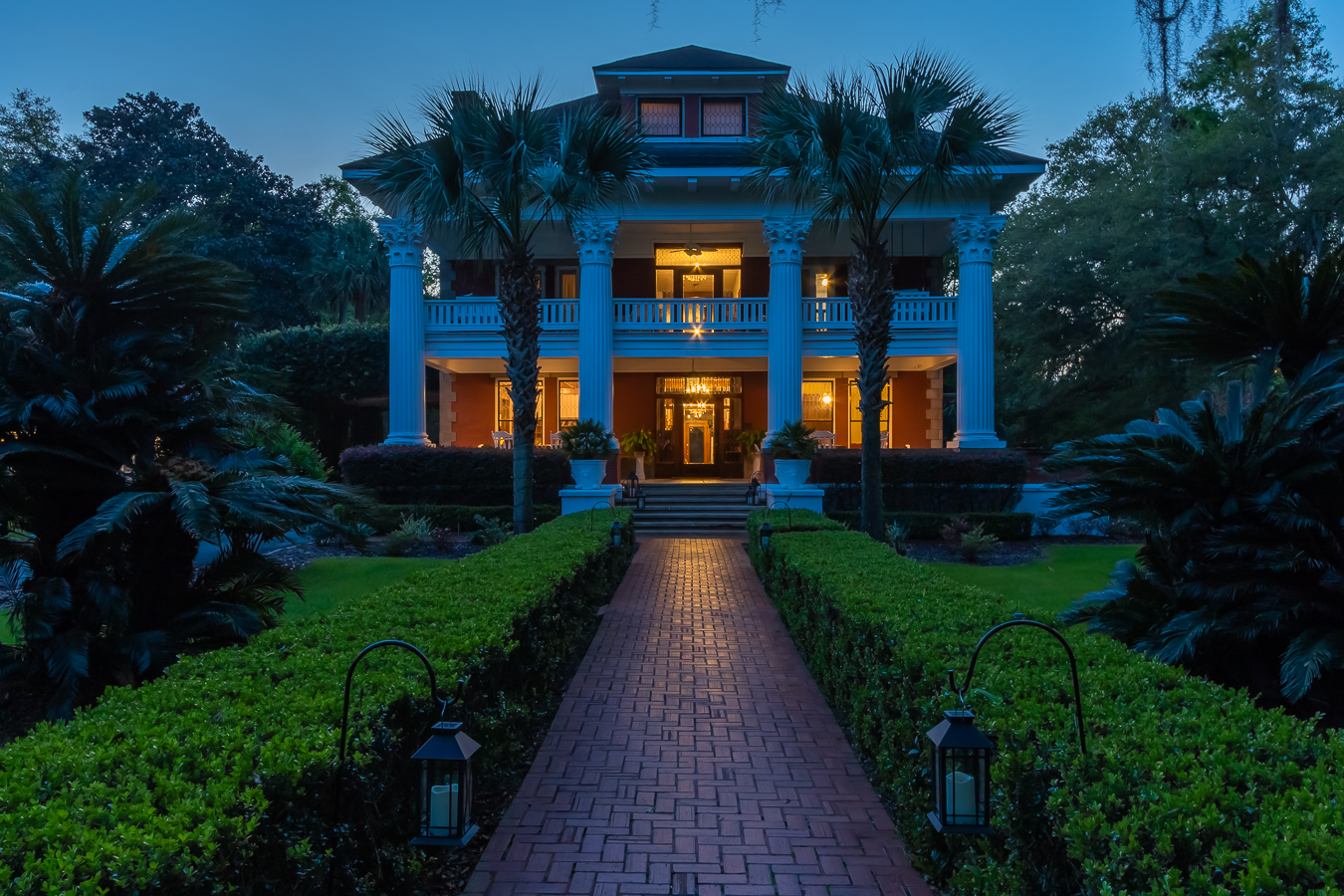
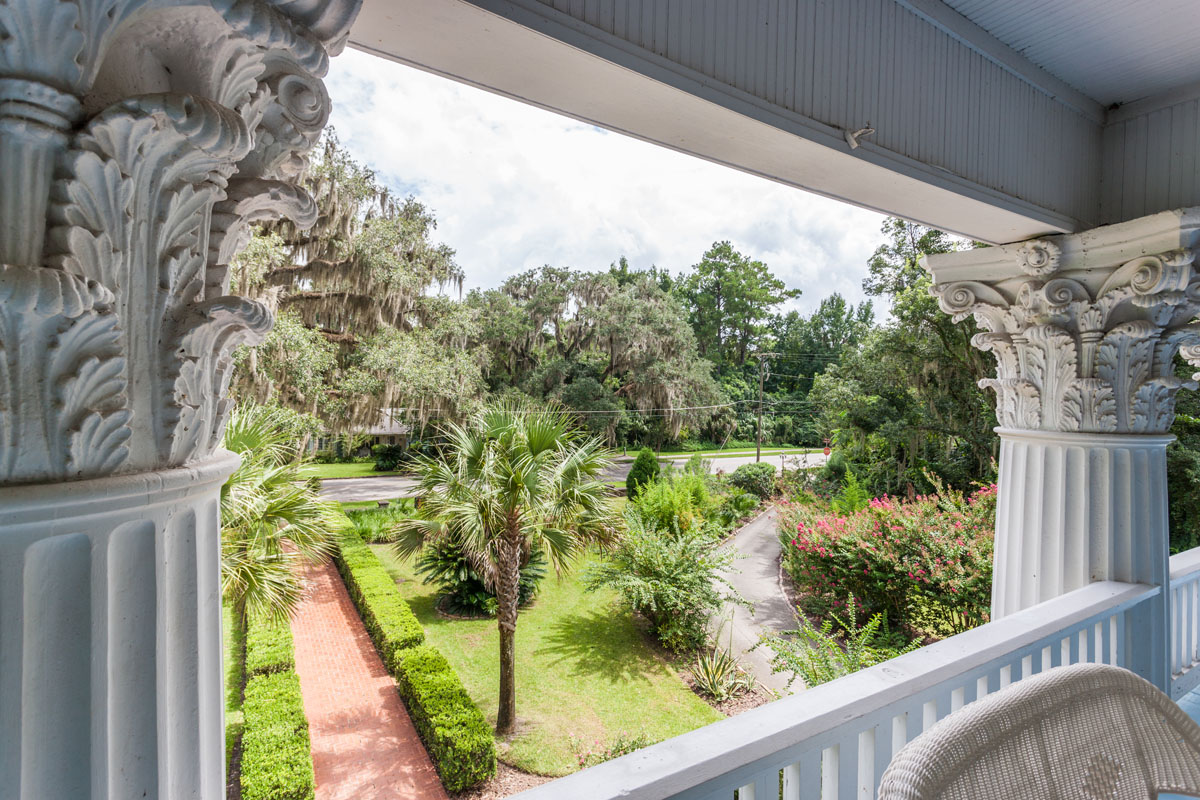
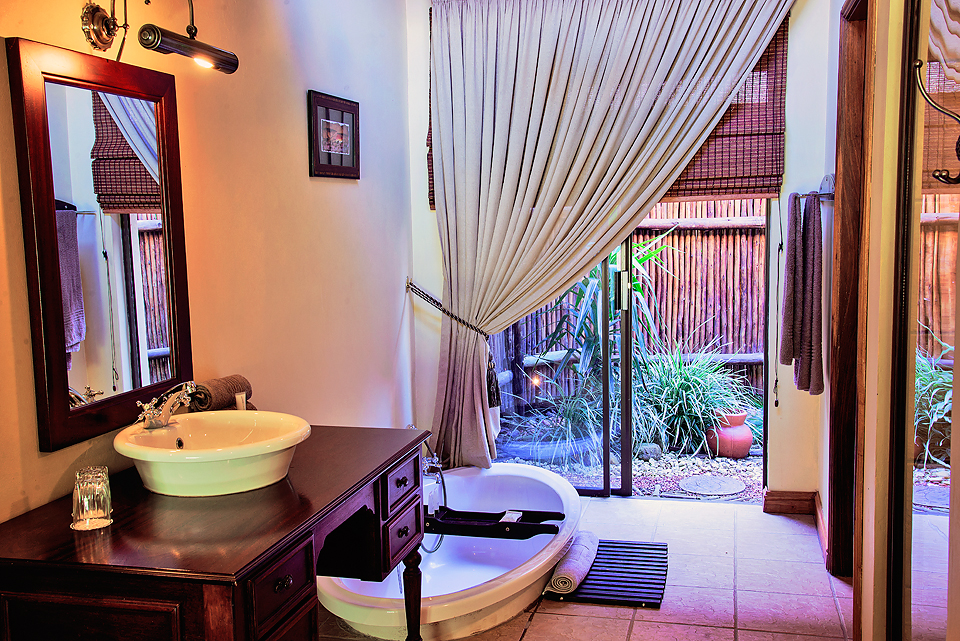
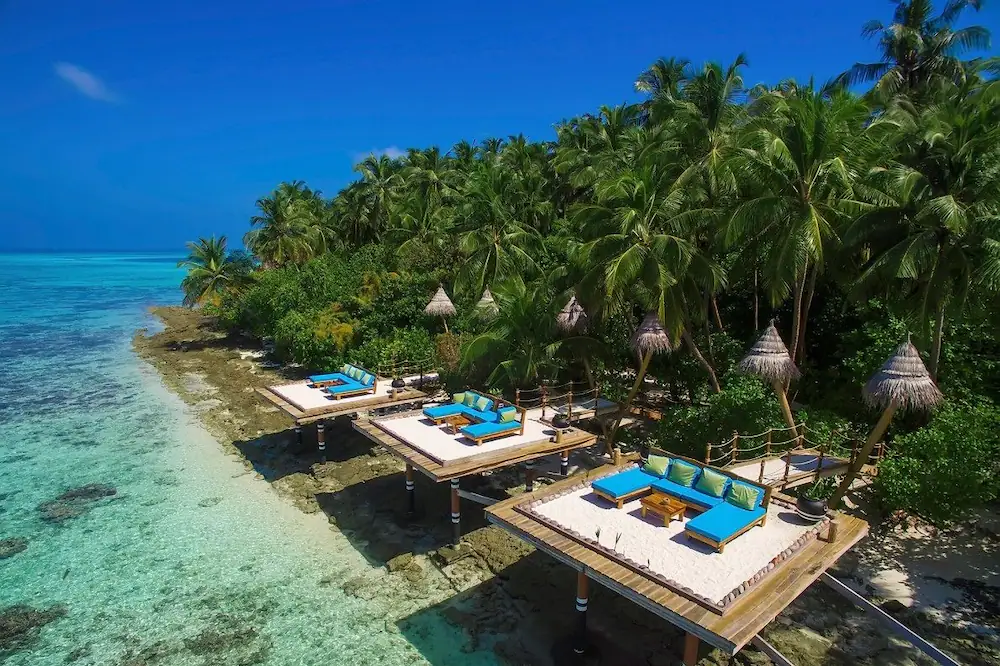
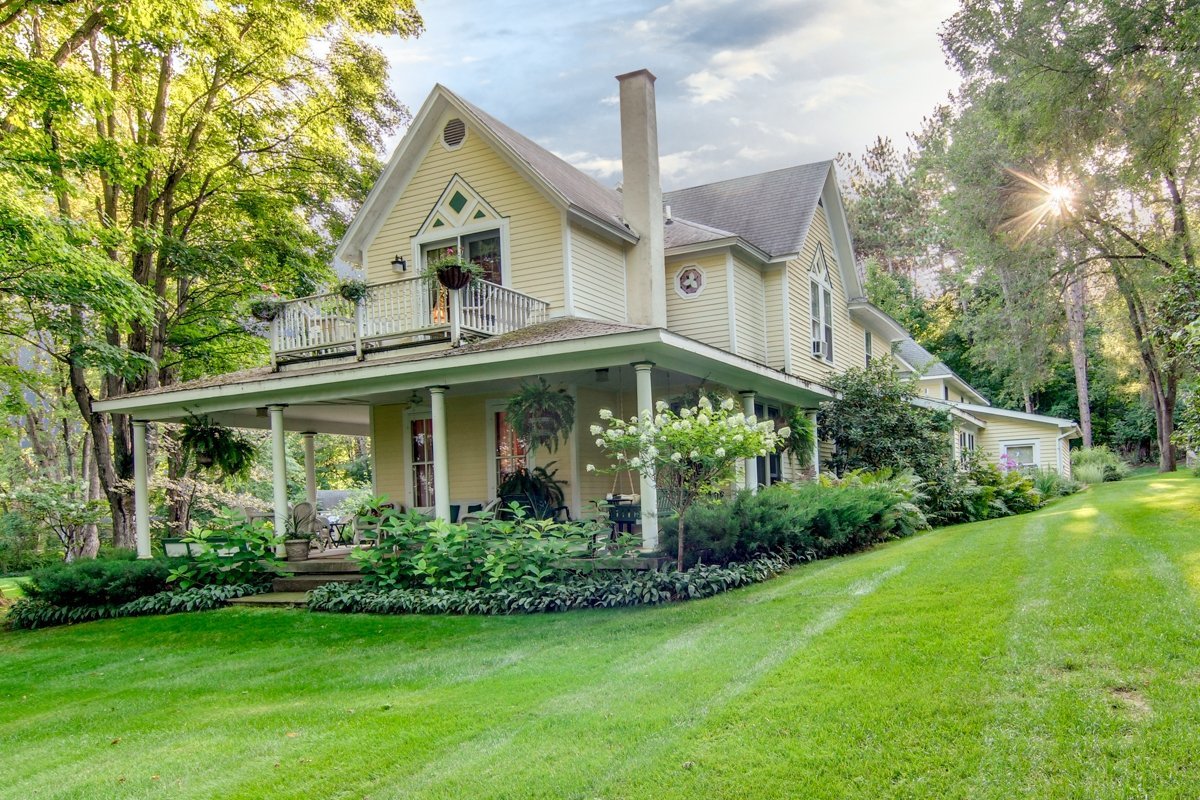
