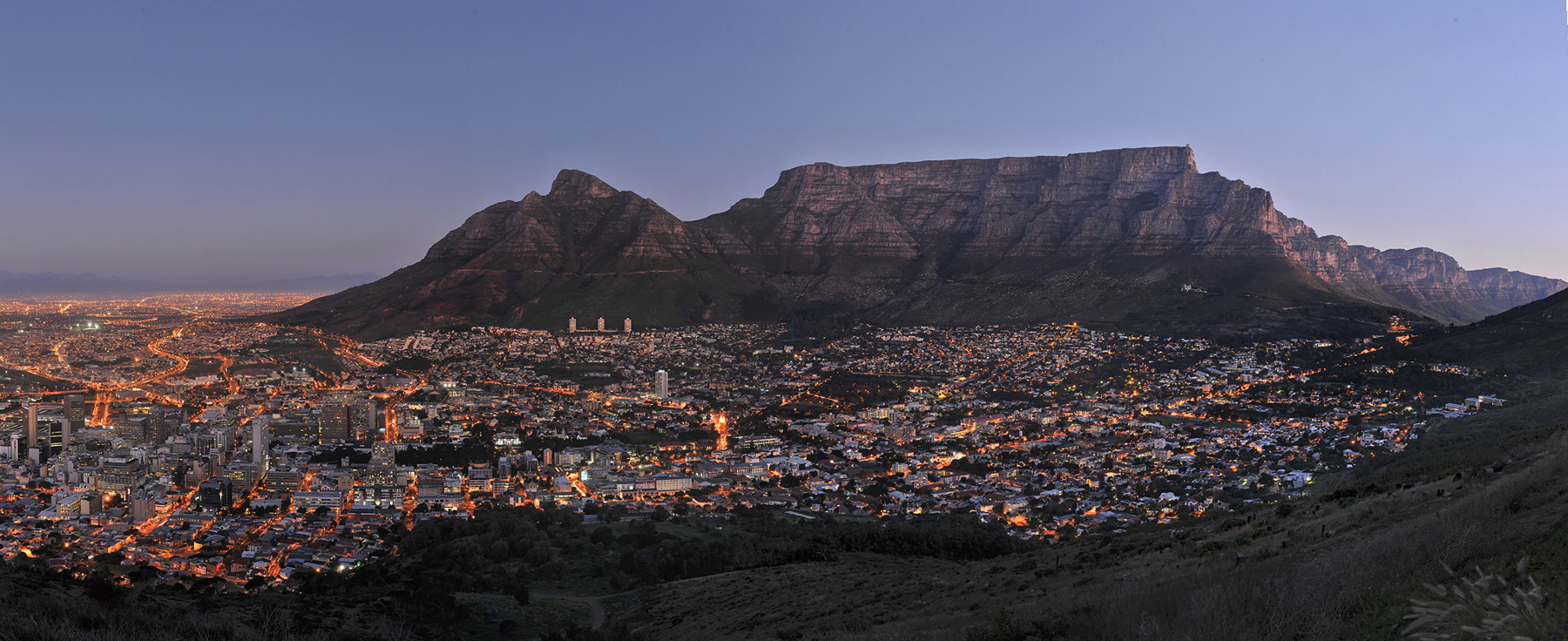
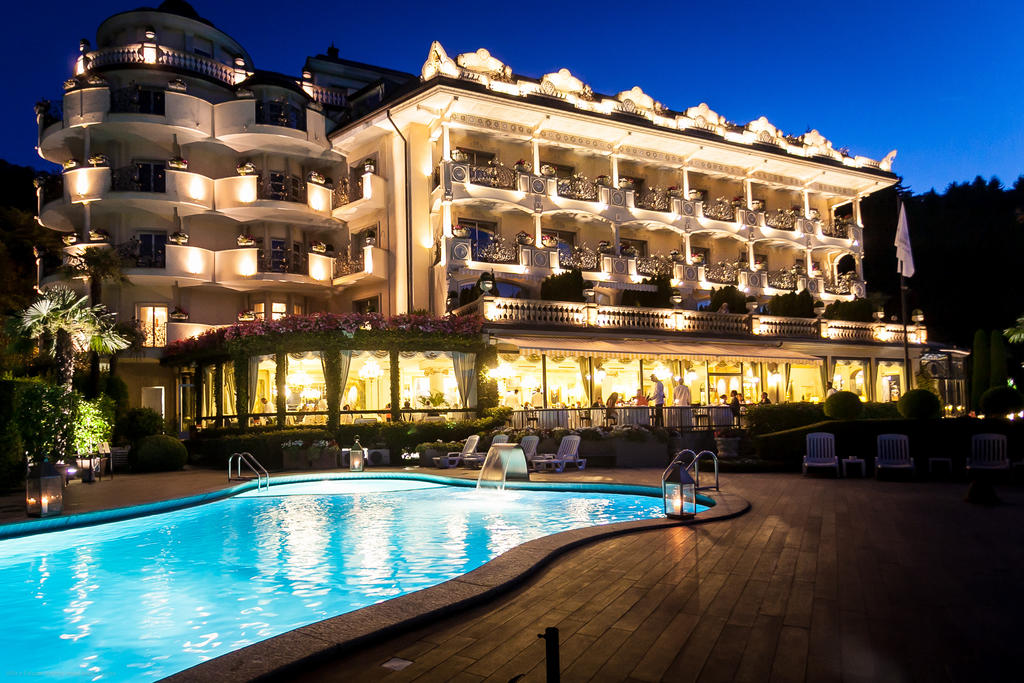
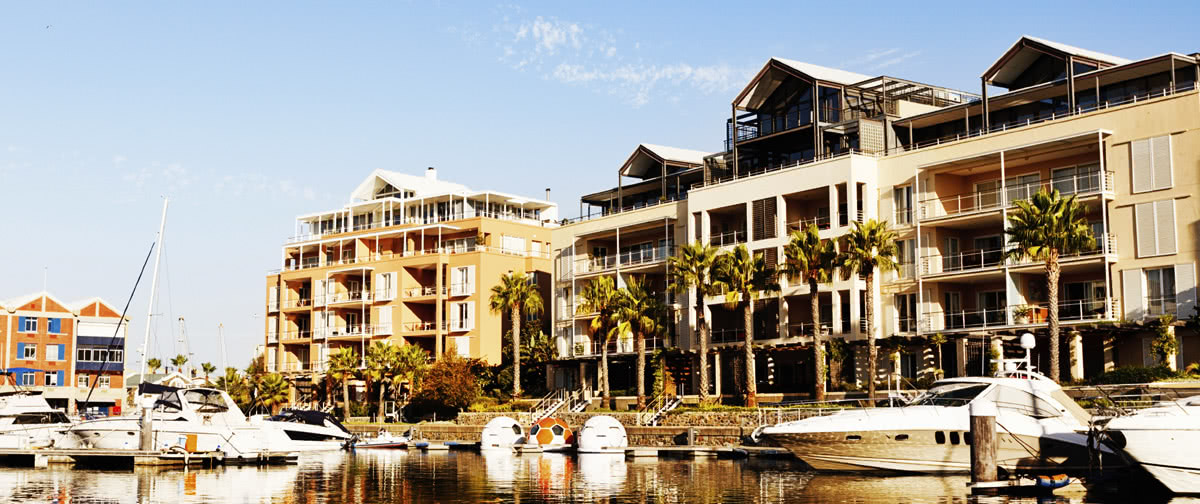
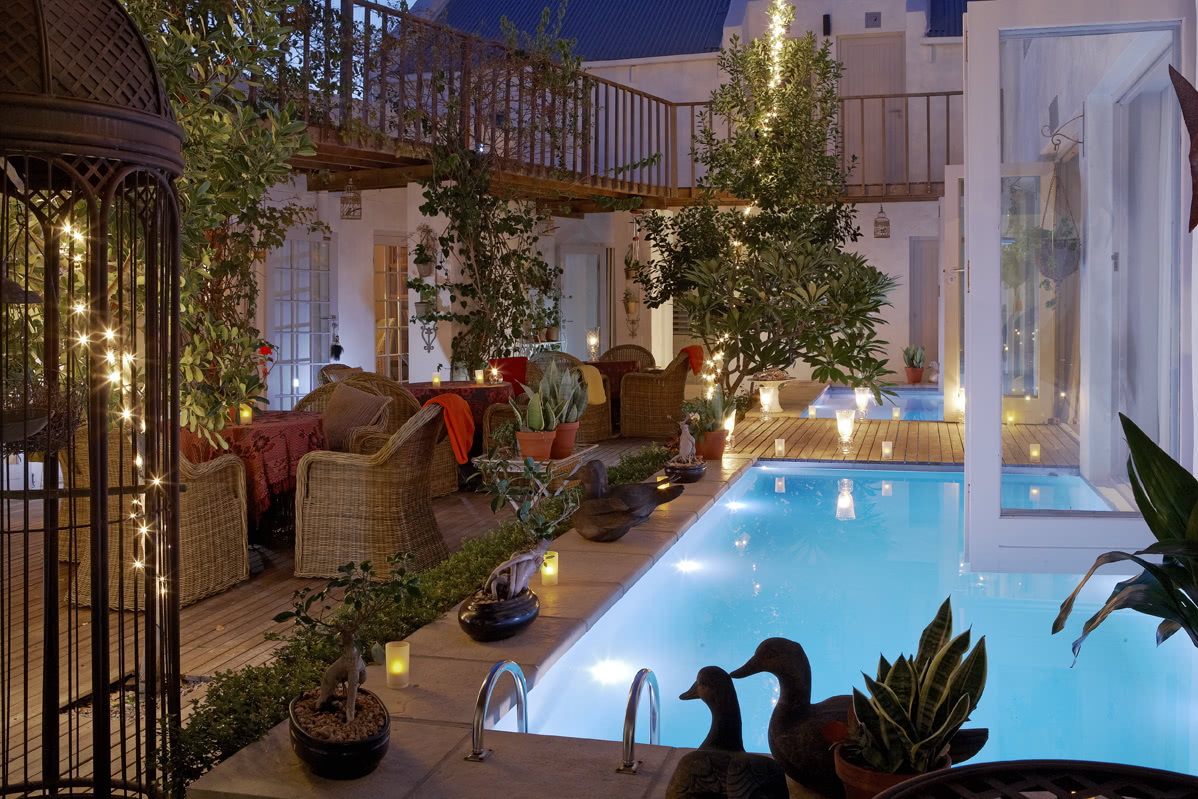
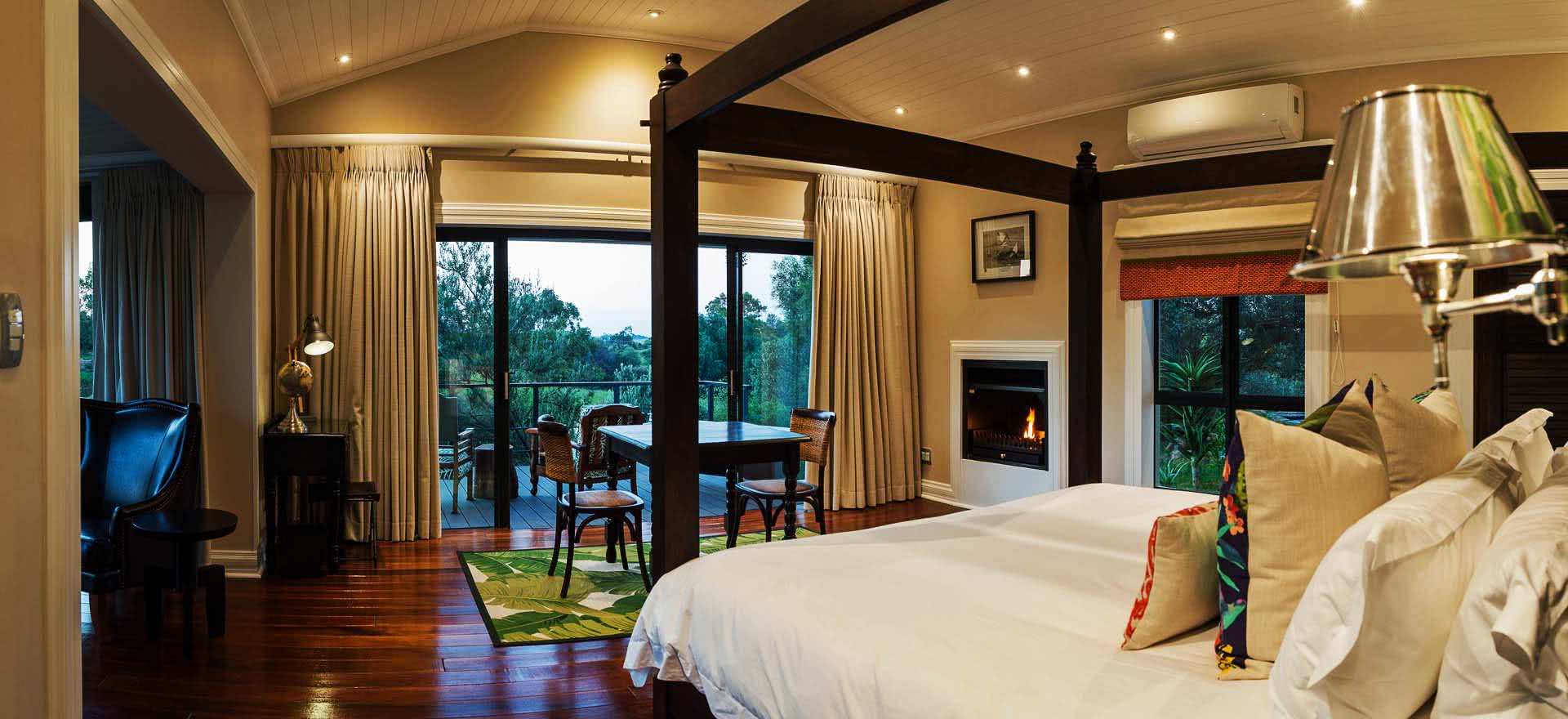
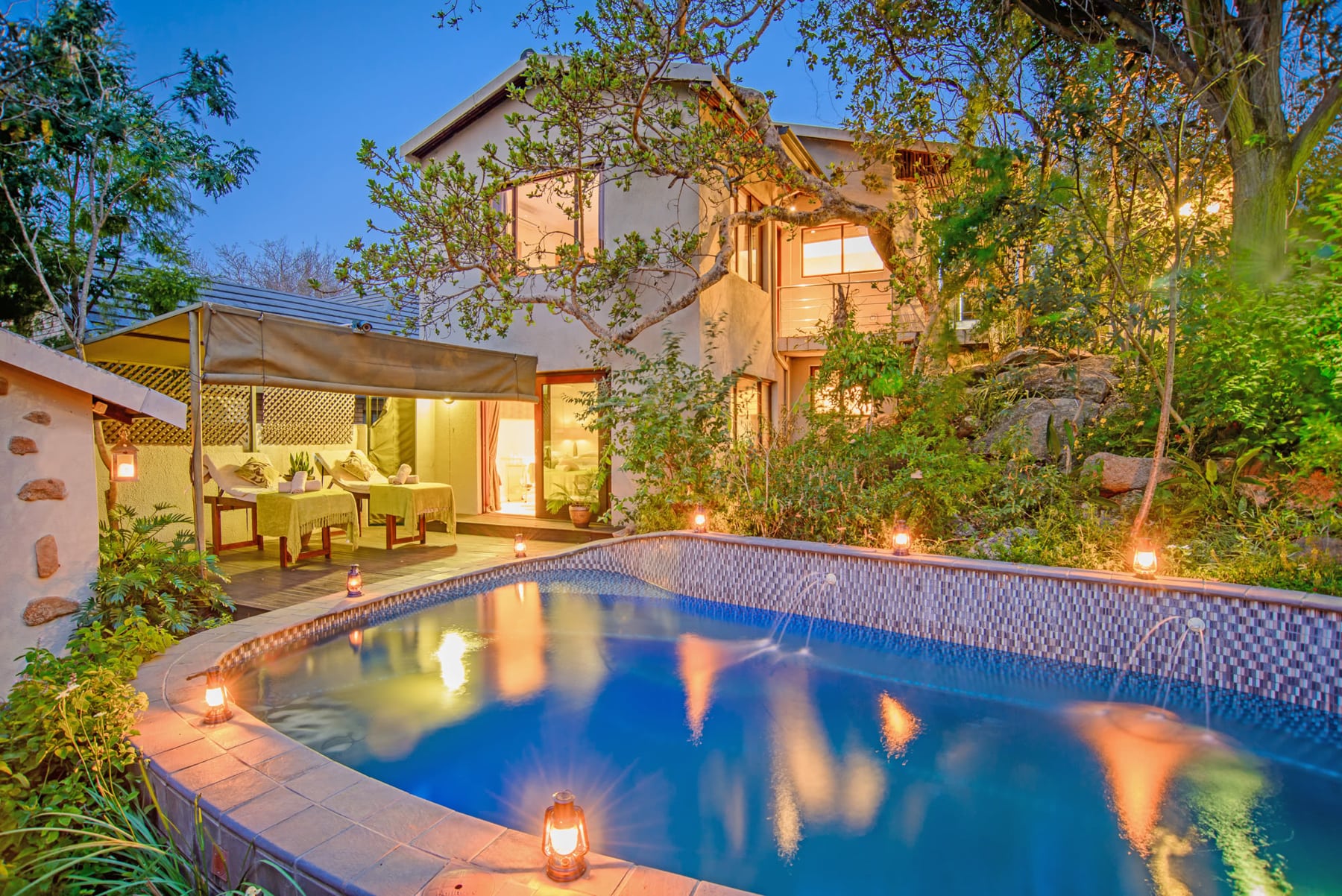
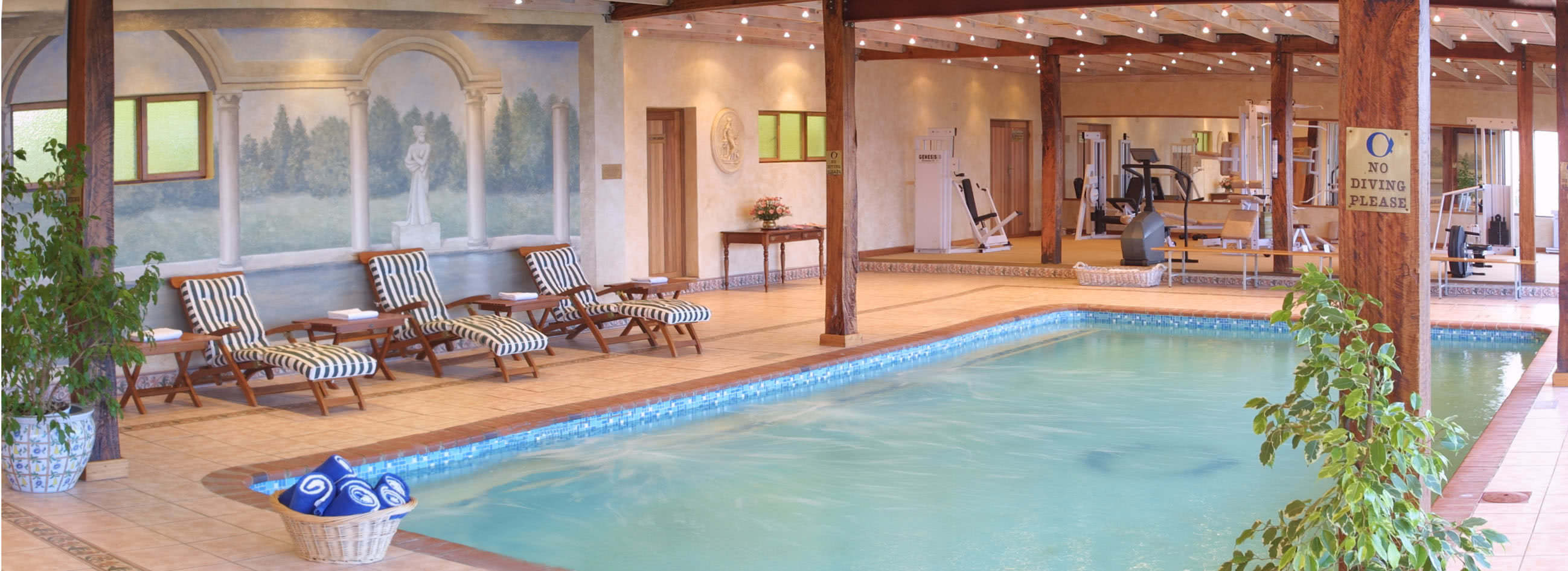
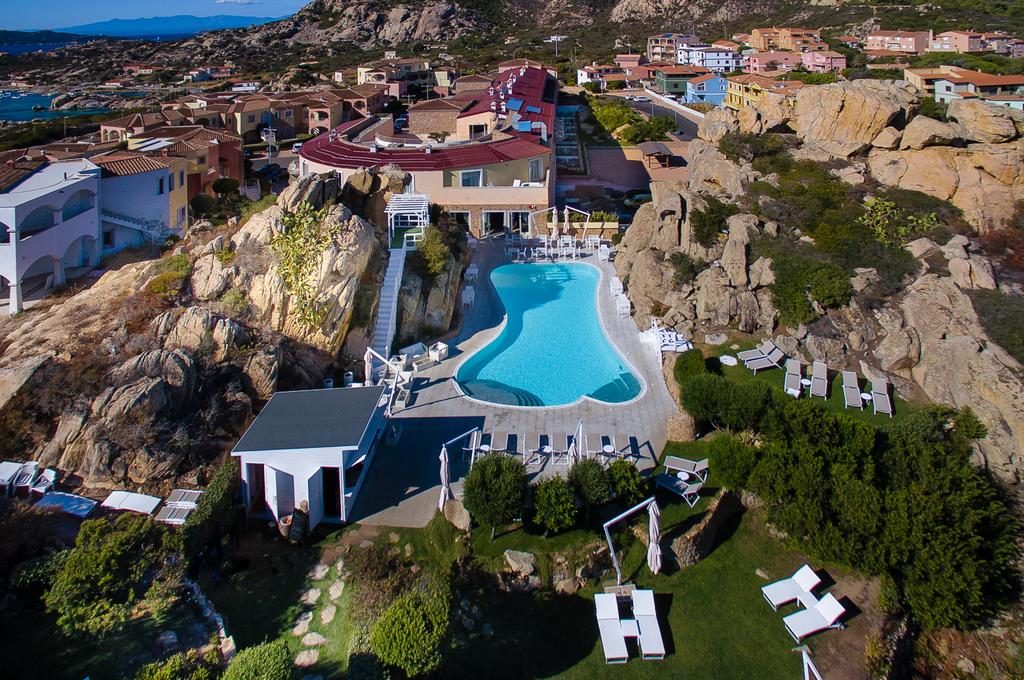
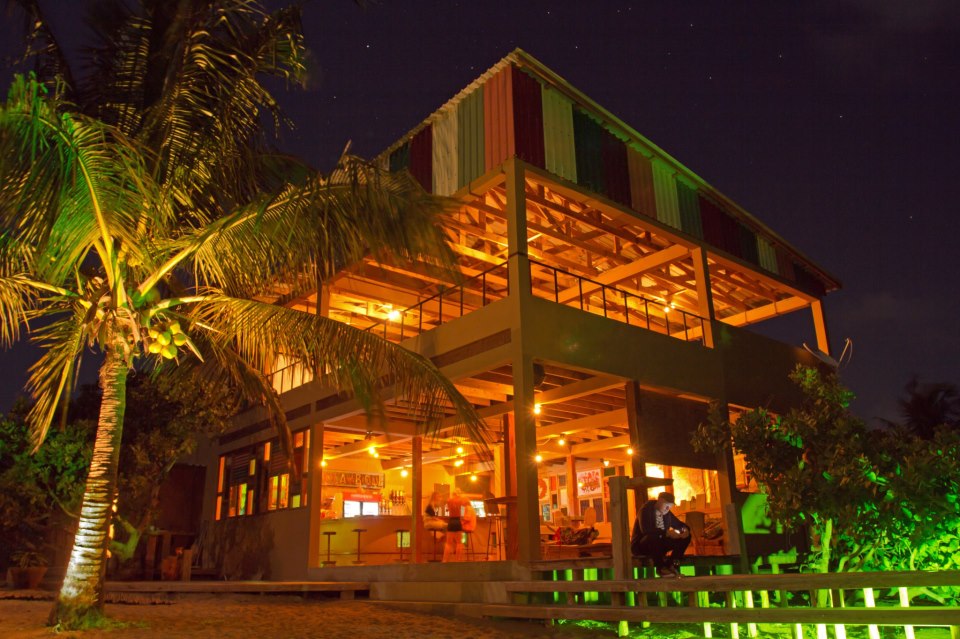
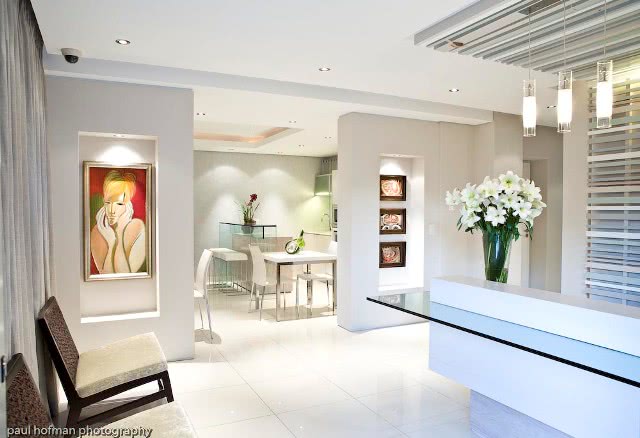
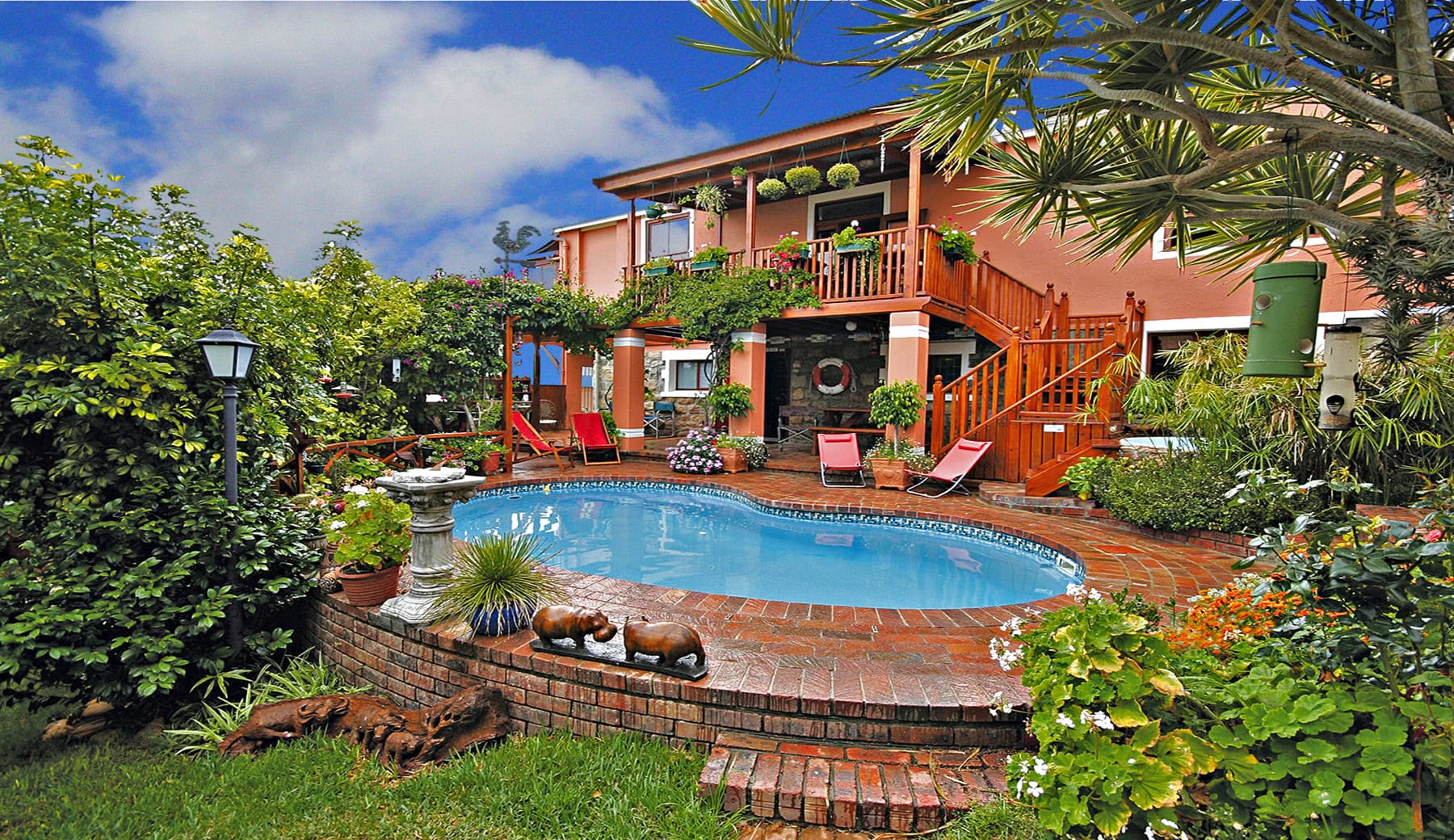
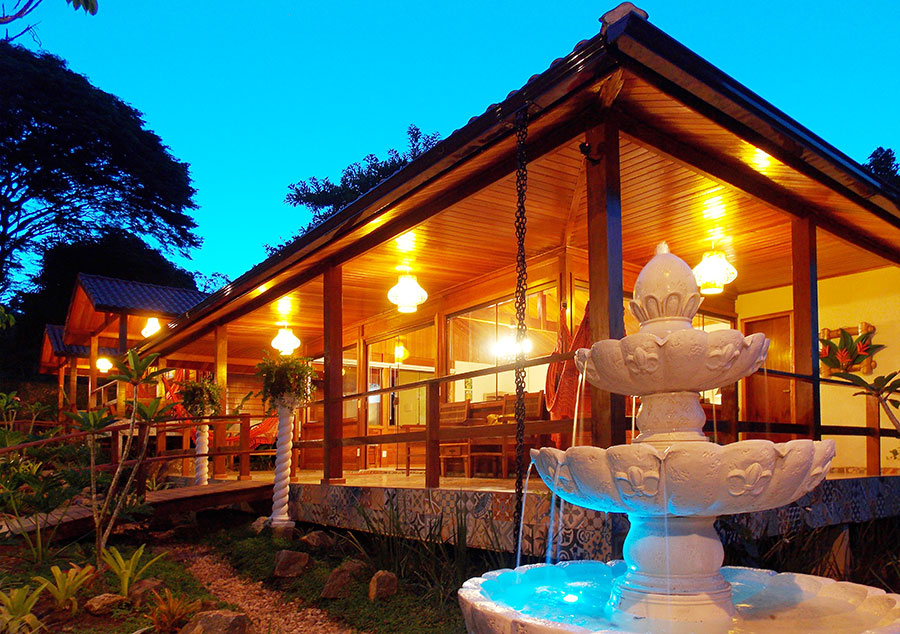
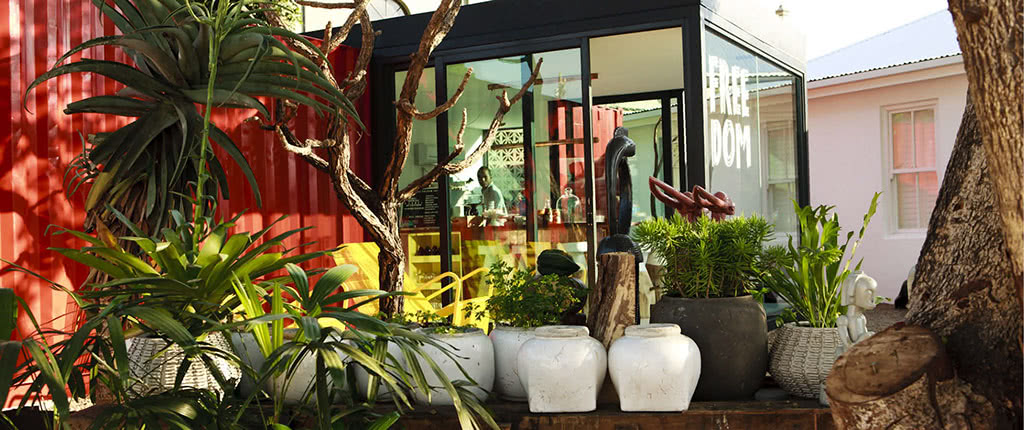
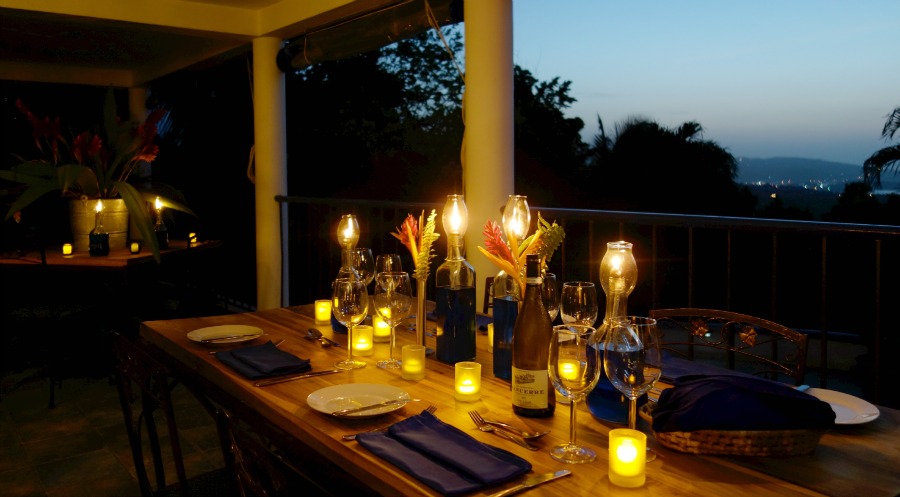
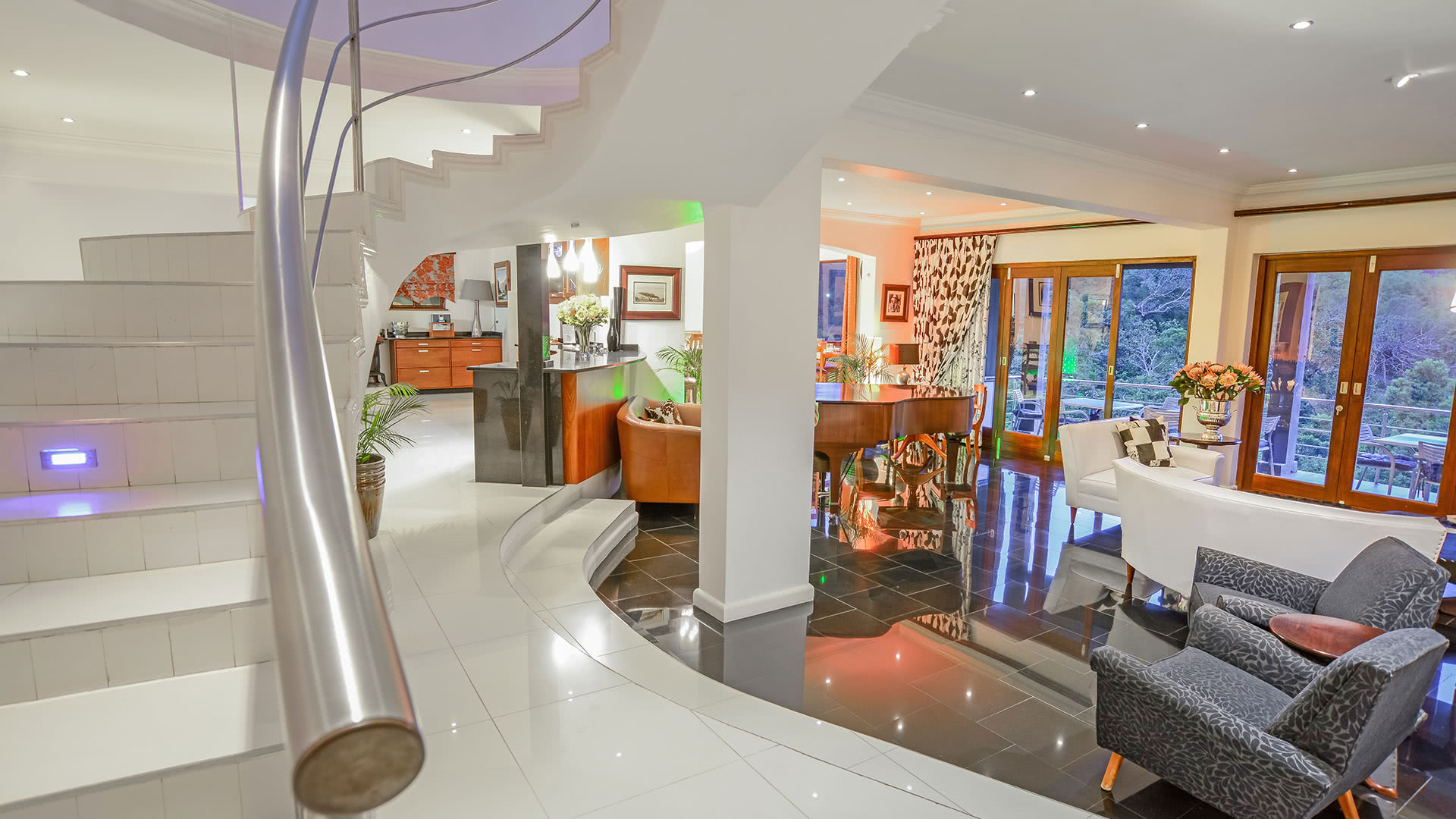
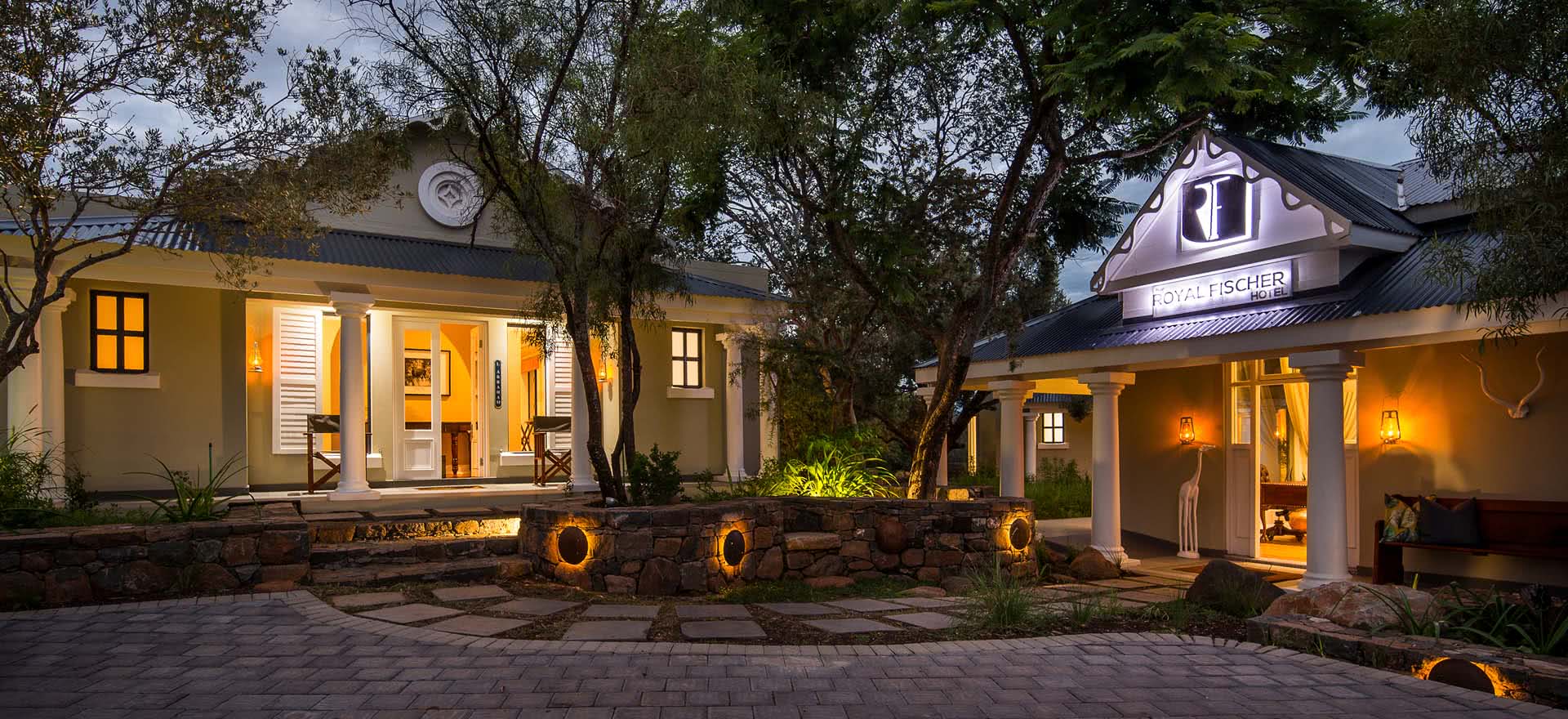
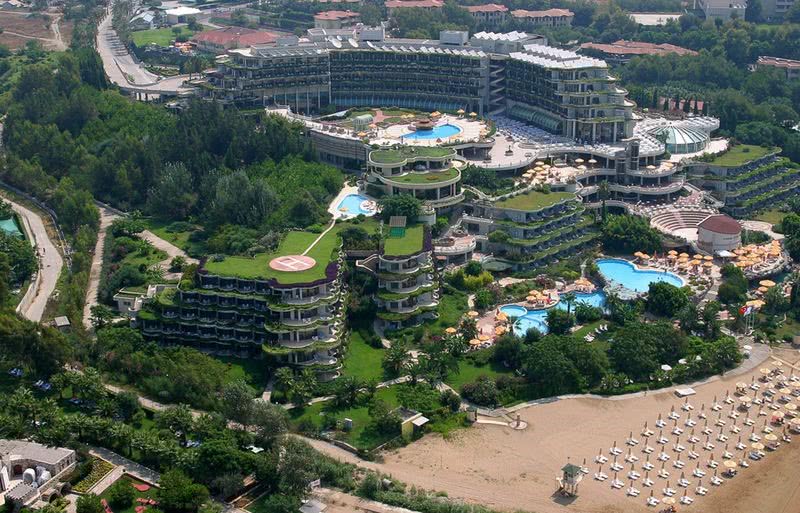
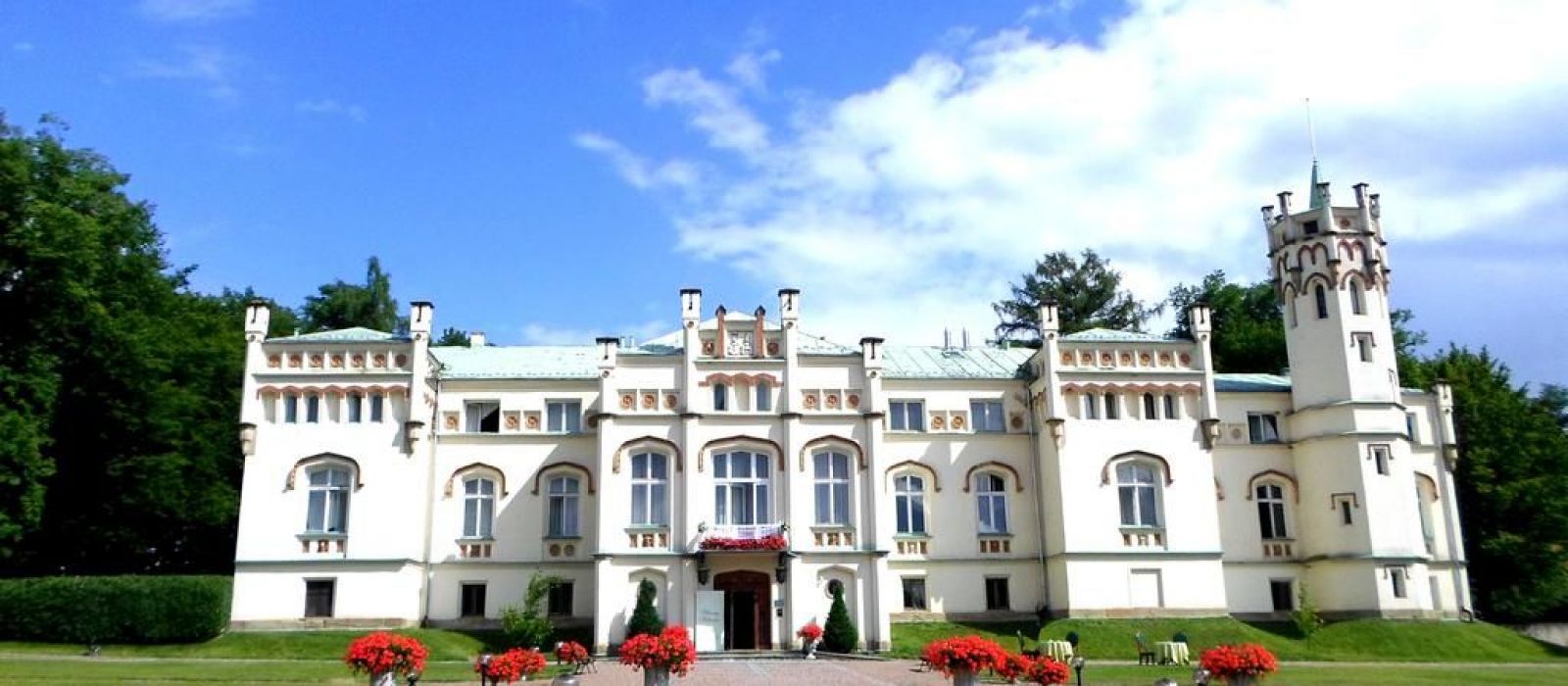
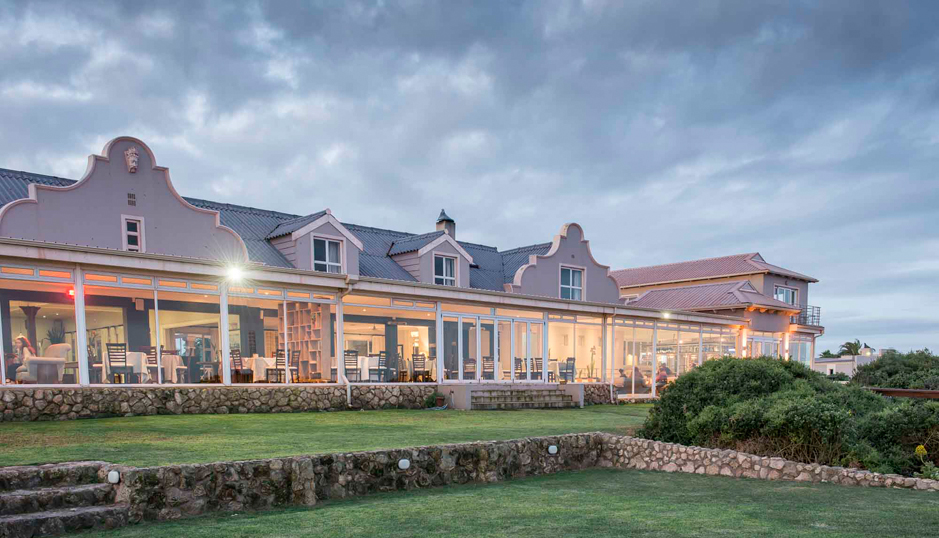
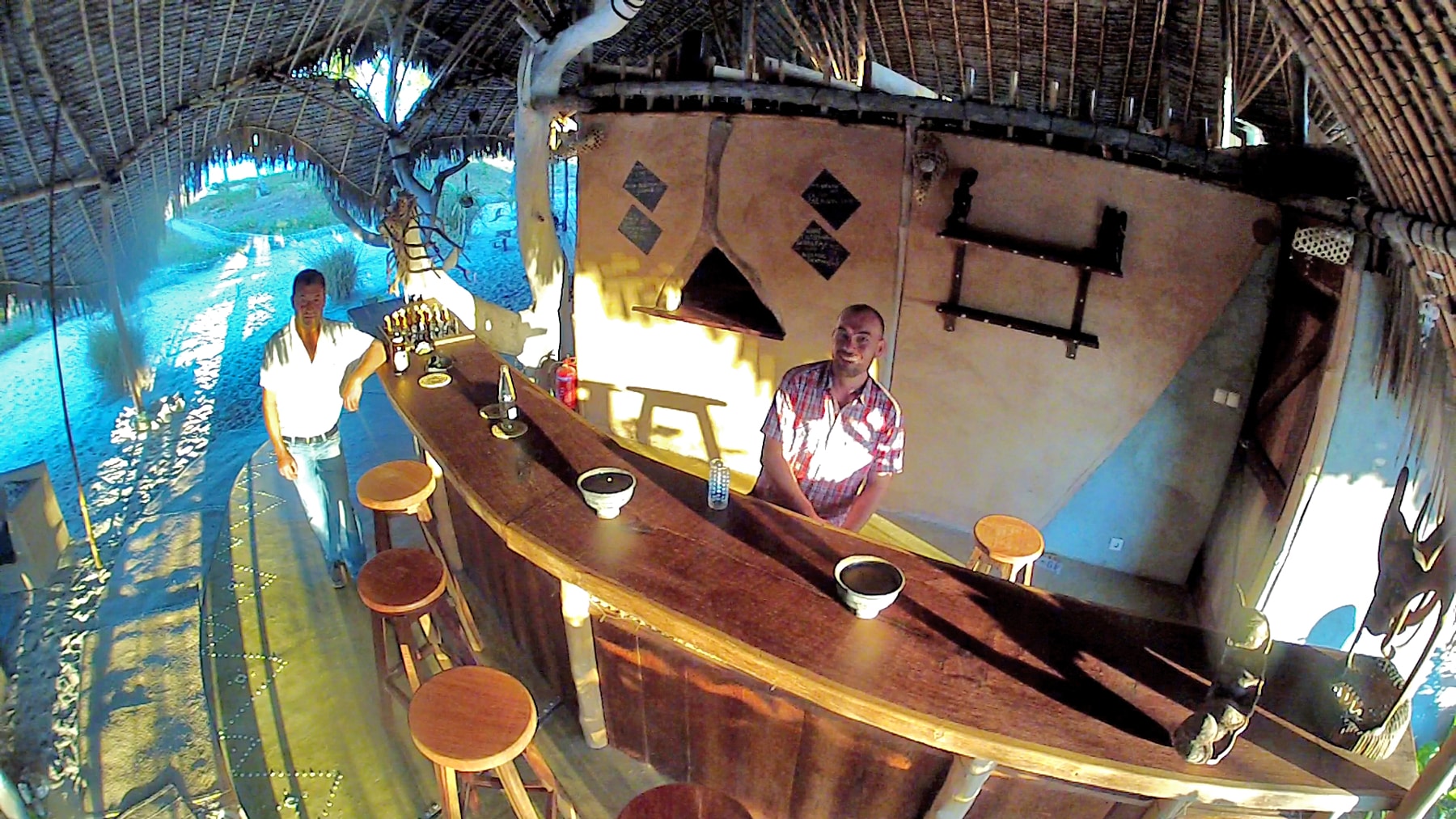
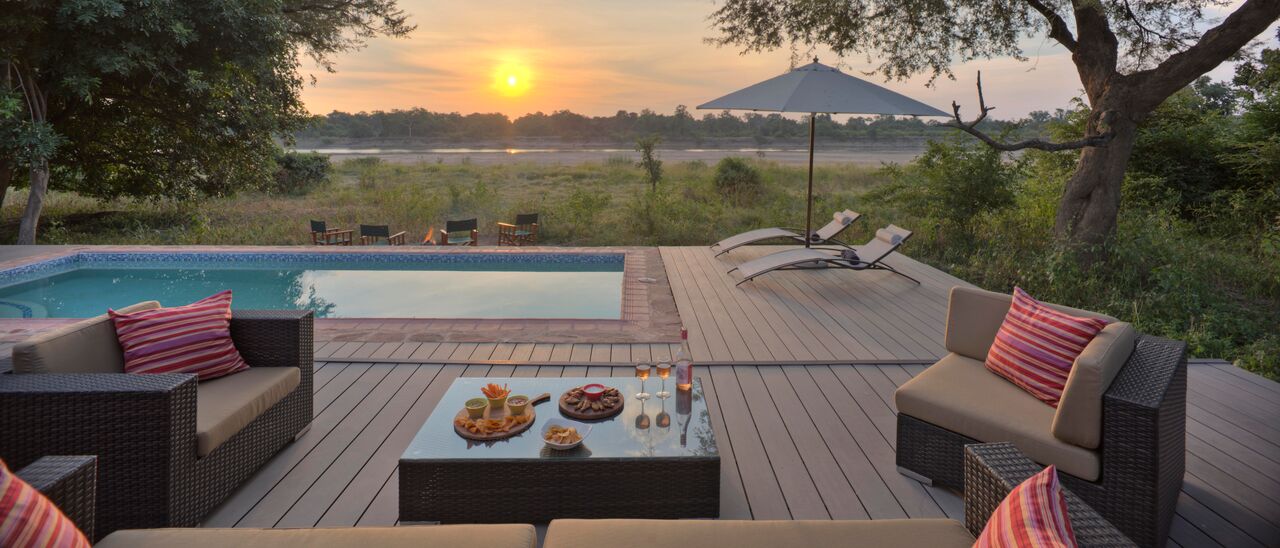
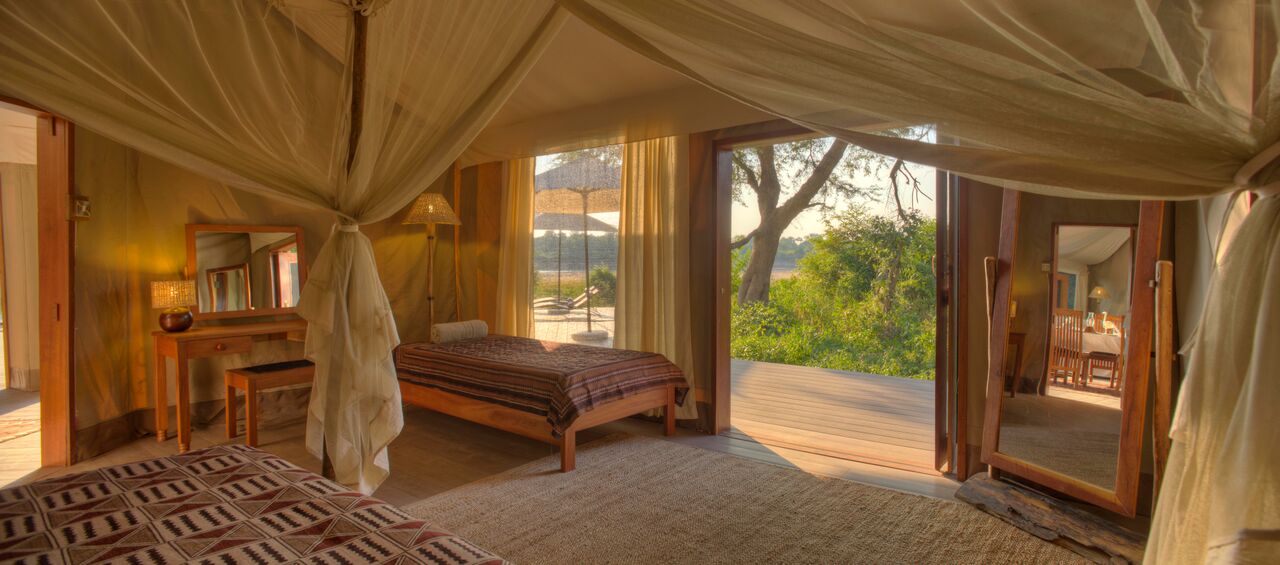
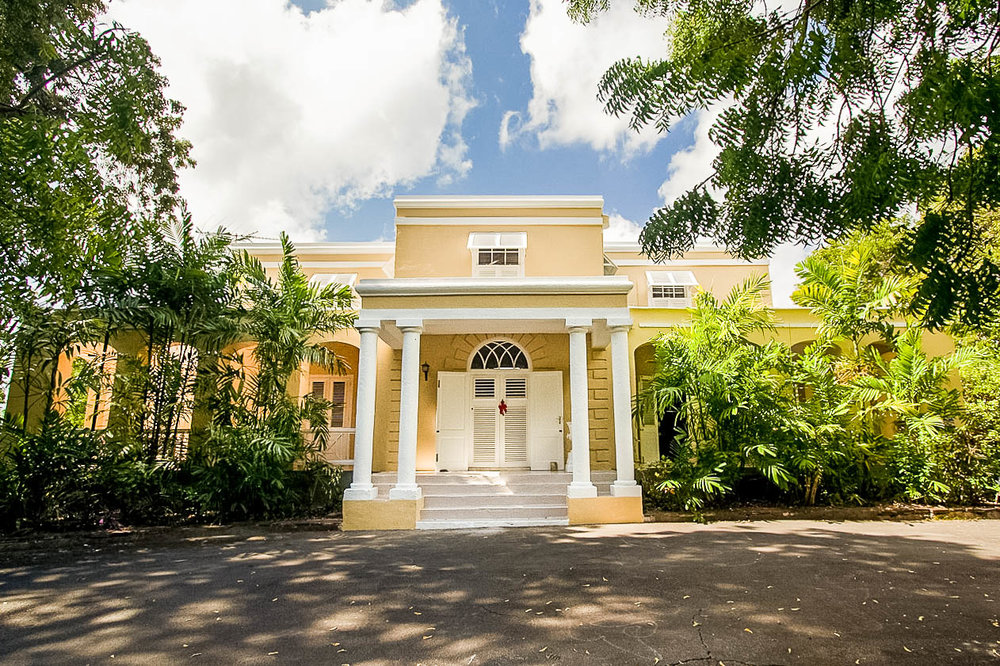
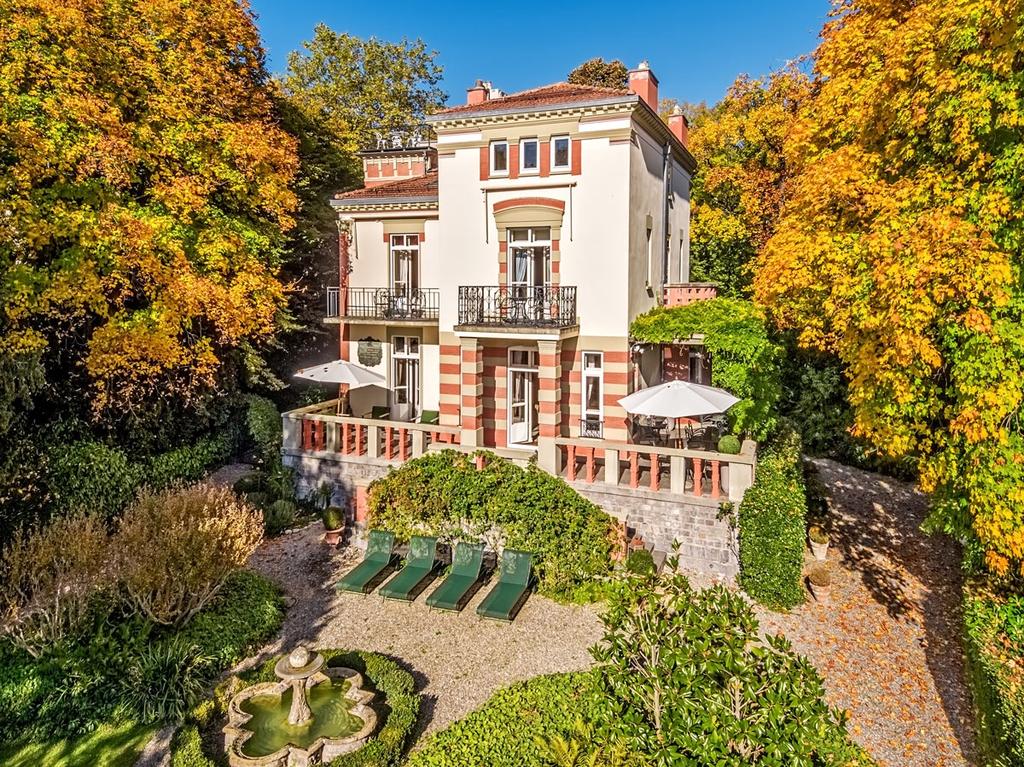
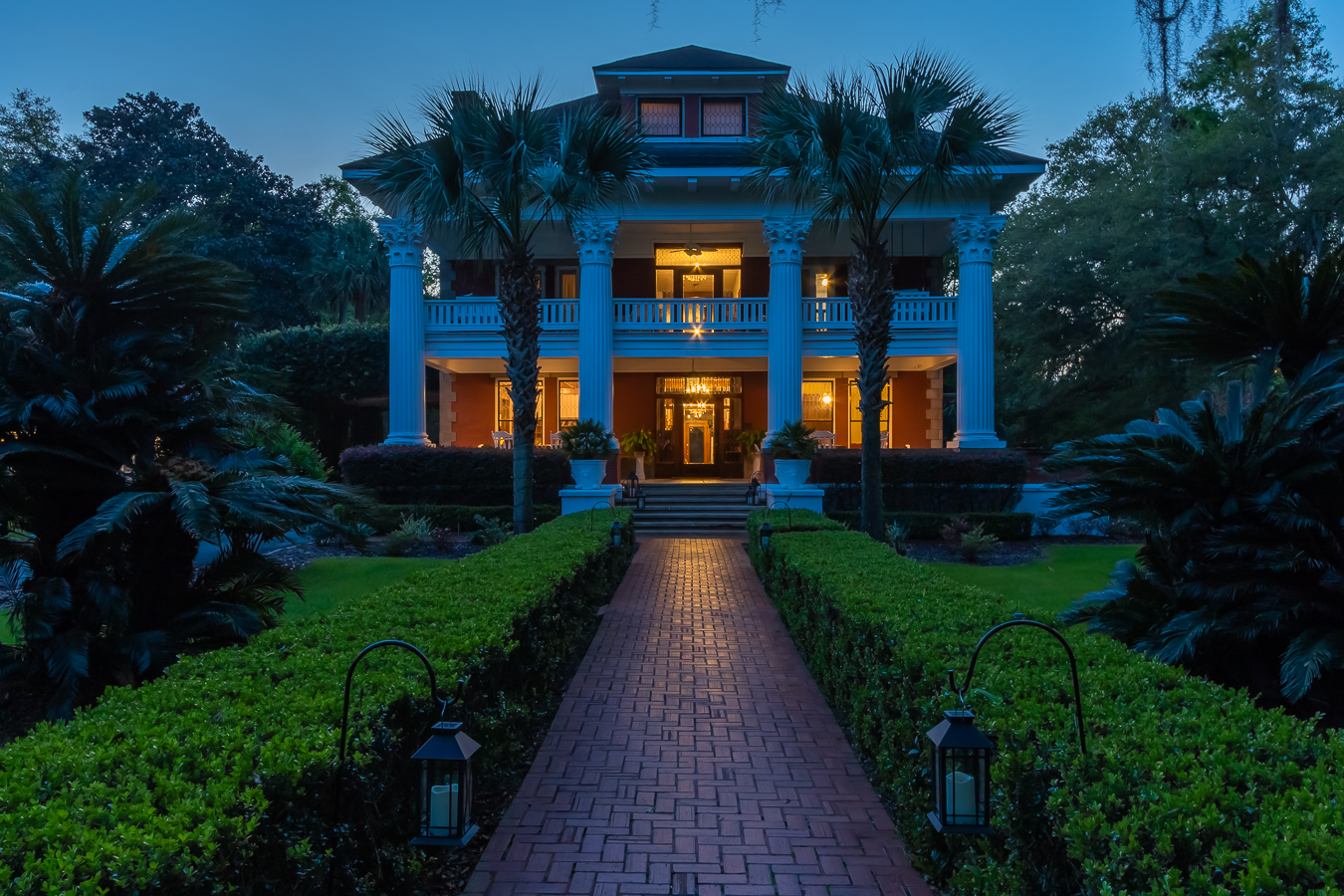
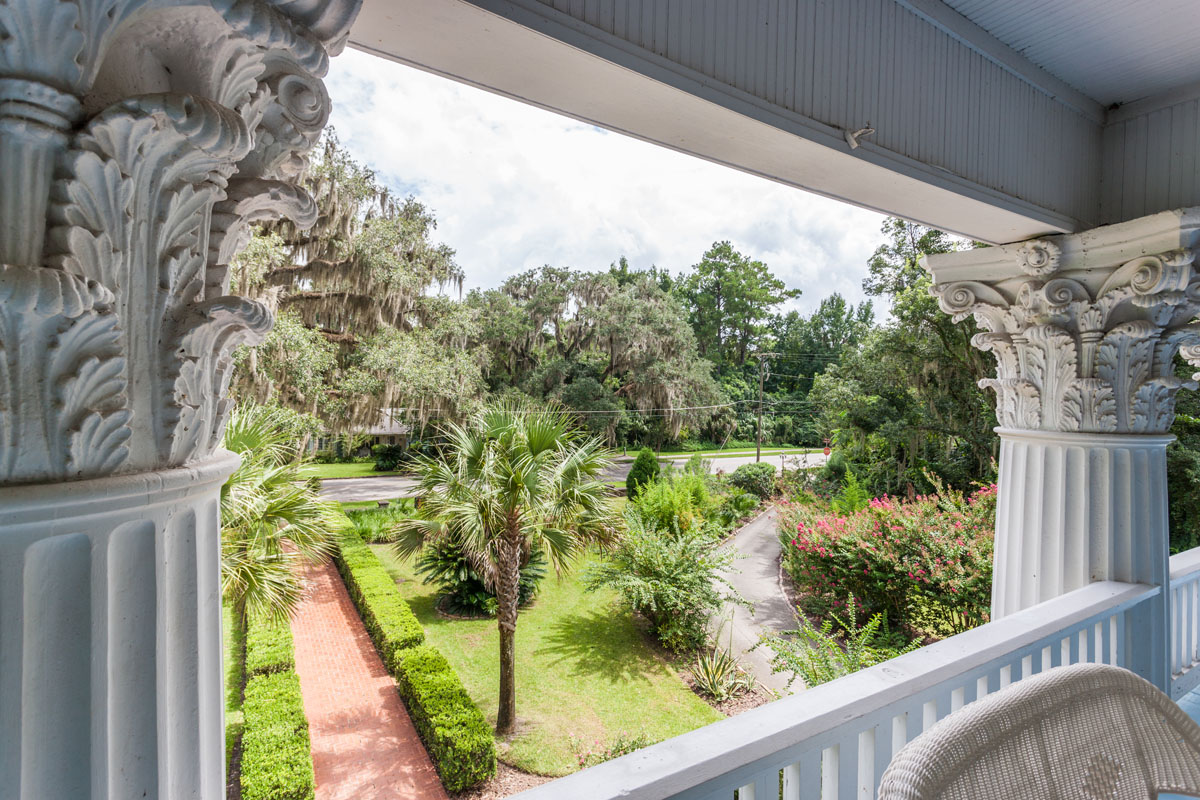
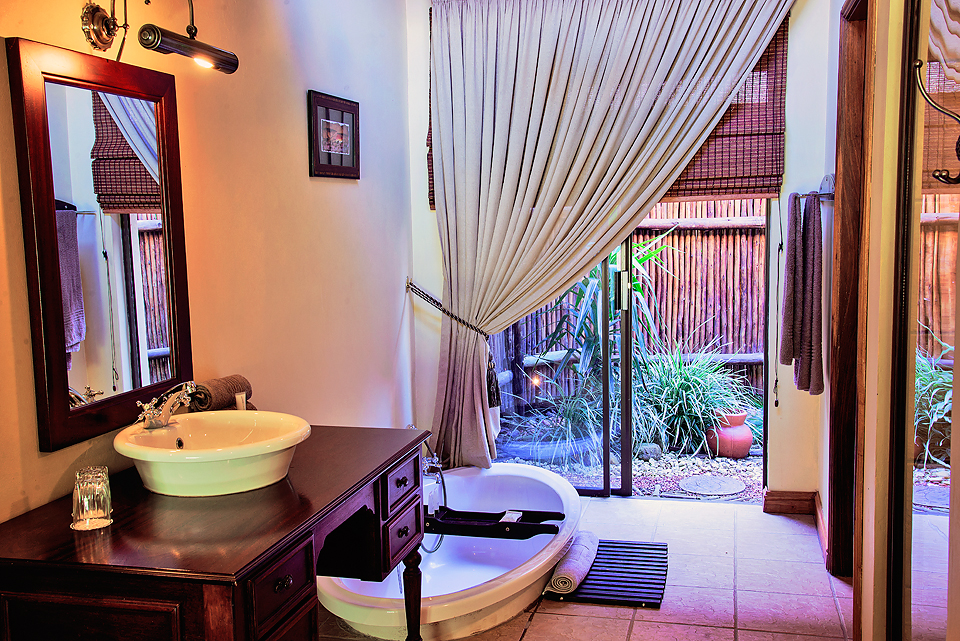
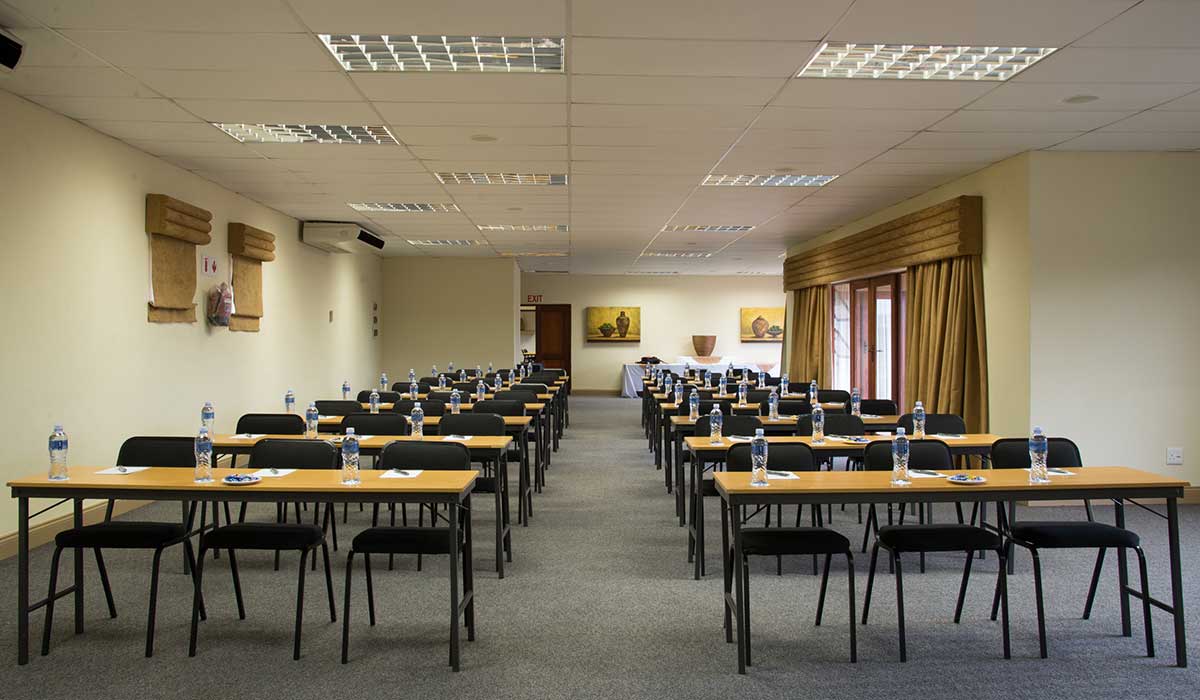
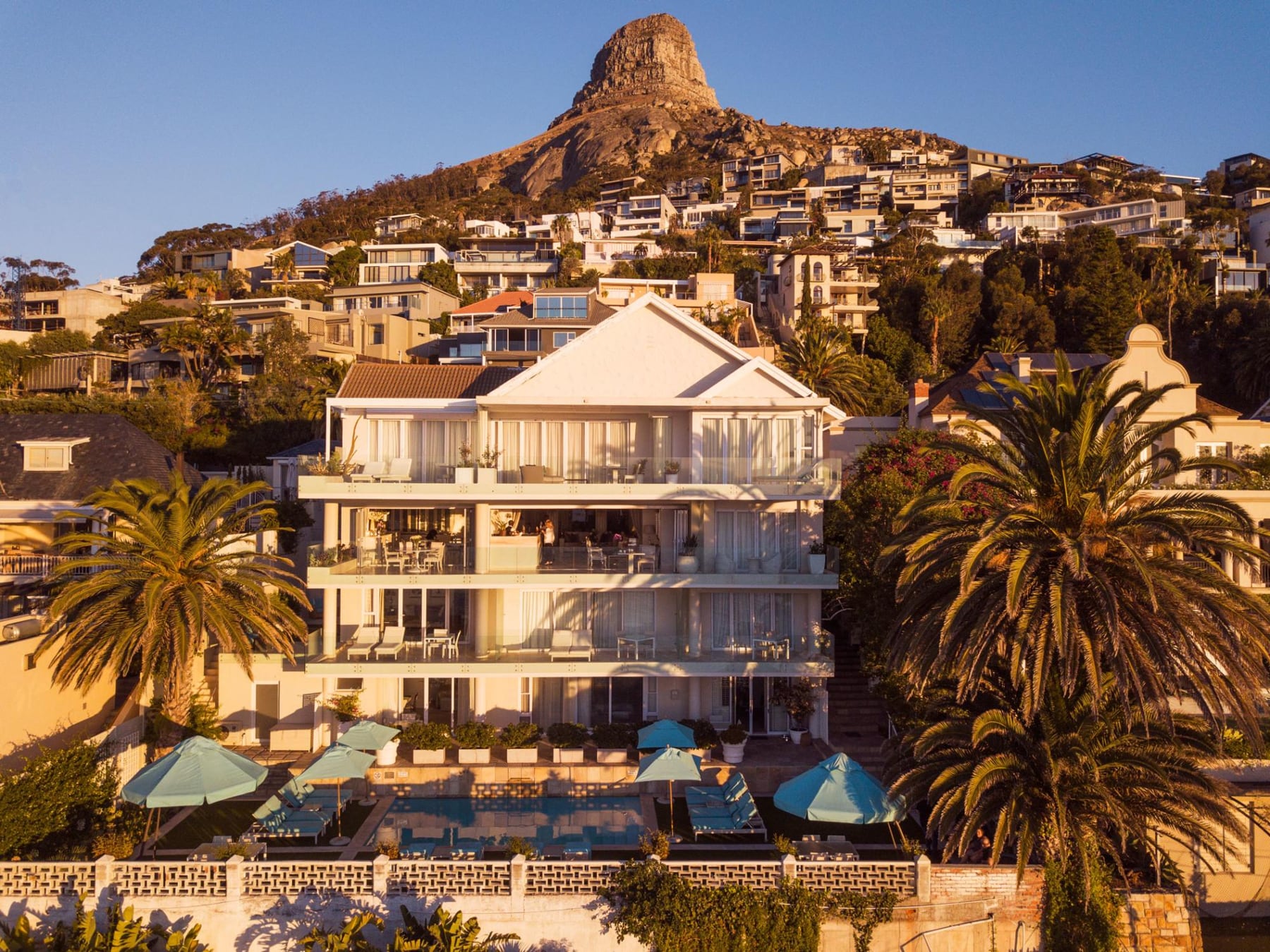
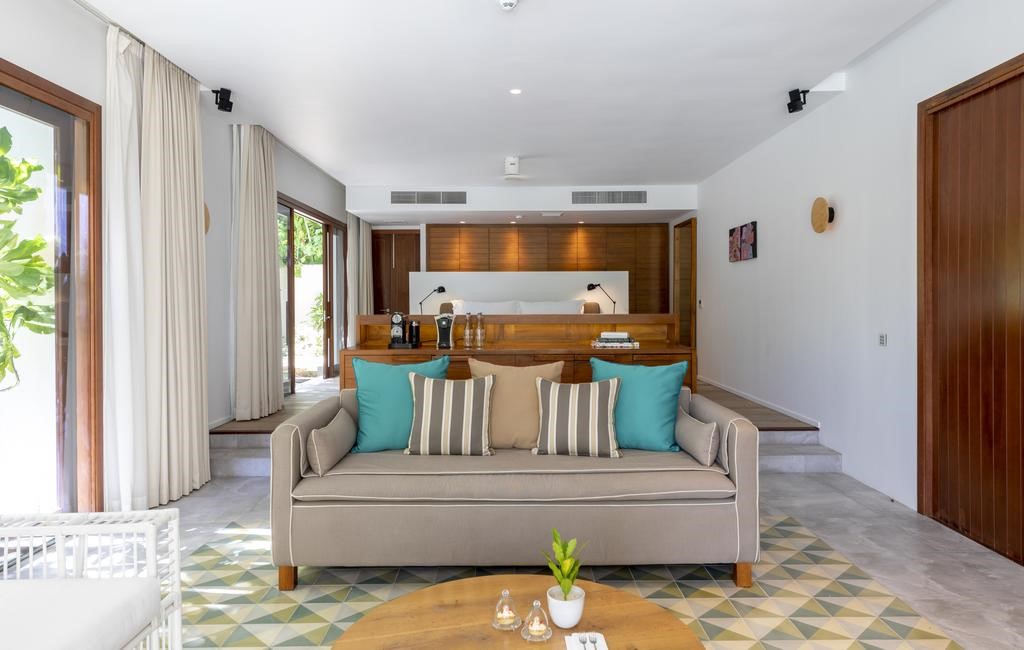
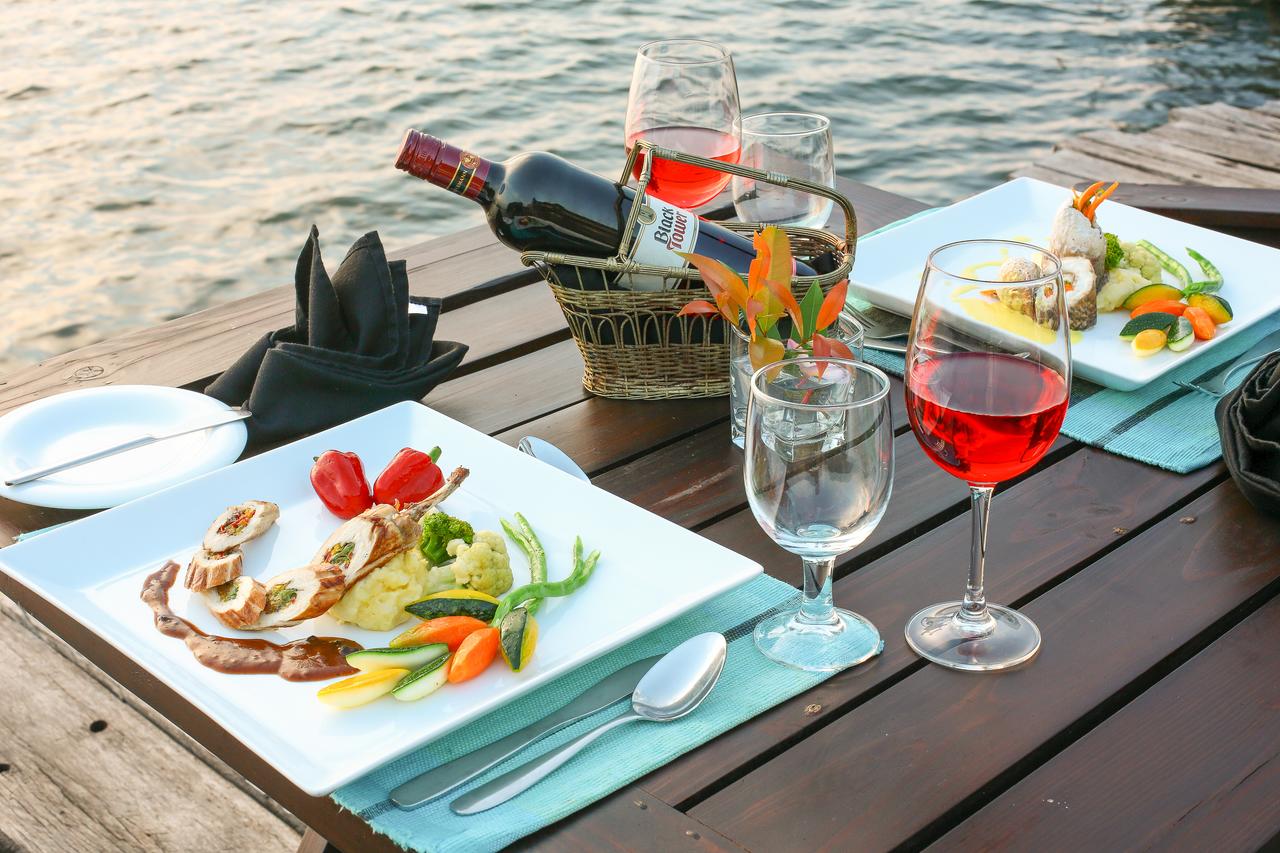
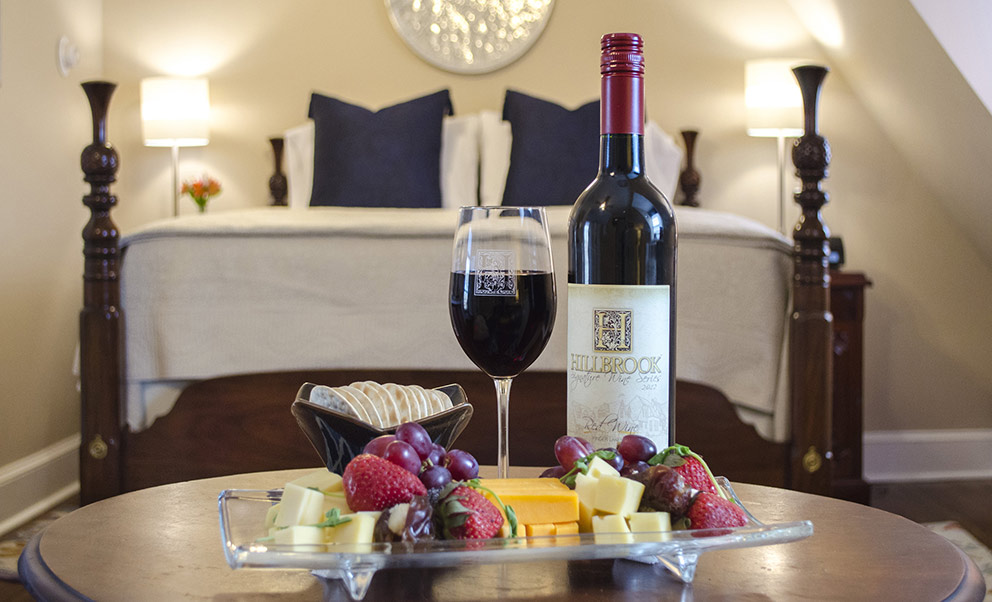
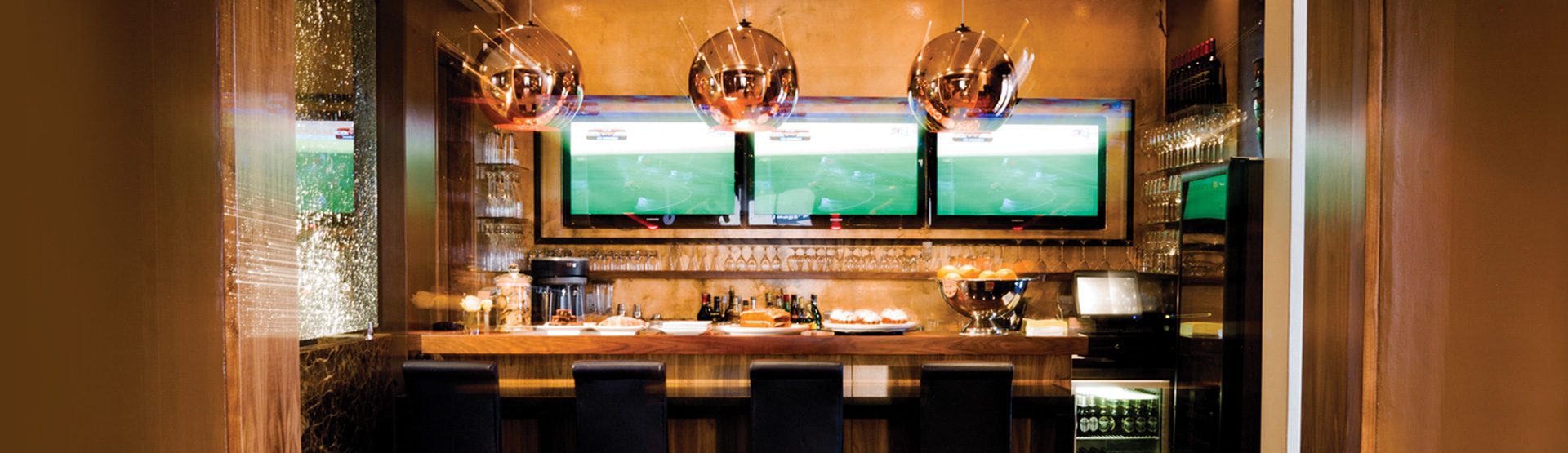
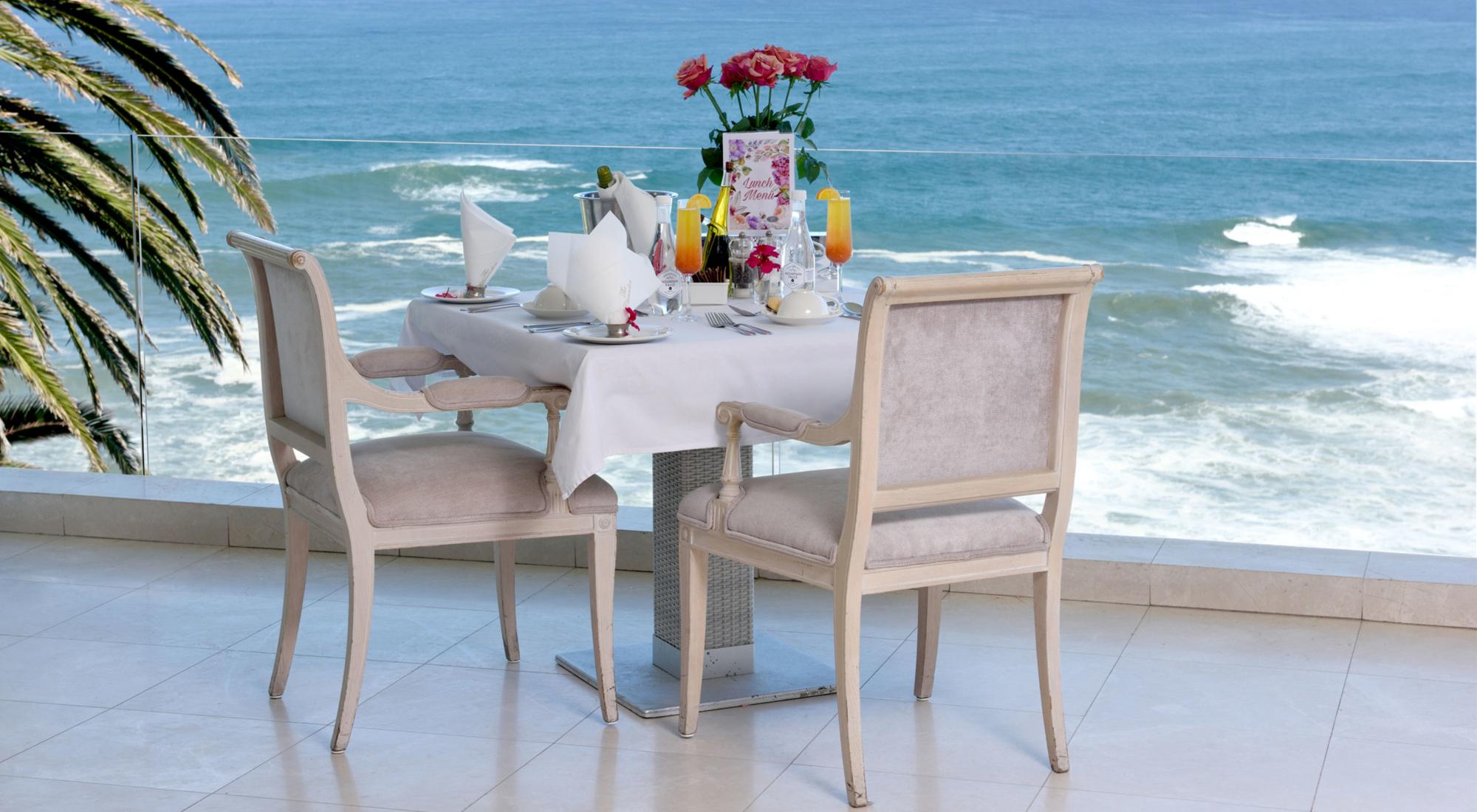
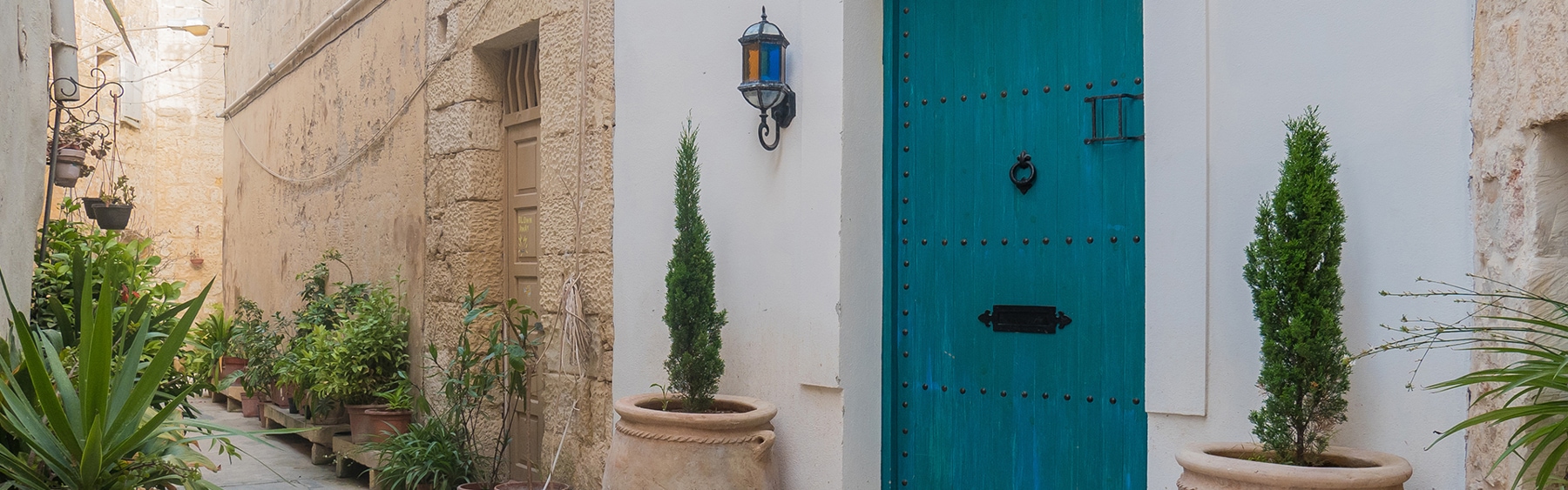
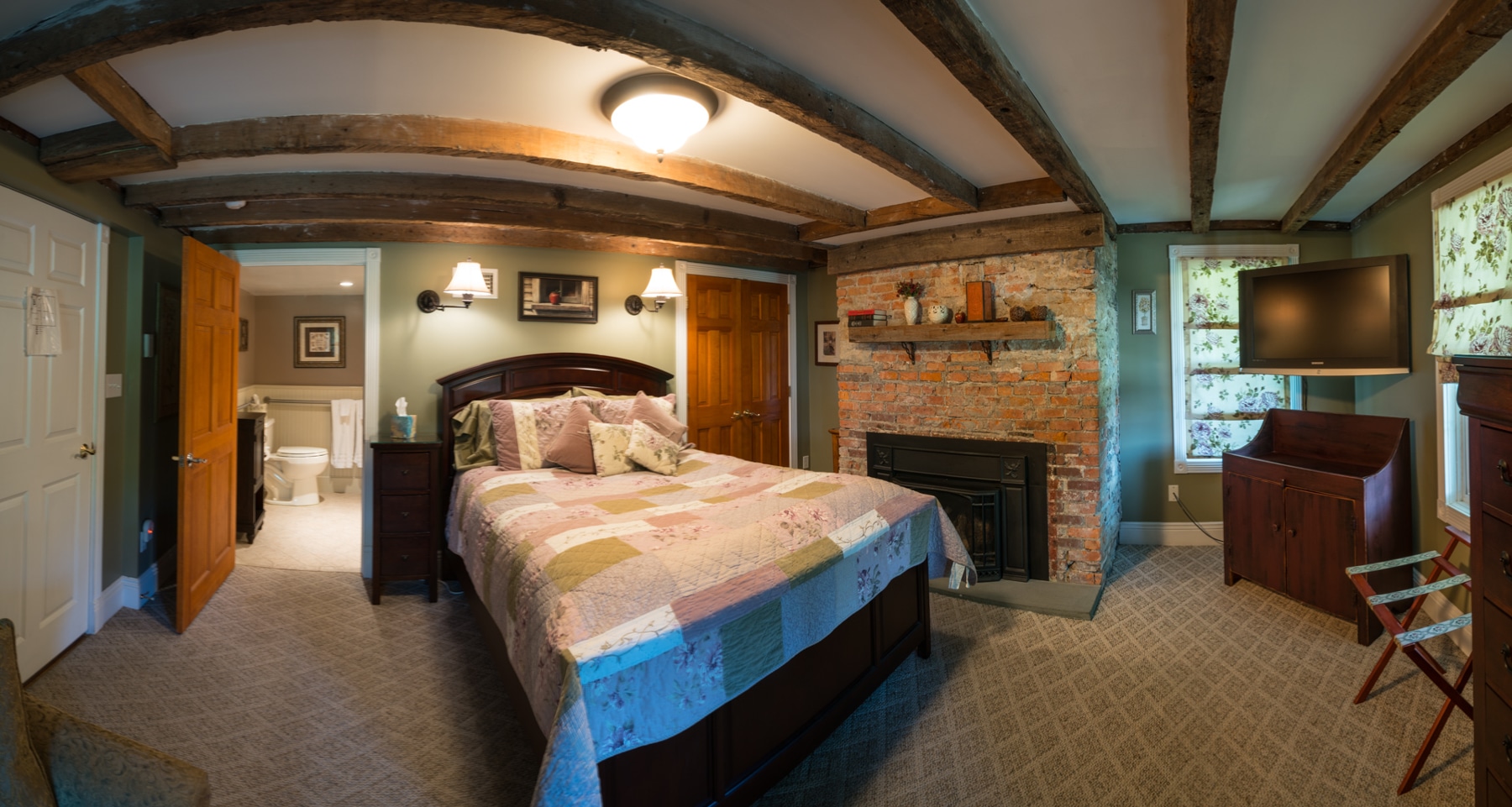
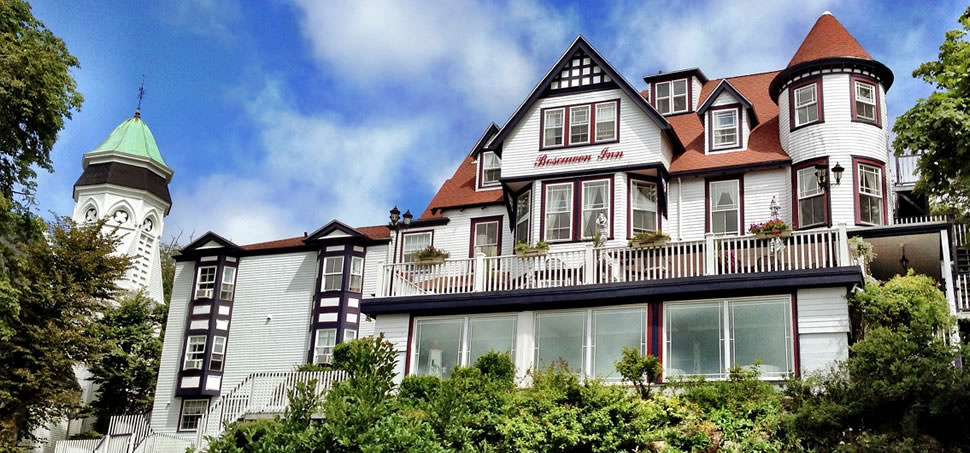
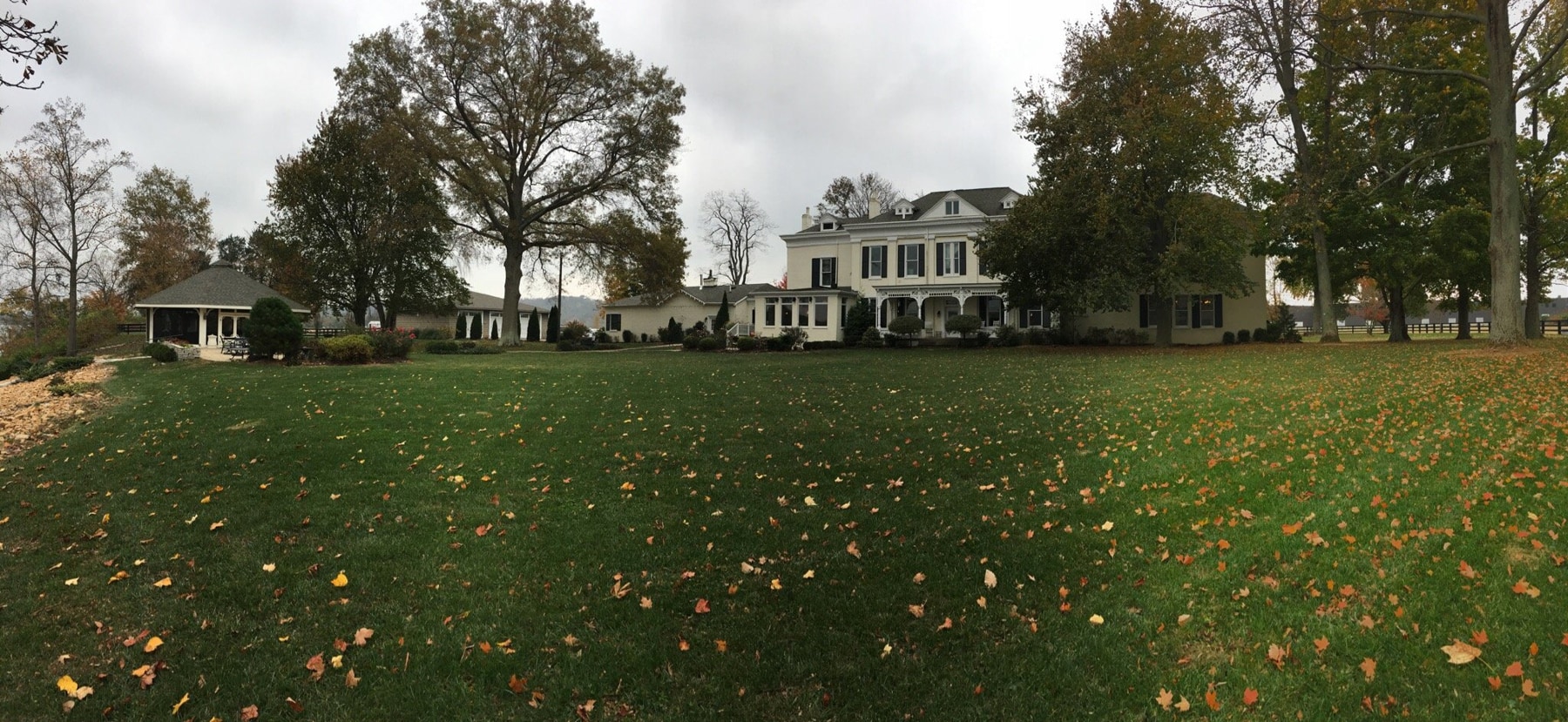
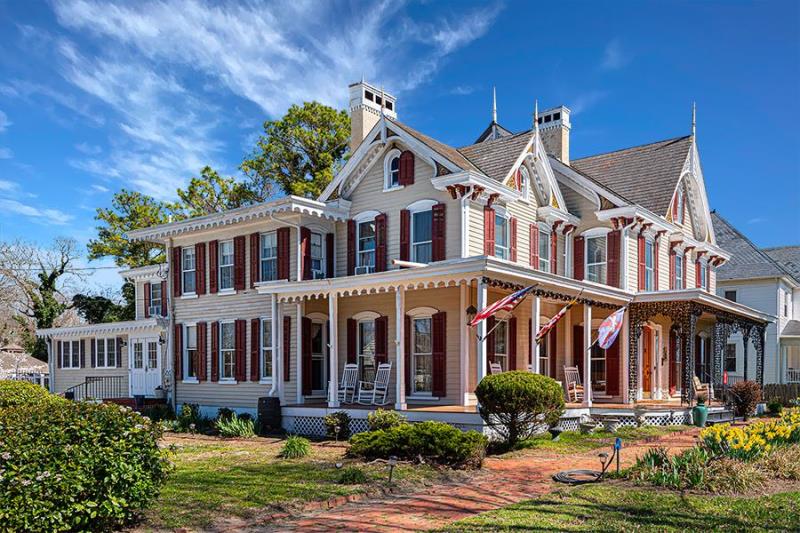
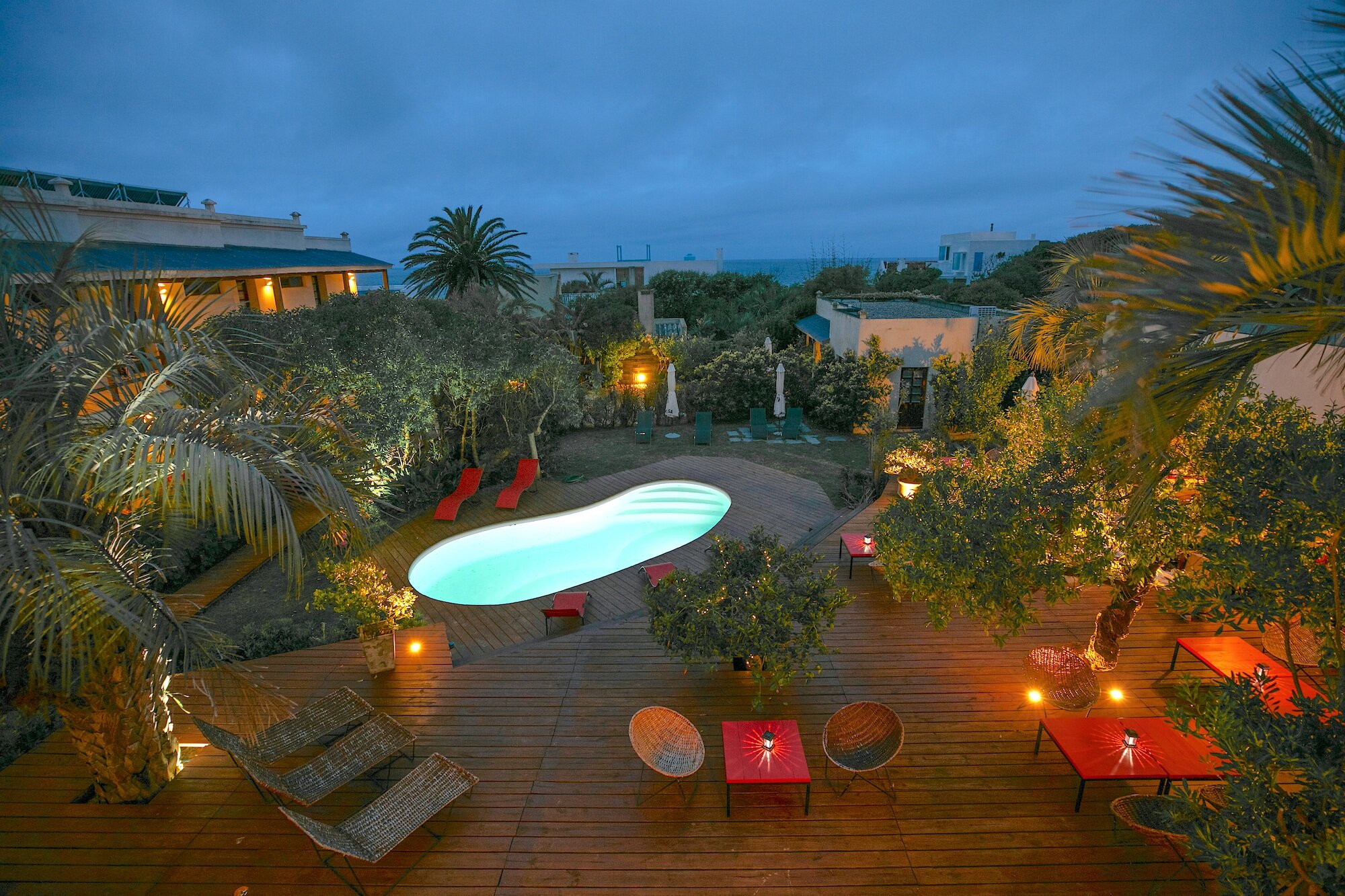
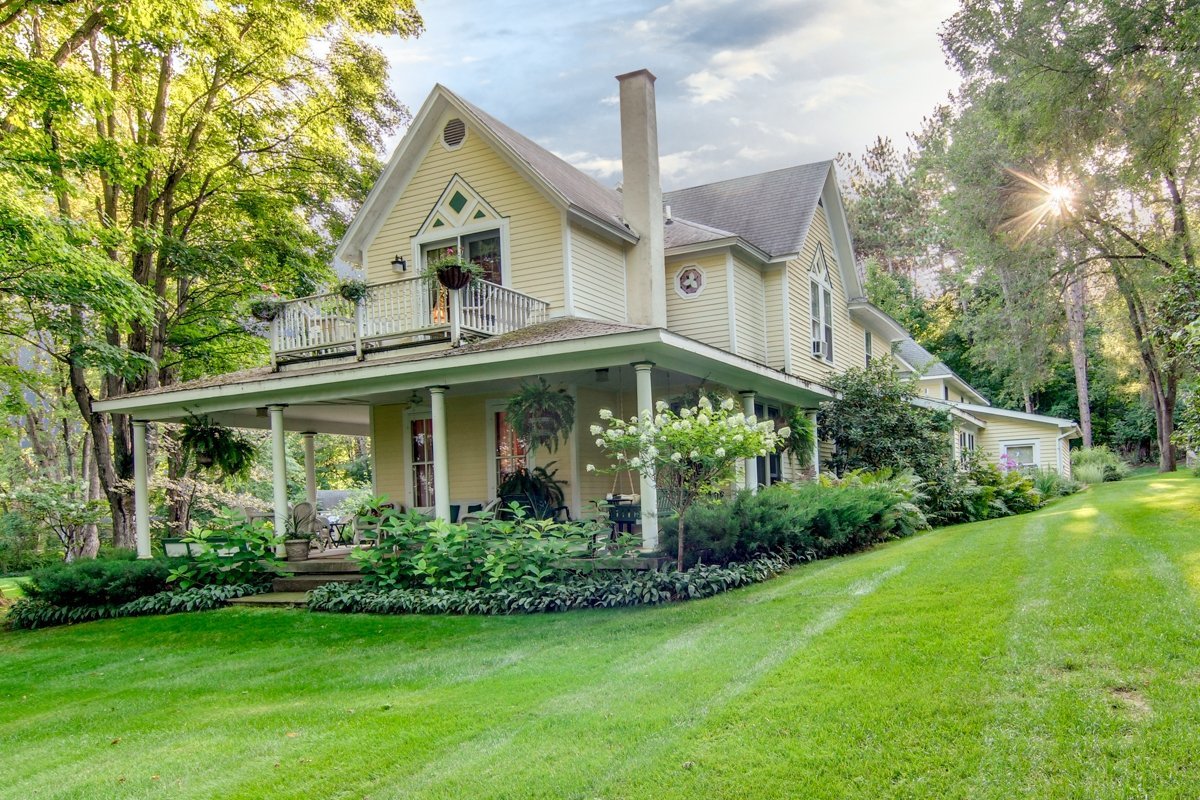
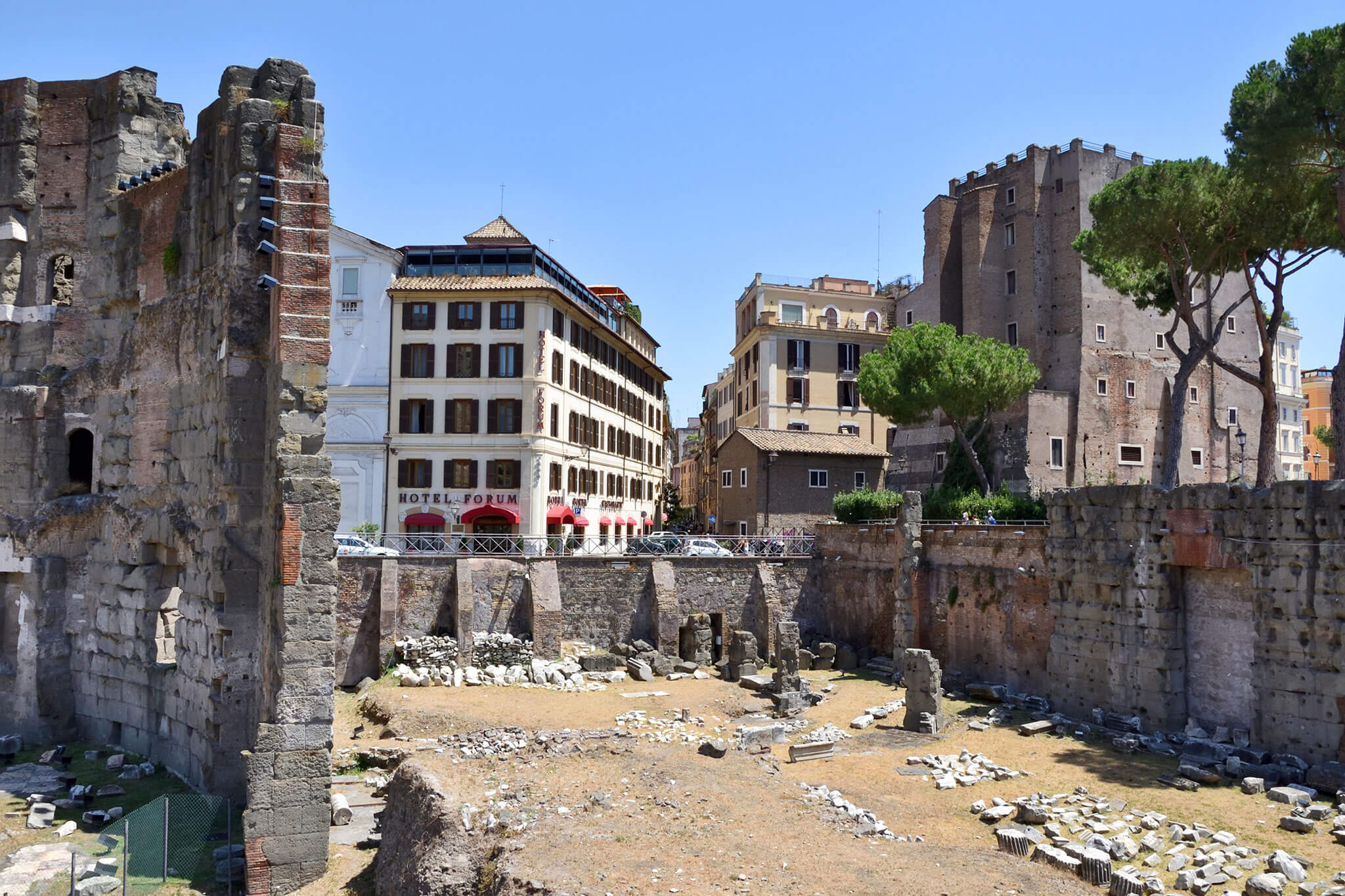
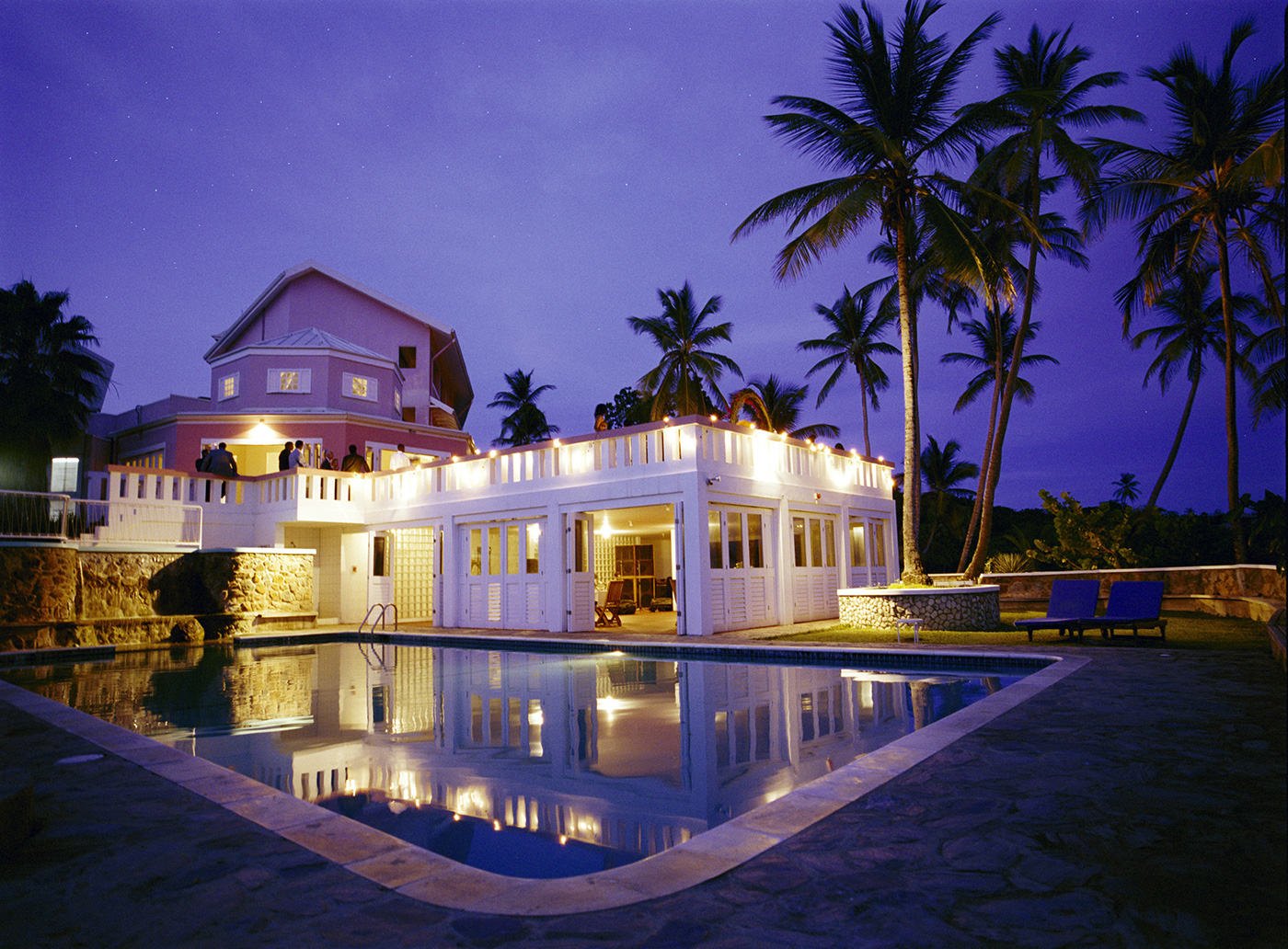
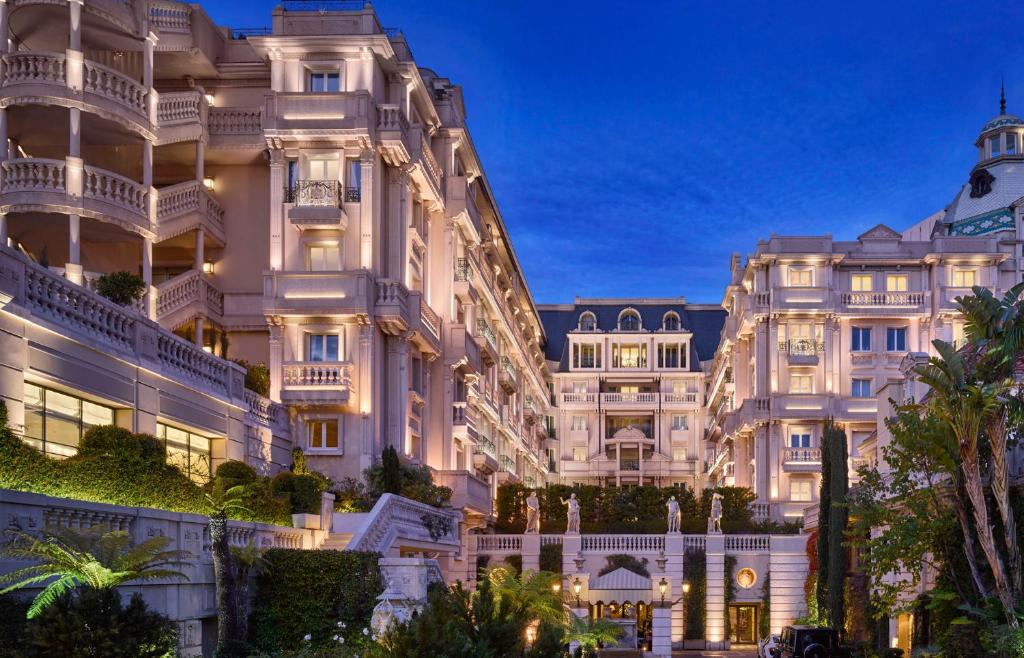