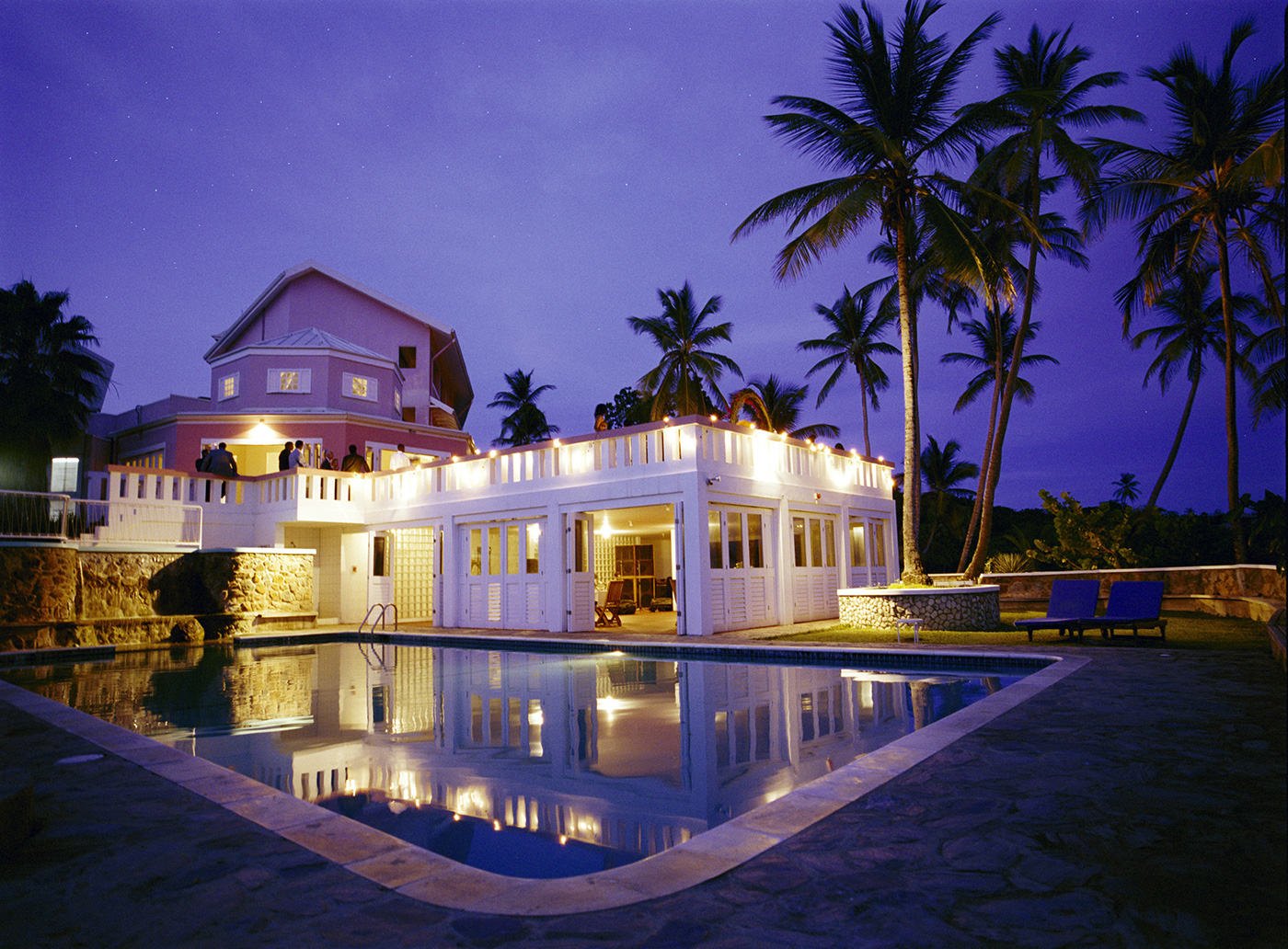








































































Salento, Quindio, Colombia
Agent: Cliff Jacobs - Managing Principal Estate Agent & CEO (Nat.Dpl.Hotel Man (UJ). M.P.R.E.)