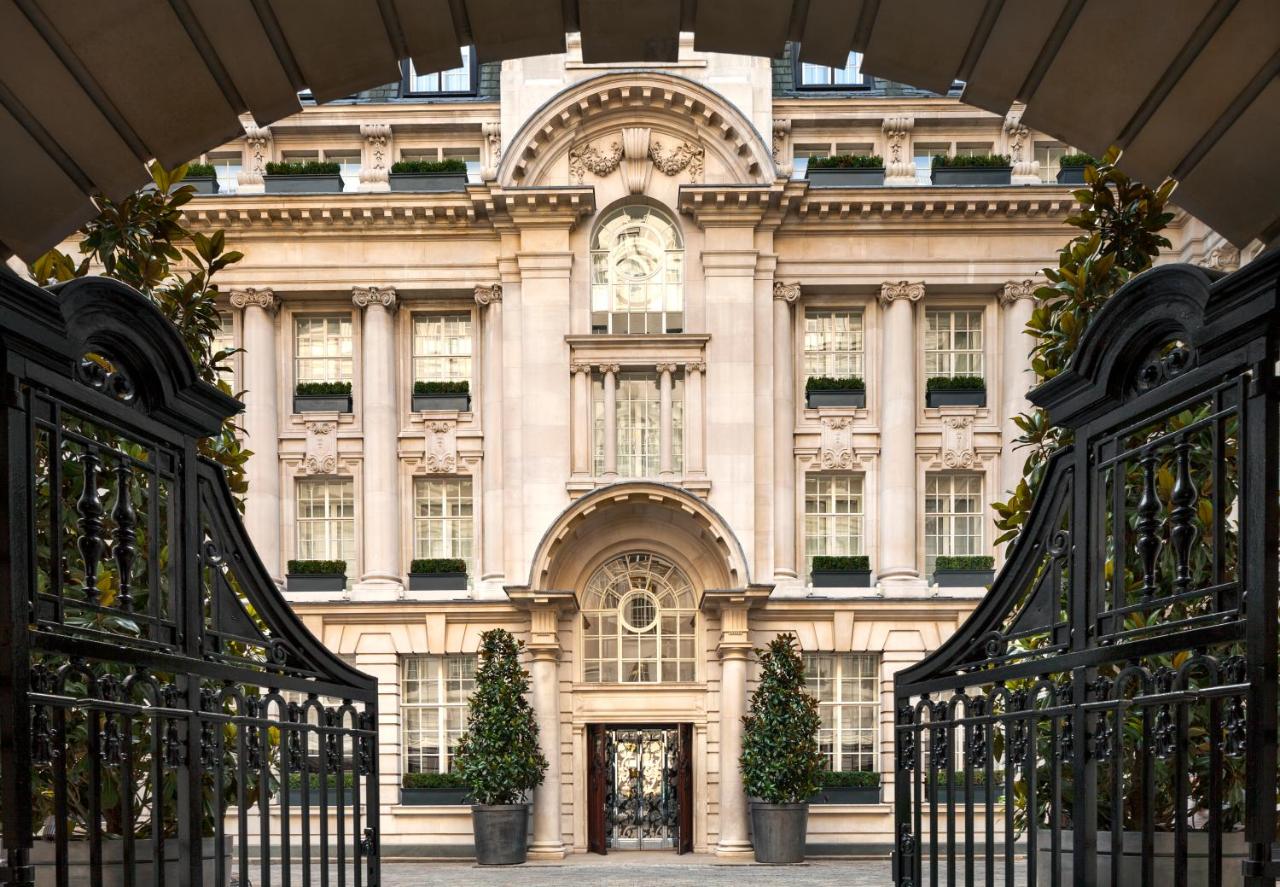







































































Ottley's Village, Saint Kitts and Nevis
Agent: Cliff Jacobs - Managing Principal Estate Agent & CEO (Nat.Dpl.Hotel Man (UJ). M.P.R.E.)
Agent Cellphone: +27 (0) 84 413 1071 / +27 (0) 61 716 6951
Agent Office Number: +27 (0) 84 413 1071
Agent Email Address: cliff@exquisitehotelconsultants.com
Type: Heritage Inn
Bedrooms: 24
Bathrooms: 24
Showers: 24
Parking: 30
Yield: Not Disclosed
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Kitts and Nevis, officially the Federation of Saint Christopher and Nevis, is an island country and microstate consisting of the two islands of Saint Kitts and Nevis, both located in the West Indies, in the Leeward Islands chain of the Lesser Antilles. With 261 square kilometres (101 sq mi) of territory, and roughly 50,000 inhabitants, it is the smallest sovereign state in the Western Hemisphere, in both area and population, as well as the world's smallest sovereign federation. The country is a Commonwealth realm, with Charles III as King and head of state. It is the only sovereign federation in the Caribbean.
The capital city is Basseterre, located on the larger island of Saint Kitts. Basseterre is also the main port for passenger entry (via cruise ships) and cargo. The smaller island of Nevis lies approximately 3 km (2 mi) to the southeast of Saint Kitts, across a shallow channel called The Narrows.
The British dependency of Anguilla was historically also a part of this union, which was known collectively as Saint Christopher-Nevis-Anguilla. However, Anguilla chose to secede from the union, and remains a British overseas territory. The islands of Sint Eustatius, Saba, Saint Barthélemy, Saint-Martin/Sint Maarten and Anguilla lie to the north-northwest of the country. To the east and northeast are Antigua and Barbuda, and to the southeast is the small uninhabited island of Redonda (part of Antigua and Barbuda) and the island of Montserrat.