Agent Cellphone: +27 (0) 84 413 1071 / +27 (0) 61 716 6951
Agent Office Number: +27 (0) 84 413 1071
Agent Email Address: cliff@exquisitehotelconsultants.com
Type: Guest Farm & Eco Estate Project
Bedrooms: 5
Bathrooms: 5
Showers: 5
Parking: 8
Yield: Not Disclosed
TGCSA Rating:

Colombia
Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country in South America. It is bounded on the north by the Caribbean Sea, the northwest by Panama, the south by Ecuador and Peru, the east by Venezuela, the southeast by Brazil, and the west by the Pacific Ocean. Colombia is composed of 32 departments and the Capital District of Bogotá, the country's largest city. It covers an area of 1,141,748 square kilometres (440,831 sq mi), with a population of 50 million. Colombia's rich cultural heritage reflects influences by various Amerindian civilizations, European settlement, African slaves, and immigration from Europe and the Middle East. Spanish is the nation's official language, besides which over 70 languages are spoken.
Colombia has been inhabited by various indigenous peoples since at least 12,000 BCE, including the Muisca, Quimbaya, and the Tairona. The Spanish landed first in La Guajira in 1499 and by the mid-16th century colonized parts of the region, establishing the New Kingdom of Granada, with Santafé de Bogotá as its capital. Independence from the Spanish Empire was achieved in 1819, with what is now Colombia emerging as the United Provinces of New Granada. The new nation experimented with federalism as the Granadine Confederation (1858), and then the United States of Colombia (1863), before the Republic of Colombia was finally declared in 1886. Panama seceded in 1903, leading to Colombia's present borders. Beginning in the 1960s, the country has suffered from an asymmetric low-intensity armed conflict and political violence, both of which escalated in the 1990s. Since 2005, there has been significant improvement in security, stability, and rule of law, as well as unprecedented economic growth and development.
Colombia is one of the world's seventeen megadiverse countries, and has the second-highest level of biodiversity in the world. Its territory encompasses Amazon rainforest, highlands, grasslands, and deserts, and it is the only country in South America with coastlines and islands along both Atlantic and Pacific oceans. Colombia is a member of major global and regional organizations including the United Nations, the WTO, the OECD, the OAS, the Pacific Alliance, the Andean Community, and a NATO Global Partner. Its diversified economy is the third-largest in South America, with macroeconomic stability and favorable long-term growth prospects.
Etymology
The name "Colombia" is derived from the last name of the Italian navigator Christopher Columbus (Italian: Cristoforo Colombo, Spanish: Cristóbal Colón). It was conceived as a reference to all of the New World. The name was later adopted by the Republic of Colombia of 1819, formed from the territories of the old Viceroyalty of New Granada (modern-day Colombia, Panama, Venezuela, Ecuador, and northwest Brazil).
When Venezuela, Ecuador, and Cundinamarca came to exist as independent states, the former Department of Cundinamarca adopted the name "Republic of New Granada". New Granada officially changed its name in 1858 to the Granadine Confederation. In 1863 the name was again changed, this time to the United States of Colombia, before finally adopting its present name – the Republic of Colombia – in 1886.
To refer to this country, the Colombian government uses the terms Colombia and República de Colombia.
History
Owing to its location, the present territory of Colombia was a corridor of early human civilization from Mesoamerica and the Caribbean to the Andes and Amazon basin. The oldest archaeological finds are from the Pubenza and El Totumo sites in the Magdalena Valley 100 kilometres (62 mi) southwest of Bogotá. These sites date from the Paleoindian period (18,000–8000 BCE). At Puerto Hormiga and other sites, traces from the Archaic Period (~8000–2000 BCE) have been found. Vestiges indicate that there was also early occupation in the regions of El Abra and Tequendama in Cundinamarca. The oldest pottery discovered in the Americas, found at San Jacinto, dates to 5000–4000 BCE.
Indigenous people inhabited the territory that is now Colombia by 12,500 BCE. Nomadic hunter-gatherer tribes at the El Abra, Tibitó and Tequendama sites near present-day Bogotá traded with one another and with other cultures from the Magdalena River Valley. A site including eight miles (13 km) of pictographs that is under study at Serranía de la Lindosa was revealed in November 2020. Their age is suggested as being 12,500 years old (c. 10,480 B.C.) by the anthropologists working on the site because of extinct fauna depicted. That would have been during the earliest known human occupation of the area now known as Colombia.
Between 5000 and 1000 BCE, hunter-gatherer tribes transitioned to agrarian societies; fixed settlements were established, and pottery appeared. Beginning in the 1st millennium BCE, groups of Amerindians including the Muisca, Zenú, Quimbaya, and Tairona developed the political system of cacicazgos with a pyramidal structure of power headed by caciques. The Muisca inhabited mainly the area of what is now the Departments of Boyacá and Cundinamarca high plateau (Altiplano Cundiboyacense) where they formed the Muisca Confederation. They farmed maize, potato, quinoa, and cotton, and traded gold, emeralds, blankets, ceramic handicrafts, coca and especially rock salt with neighboring nations. The Tairona inhabited northern Colombia in the isolated mountain range of Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta.The Quimbaya inhabited regions of the Cauca River Valley between the Western and Central Ranges of the Colombian Andes. Most of the Amerindians practiced agriculture and the social structure of each indigenous community was different. Some groups of indigenous people such as the Caribs lived in a state of permanent war, but others had less bellicose attitudes.
European annexation
Alonso de Ojeda (who had sailed with Columbus) reached the Guajira Peninsula in 1499. Spanish explorers, led by Rodrigo de Bastidas, made the first exploration of the Caribbean coast in 1500. Christopher Columbus navigated near the Caribbean in 1502. In 1508, Vasco Núñez de Balboa accompanied an expedition to the territory through the region of Gulf of Urabá and they founded the town of Santa María la Antigua del Darién in 1510, the first stable settlement on the continent.
Santa Marta was founded in 1525, and Cartagena in 1533. Spanish conquistador Gonzalo Jiménez de Quesada led an expedition to the interior in April 1536, and christened the districts through which he passed "New Kingdom of Granada". In August 1538, he founded provisionally its capital near the Muisca cacicazgo of Muyquytá, and named it "Santa Fe". The name soon acquired a suffix and was called Santa Fe de Bogotá. Two other notable journeys by early conquistadors to the interior took place in the same period. Sebastián de Belalcázar, conqueror of Quito, traveled north and founded Cali, in 1536, and Popayán, in 1537; from 1536 to 1539, German conquistador Nikolaus Federmann crossed the Llanos Orientales and went over the Cordillera Oriental in a search for El Dorado, the "city of gold". The legend and the gold would play a pivotal role in luring the Spanish and other Europeans to New Granada during the 16th and 17th centuries.