Saint Kitts and Nevis were among the first islands in the Caribbean to be colonised by Europeans. Saint Kitts was home to the first British and French Caribbean colonies, and thus has also been titled "The Mother Colony of the West Indies". It is also the most recent British territory in the Caribbean to become independent, gaining independence in 1983.
Etymology
The Kalinago, the pre-European inhabitants of Saint Kitts, called the island Liamuiga, roughly translating as "fertile land".
It is thought that Christopher Columbus, the first European to see the islands in 1493, named the larger island San Cristóbal, after Saint Christopher, his patron saint and that of travellers. New studies suggest that Columbus named the island Sant Yago (Saint James), and that the name San Cristóbal was in fact given by Columbus to the island now known as Saba, 32 km (20 mi) northwest. Saint Kitts was well documented as San Cristóbal by the 17th century. The first English colonists kept the English translation of this name, and dubbed it St. Christopher's Island. In the 17th century, a common nickname for Christopher was Kit(t); hence, the island came to be informally referred to as Saint Kitt's Island, later further shortened to Saint Kitts.
Columbus gave Nevis the name San Martín (Saint Martin). The current name Nevis is derived from a Spanish name Nuestra Señora de las Nieves, meaning "Our Lady of the Snows", a reference to the 4th-century Catholic miracle of a summertime snowfall on the Esquiline Hill in Rome.[1] It is not known who chose this name for the island, but it is thought that white clouds which usually wreath the top of Nevis Peak reminded someone of the miracle.
Today, the Constitution refers to the state as both Saint Kitts and Nevis and Saint Christopher and Nevis; the former is the one most commonly used, but the latter is generally used for diplomatic relations.
History
Pre-colonial period
The name of the first inhabitants, pre-Arawakan peoples who settled the islands perhaps as early as 3000 years ago, is not known. They were followed by the Arawak peoples, or Taíno, about 1000 BC. The Island Caribs invaded about 800 AD.
European arrival and early colonial period
Christopher Columbus was the first European to sight the islands in 1493. The first settlers were the English in 1623, led by Thomas Warner, who established a settlement at Old Road Town on the west coast of St Kitts after achieving an agreement with the Carib chief Ouboutou Tegremante.The French later also settled on St Kitts in 1625 under Pierre Belain d'Esnambuc. As a result, both parties agreed to partition the island into French and English sectors. From 1628 onward the English also began settling on Nevis.
The French and English, intent on exploitation of the island's resources, encountered resistance from the native Caribs (Kalinago), who waged war during the first three years of the settlements' existence. The Europeans resolved to rid themselves of this problem. An ideological campaign was waged by colonial chroniclers, dating back to the Spanish, as they produced literature which denied the Kalinagos' humanity (a literary tradition carried through the late-seventeenth century by such authors as Jean-Baptiste du Tertre and Pere Labat). In 1626 the Anglo-French settlers joined forces to massacre the Kalinago at a place that became known as Bloody Point, allegedly to preempt a Carib plan to expel or kill all European settlers. Thereafter, the English and French established large sugar plantations which were worked by imported African slaves. This made the planter-colonists rich, but drastically altered the islands' demographics as black slaves soon came to outnumber Europeans.