The conquistadors made frequent alliances with the enemies of different indigenous communities. Indigenous allies were crucial to conquest, as well as to creating and maintaining an empire. Indigenous peoples in New Granada experienced a decline in population due to conquest as well as Eurasian diseases, such as smallpox, to which they had no immunity. Regarding the land as deserted, the Spanish Crown sold properties to all persons interested in colonized territories, creating large farms and possession of mines.
In the 16th century, nautical science in Spain reached a great development thanks to numerous scientific figures of the Casa de Contratación and nautical science was an essential pillar of the Iberian expansion.
Economy
Historically an agrarian economy, Colombia urbanized rapidly in the 20th century, by the end of which just 15.8% of the workforce were employed in agriculture, generating just 6.6% of GDP; 19.6% of the workforce were employed in industry and 64.6% in services, responsible for 33.4% and 59.9% of GDP respectively. The country's economic production is dominated by its strong domestic demand. Consumption expenditure by households is the largest component of GDP.
Colombia's market economy grew steadily in the latter part of the 20th century, with the gross domestic product (GDP) increasing at an average rate of over 4% per year between 1970 and 1998. The country suffered a recession in 1999 (the first full year of negative growth since the Great Depression), and the recovery from that recession was long and painful. However, in recent years growth has been impressive, reaching 6.9% in 2007, one of the highest rates of growth in Latin America. According to International Monetary Fund estimates, in 2012, Colombia's GDP (PPP) was US$500 billion (28th in the world and third in South America). Colombia's economy shrank by 6.8 percent in 2020 due to the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic. By July 2021, Colombia had more than 3.6 million COVID-19 cases and 95,000 deaths which resulted in increased medical bills and income supplements for the poor.