A Spanish expedition of 1629 sent to enforce Spanish claims destroyed the English and French colonies and deported the settlers back to their respective countries. As part of the war settlement in 1630, the Spanish permitted the re-establishment of the English and French colonies. Spain later formally recognised Britain's claim to St Kitts with the Treaty of Madrid (1670), in return for British cooperation in the fight against piracy.
As Spanish power declined, Saint Kitts became a key base for English and French expansion in the Caribbean. From St Kitts the British settled the islands of Antigua, Montserrat, Anguilla and Tortola, and the French settled Martinique, the Guadeloupe archipelago and Saint Barthélemy. During the late 17th century, France and England fought for control over St Kitts and Nevis, fighting wars in 1667, 1689–90 and 1701–13. The French renounced their claim to the islands with the Treaty of Utrecht in 1713. The islands' economy, already shattered by war, was further harmed by natural disasters: In 1690 an earthquake destroyed Jamestown, capital of Nevis, forcing the construction of a new capital at Charlestown; further damage was caused by a hurricane in 1707.
British colonial period
The colony had recovered by the turn of the 18th century, and St Kitts had become the richest British Crown Colony per capita in the Caribbean as result of its slave-based sugar industry by the close of the 1700s. The 18th century also saw Nevis, formerly the richer of the two islands, being eclipsed by St Kitts in economic importance. Alexander Hamilton, the future U.S. secretary of the Treasury, was born on Nevis in 1755 or 1757.