Total government expenditures account for 27.9 percent of the domestic economy. External debt equals 39.9 percent of gross domestic product. A strong fiscal climate was reaffirmed by a boost in bond ratings. Annual inflation closed 2017 at 4.09% YoY (vs. 5.75% YoY in 2016). The average national unemployment rate in 2017 was 9.4%, although informality is the biggest problem facing the labour market (the income of formal workers climbed 24.8% in 5 years while labor incomes of informal workers rose only 9%). Colombia has free-trade zones (FTZ), such as Zona Franca del Pacifico, located in the Valle del Cauca, one of the most striking areas for foreign investment.
The financial sector has grown favorably due to good liquidity in the economy, the growth of credit and the positive performance of the Colombian economy. The Colombian Stock Exchange through the Latin American Integrated Market (MILA) offers a regional market to trade equities. Colombia is now one of only three economies with a perfect score on the strength of legal rights index, according to the World Bank
The electricity production in Colombia comes mainly from Renewable energy sources. 69.93% is obtained from hydroelectric generation. Colombia's commitment to renewable energy was recognized in the 2014 Global Green Economy Index (GGEI), ranking among the top 10 nations in the world in terms of greening efficiency sectors.
Colombia is rich in natural resources, and its main exports include mineral fuels, oils, distillation products, fruit and other agricultural products, sugars and sugar confectionery, food products, plastics, precious stones, metals, forest products, chemical goods, pharmaceuticals, vehicles, electronic products, electrical equipment, perfumery and cosmetics, machinery, manufactured articles, textile and fabrics, clothing and footwear, glass and glassware, furniture, prefabricated buildings, military products, home and office material, construction equipment, software, among others. Principal trading partners are the United States, China, the European Union and some Latin American countries.
Non-traditional exports have boosted the growth of Colombian foreign sales as well as the diversification of destinations of export thanks to new free trade agreements.
In 2017, the National Administrative Department of Statistics (DANE) reported that 26.9% of the population were living below the poverty line, of which 7.4% were in "extreme poverty". The multidimensional poverty rate stands at 17.0 percent of the population. The Government has also been developing a process of financial inclusion within the country's most vulnerable population.
Recent economic growth has led to a considerable increase of new millionaires, including the new entrepreneurs, Colombians with a net worth exceeding US$1 billion.
The contribution of Travel & Tourism to GDP was US$5,880.3bn (2.0% of total GDP) in 2016. Tourism generated 556,135 jobs (2.5% of total employment) in 2016. Foreign tourist visits were predicted to have risen from 0.6 million in 2007 to 4 million in 2017.
Description by the owners
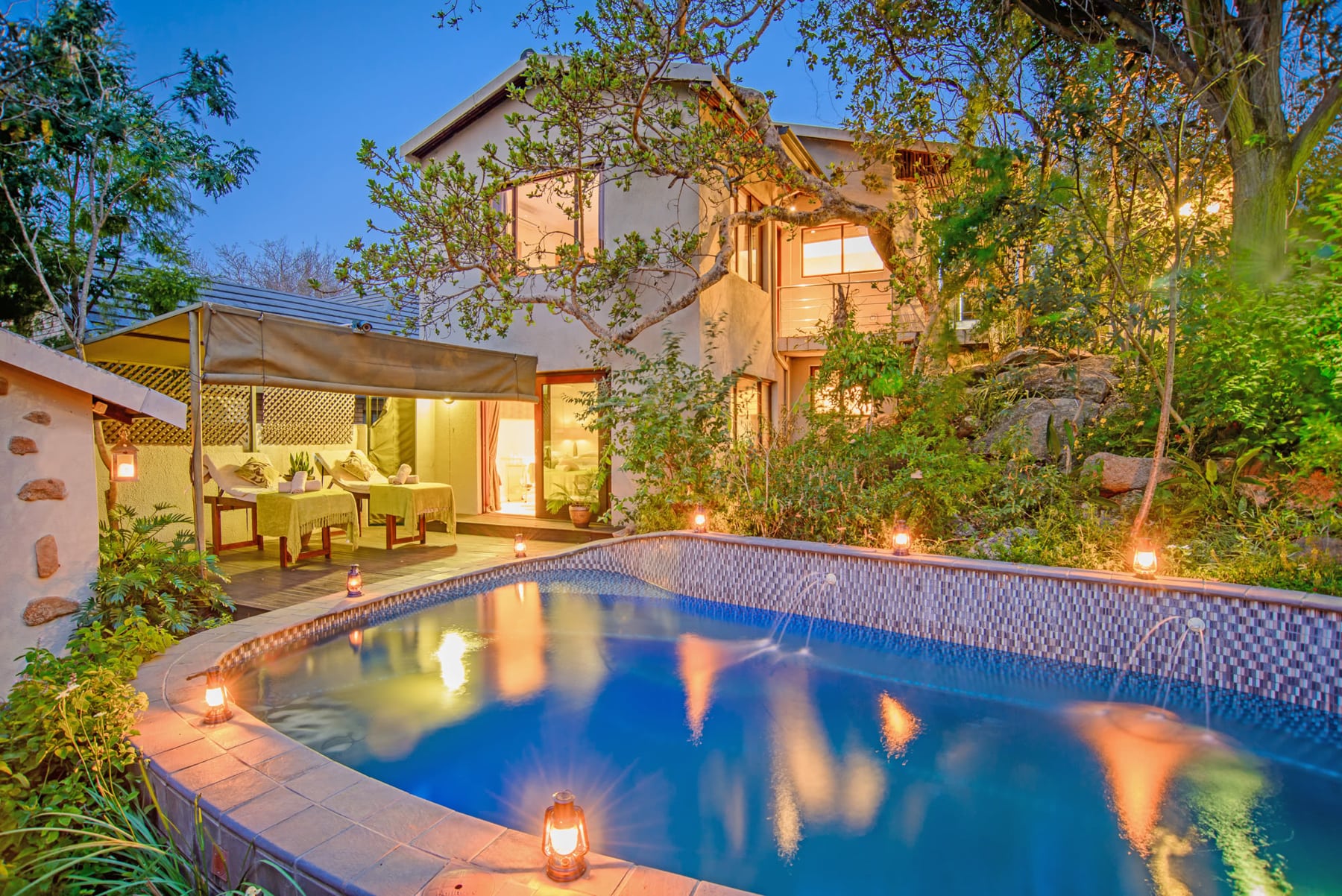
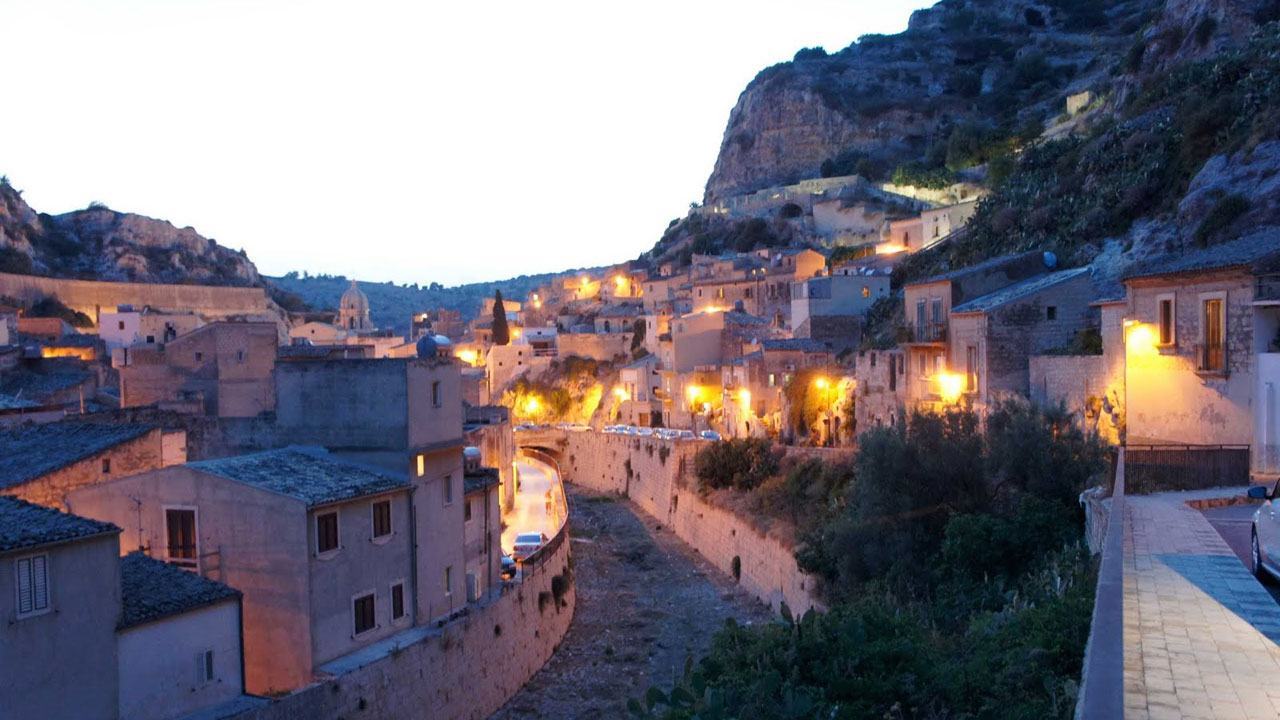
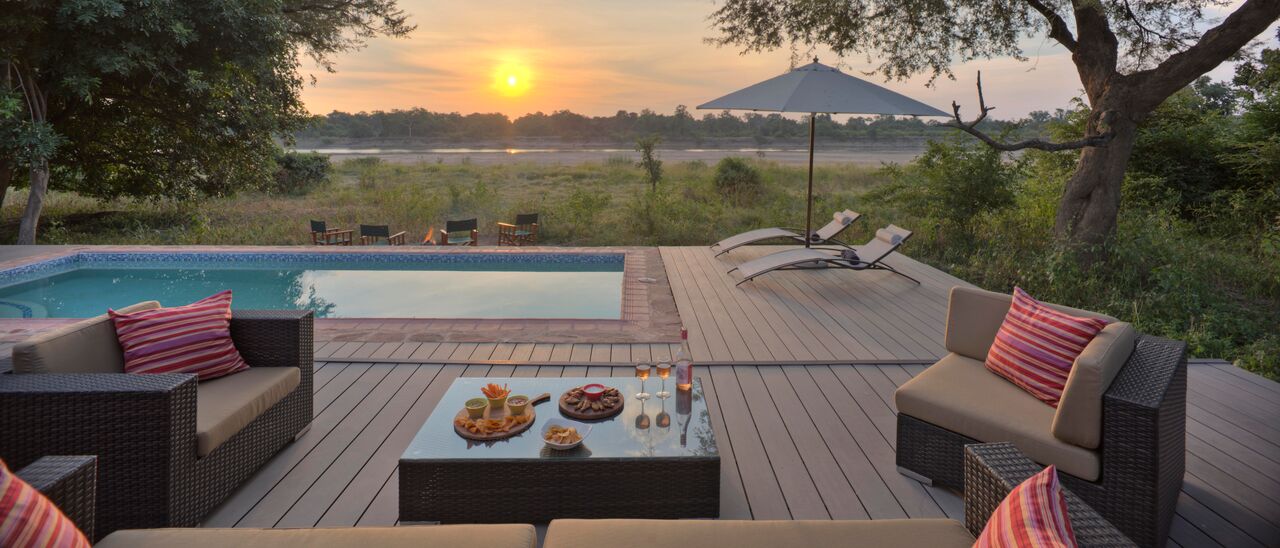
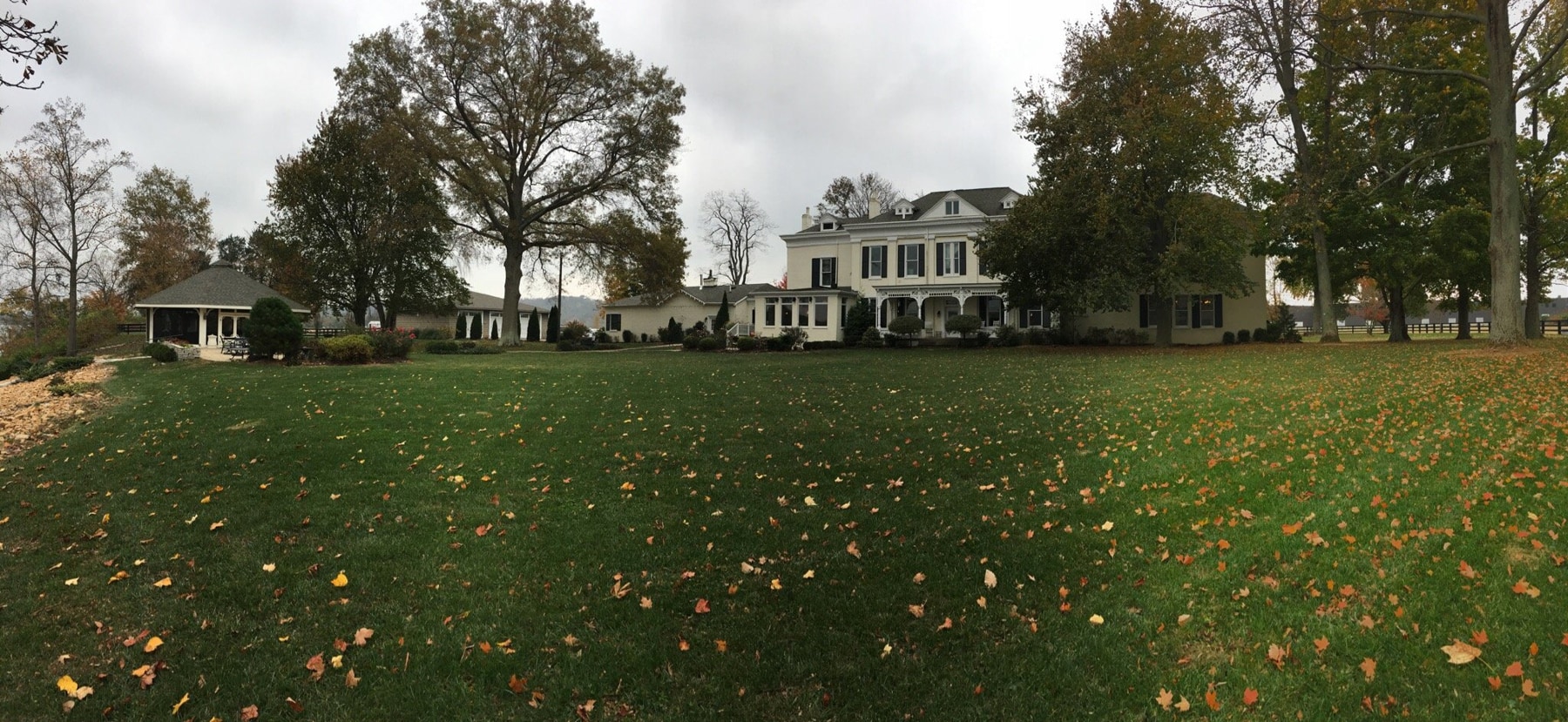
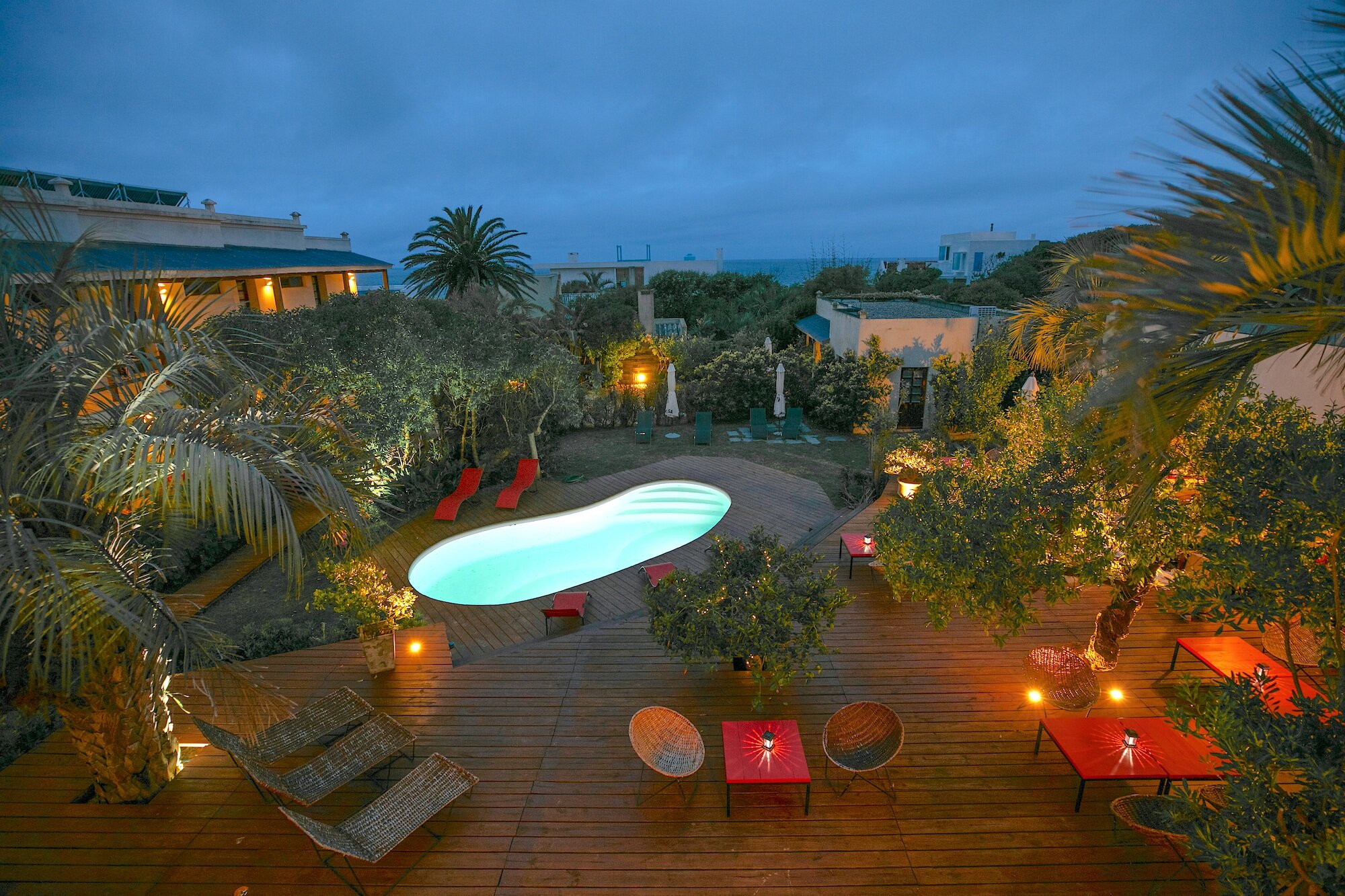
Our Ecoresort offers wonderful accommodation located in the Colombian Andes at 2000 meters altitude, within a beautiful rural location. You will find us only a 5-minute walk (700 metres) from the colourful and traditional village of Salento, one of the most welcoming villages in Colombia, in the coffee cultural landscape of this patrimonial municipality.
Our philosophy
This project was born out of a dream. After spending the past three years sailing with our 4-year-old daughter in the Atlantic Ocean, we decided to settle down in Colombia and to travel through the Eje Cafetero looking for a piece of land for our project. We fell in love at first sight with a site surrounded by a fascinating landscape full of fauna and flora, and we started building the future Ecoresort.
Guest Facilities On-Site
Attractions For Guests In The Local Area
Activities For Guests In The Local Area
Owner Facilities On-Site
Installations
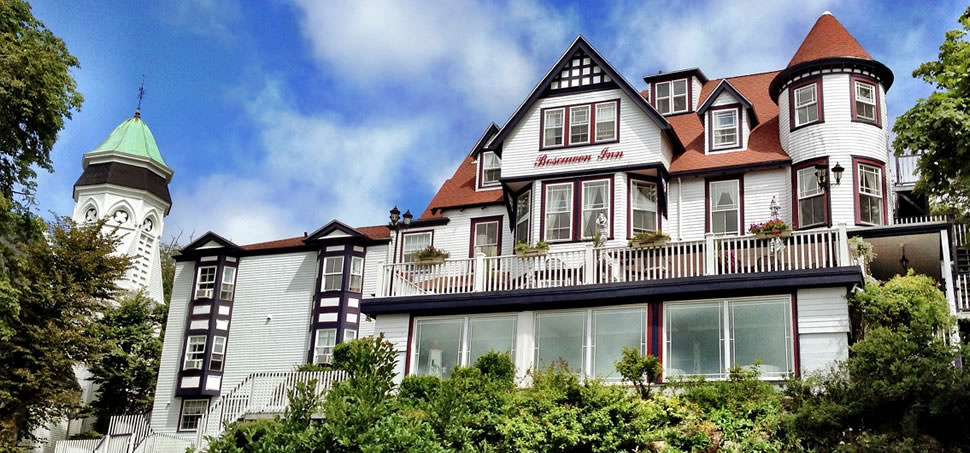
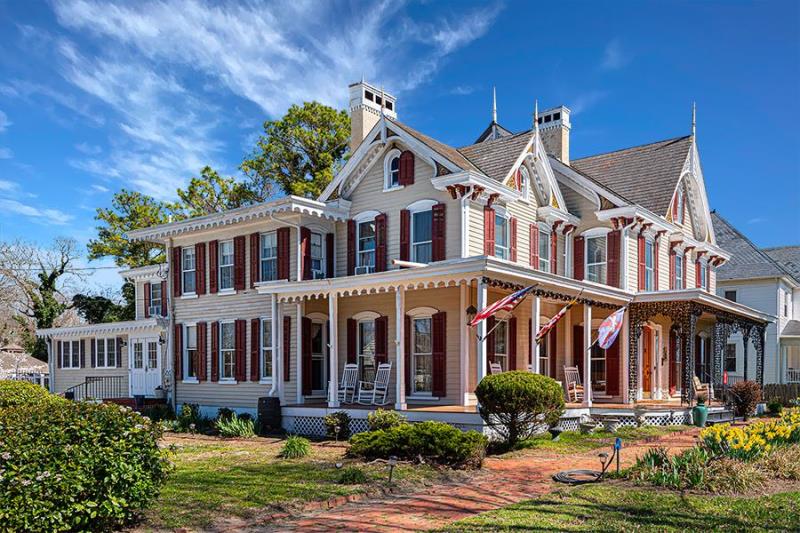
The Hotel was built throughout 2016. In it, the owners decided to reflect all their illusions, their positivism and their creativity. In short, his passions: for the detail, for the pampering, for achieving a familiar, close, perfect atmosphere, and magical. Construction culminated with the official inauguration in September 2016. His dream became a reality.