As Britain became embroiled in war with its American colonies, the French decided to use the opportunity to re-capture St Kitts in 1782; however St Kitts was given back and recognised as British territory in the Treaty of Paris (1783).
The African slave trade was terminated within the British Empire in 1807, and slavery outlawed completely in 1834. A four-year "apprenticeship" period followed for each slave, in which they worked for their former owners for wages. On Nevis 8,815 slaves were freed, while St Kitts freed 19,780.
Saint Kitts and Nevis, along with Anguilla, were federated in 1882. In the first few decades of the 20th century economic hardship and lack of opportunities led to the growth of a labour movement; the Great Depression prompted sugar workers to go on strike in 1935. The 1940s saw the founding of the St Kitts-Nevis-Anguilla Labour Party (later renamed the Saint Kitts and Nevis Labour Party, or SKNLP) under Robert Llewellyn Bradshaw. Bradshaw later became Chief Minister and then Premier of the colony from 1966 to 1978; he sought to gradually bring the sugar-based economy under greater state control. The more conservative-leaning People's Action Movement party (PAM) was founded in 1965.
After a brief period as part of the West Indies Federation (1958–62), the islands became an associated state with full internal autonomy in 1967. Residents of Nevis and Anguilla were unhappy with St Kitts's domination of the federation, and Anguilla unilaterally declared independence in 1967. In 1971 Britain resumed full control of Anguilla, but it was formally separated in 1980.Attention then focused on Nevis, with the Nevis Reformation Party seeking to safeguard the smaller island's interests in any future independent state. Eventually it was agreed that the island would have a degree of autonomy with its own Premier and Assembly, as well as the constitutionally-protected right to unilaterally secede if a referendum on independence resulted in a two-thirds majority in favour. St Kitts and Nevis achieved full independence on 19 September 1983. Kennedy Simmonds of the PAM, Premier since 1980, duly became the country's first Prime Minister. St Kitts and Nevis opted to remain within the British Commonwealth, retaining Queen Elizabeth as Monarch, represented locally by a Governor-General.
Post independence era
Kennedy Simmonds went on to win elections in 1984, 1989 and 1993, before being unseated when the SKNLP returned to power in 1995 under Denzil Douglas.
In Nevis, growing discontent with their perceived marginalisation within the federation led to a referendum to separate from St Kitts in 1998, which though resulting a 62% vote to secede, fell short of the required two-thirds majority to be legally enacted.
In late-September 1998, Hurricane Georges caused approximately $458,000,000 in damages and limited GDP growth for the year and beyond. Meanwhile, the sugar industry, in decline for years and propped up only by government subsidies, was closed completely in 2005.
The 2015 Saint Kitts and Nevis general election was won by Timothy Harris and his recently formed People's Labour Party, with backing from the PAM and the Nevis-based Concerned Citizens' Movement under the 'Team Unity' banner.
In June 2020, Team Unity coalition of the incumbent government, led by Prime Minister Timothy Harris, won general elections by defeating Saint Kitts and Nevis Labour Party (SKNLP).
In snap general elections held in August 2022, the SKNLP again won, and Terrance Drew became the fourth prime minister of Saint Kitts and Nevis.
Geography