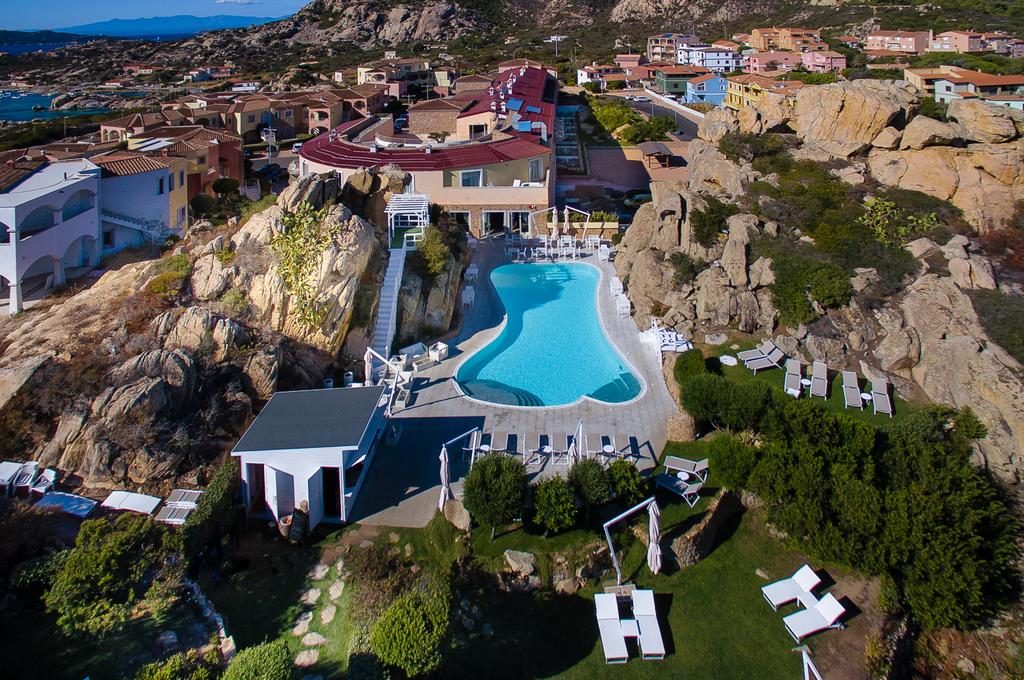
The Ecoresort is located on a one-hectare lot with excellent views. It is a 40-minute drive from the airports in the cities of Pereira and Armenia, which receive daily international flights.
It is an ideal hotel for couples seeking the tranquillity of nature, travellers who love bird watching, mountain-bike excursions, hikes and high mountain excursions.
But they also welcome families with children who want a different experience integrated into this wonderful environment.
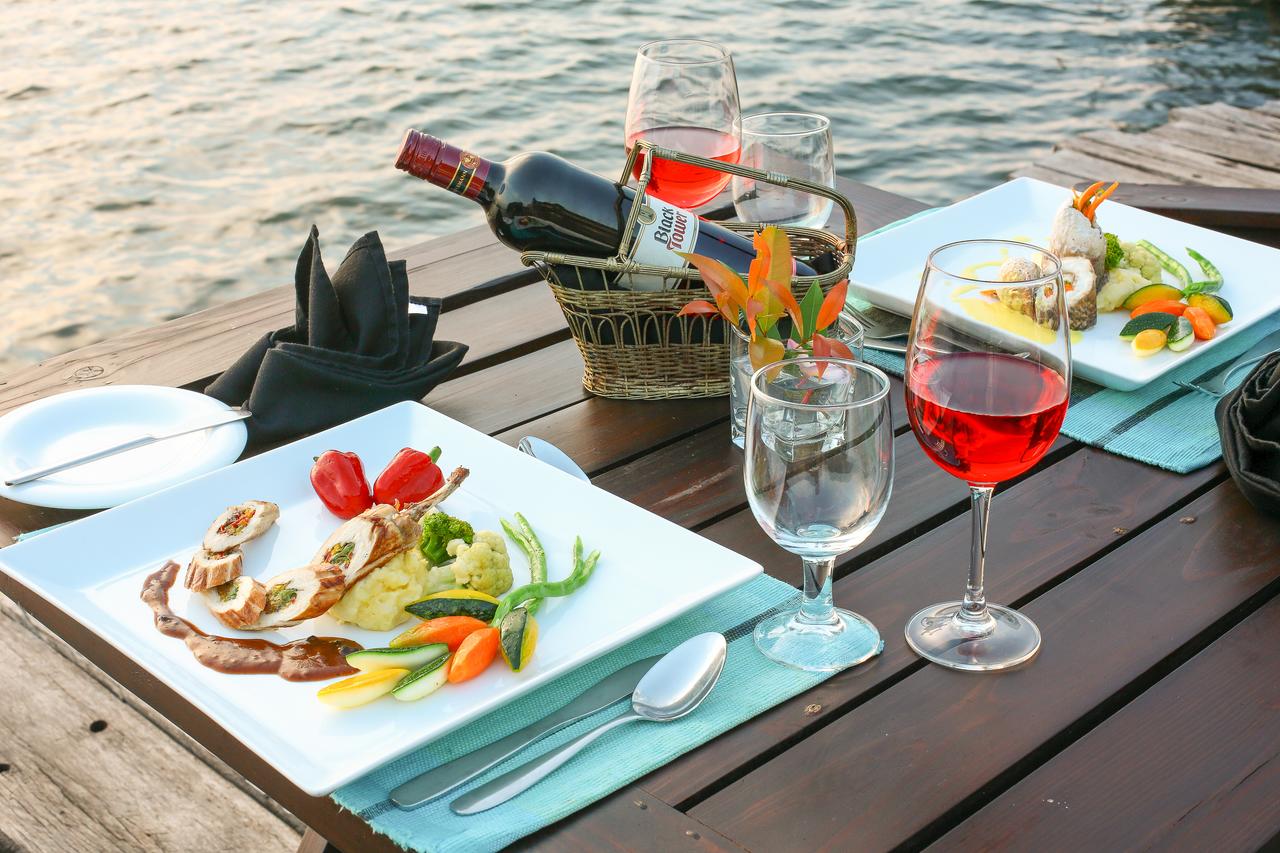
We have facilities and areas for children to play quietly, while adults enjoy the green areas, a cozy chat around the fireplace in the living room, breakfasts in our spacious dining room, a visit to our organic garden, or a hike along our Eco-Trail that runs through the entire terrain.
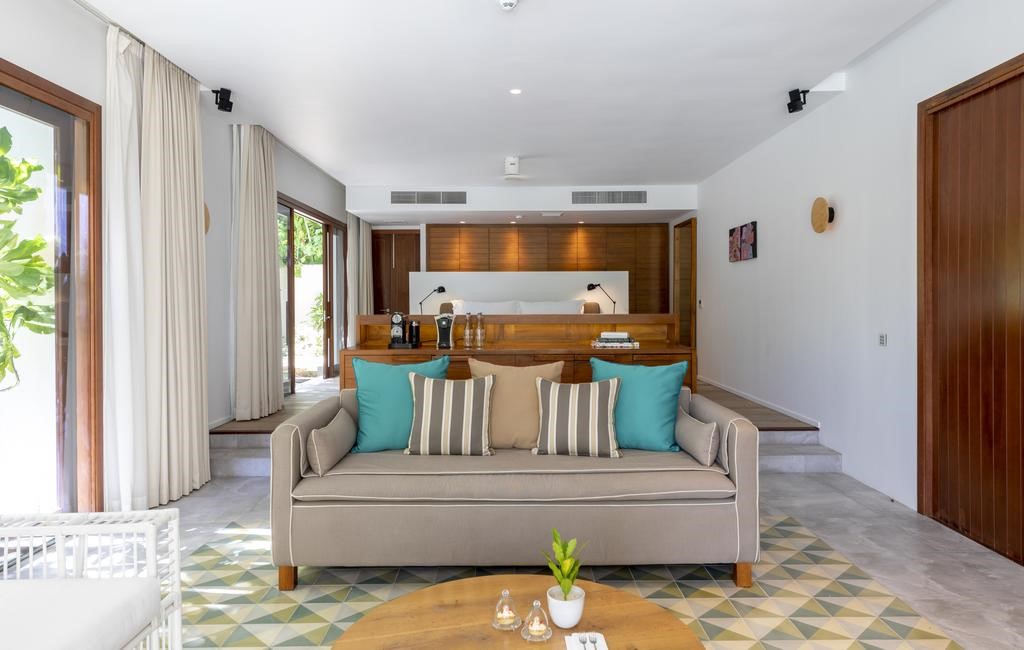
Hotel Rooms
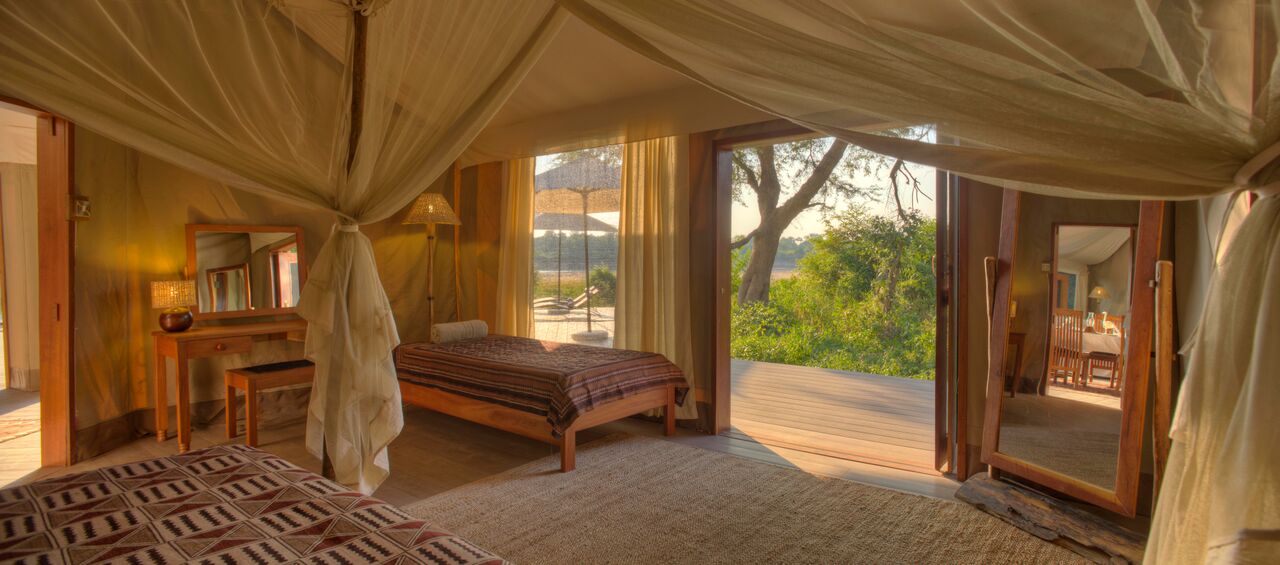
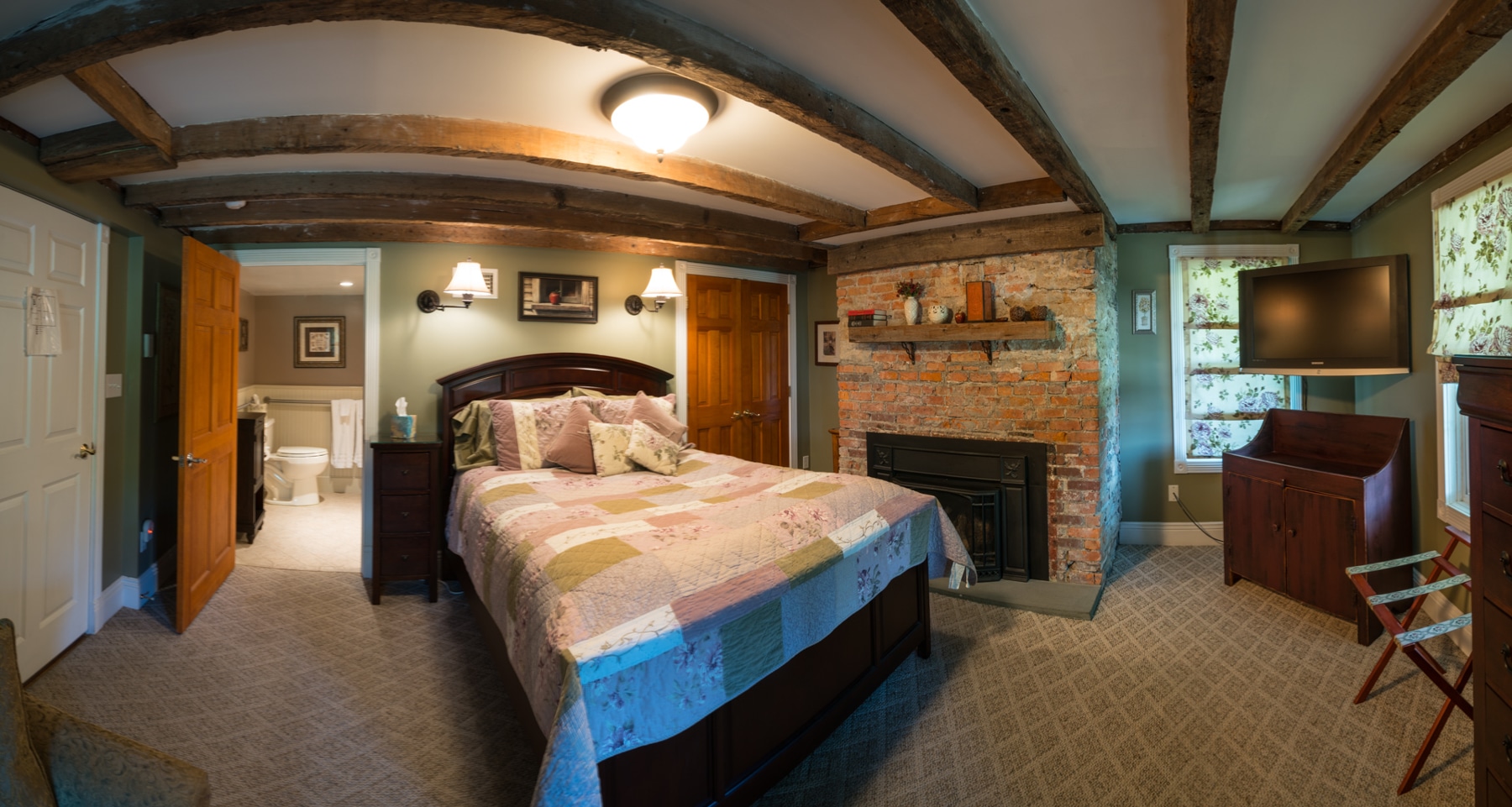
We have five rooms with stunning views, as well as an apartment located in an adjacent little house.
The spacious rooms accommodate two, three or four people: they have a large double bed (1.80m) that can be converted into two single beds, as well as a sofa bed for two children or one adult. They have a private bathroom and internet access.
The rooms are all the same and are linked by a paisa-style corridor and separated from the main building by stairs and a garden area. In the main building, a delicious and healthy breakfast (included) will be served every day between 7 am and 9 am, a buffet that includes local and garden products.
Apartment
The apartment is located in a 40 square metre house in the upper part of the property. It has three spaces: a bedroom with a double bed, a bathroom and a kitchen/living room, where there is a sofa bed for two children or an adult. It has absolute autonomy since the house includes a complete kitchen with a refrigerator and all the necessary utensils for cooking. Breakfast served at the hotel is not included for guests of the apartment.
Activities
In the Ecoresort, you will find all the information and we will be happy to assist you to organize any activity.
Salento is known as the birthplace of La Palma de Cera, the national tree of Colombia, and has a great variety of tourist attractions, all of them closely linked to the observation of nature. Our traditional "Willys" will take you to know the Natural Park of the Cocora Valley where you can admire the spectacular landscape, go on ecological walks, excursions on horseback or mountain bike.























































Cliff Jacobs (Nat Dpl Hotel Man (UJ). MPRE. GA Level 5 TEFL) Managing Principal / CEO Exquisite Hotel Consultants (Pty) Ltd Mobile: +27 (0) 84 413 1071 / +27 (0) 61 716 6951 Email: cliff@exquisitehotelconsultants.com Web: https://www.exquisitehotelconsultants.com © All rights reserved Terms and Conditions apply Scroll down to view our Hospitality Properties and Businesses for sale or lease or lease-to-buy or partnership arrangement or management agreement arrangement.