The country consists of two main islands, Saint Kitts and Nevis, separated at a distance of 2 miles (3 km) by The Narrows strait. Both are of volcanic origin, with large central peaks covered in tropical rainforest. The majority of the population live along the flatter coastal areas. St Kitts contains several mountain ranges (the North West Range, Central Range and South-West Range) in its centre, where the highest peak of the country, Mount Liamuiga 1,156 metres (3,793 ft) can be found. Along the east coast can be found the Canada Hills and Conaree Hills. The land narrows considerably in the south-east, forming a much flatter peninsula which contains the largest body of water, the Great Salt Pond. To the southeast, in The Narrows, lies the small isle of Booby Island. There are numerous rivers descending from the mountains of both islands, which provide fresh water to the local population. Nevis, the smaller of the two main islands and roughly circular in shape, is dominated by Nevis Peak 985 metres (3,232 ft).
Saint Kitts and Nevis contains two terrestrial ecoregions: Leeward Islands moist forests and Leeward Islands dry forests. The country had a 2019 Forest Landscape Integrity Index mean score of 4.55/10, ranking it 121st globally out of 172 countries.
Fauna
The national bird is the brown pelican. 176 species of bird have been reported from the country.
Flora
The national flower is Delonix regia. Common plants include palmetto, hibiscus, bougainvillea, and tamarind. Pinus species are common in the dense forests of islands, and are usually covered by various species of ferns.
Climate
By the Köppen climate classification, St Kitts has a tropical savanna climate (Köppen Aw) and Nevis has a tropical monsoon climate (Köppen Am). Mean monthly temperatures in Basseterre varies little from 23.9 °C (75.0 °F) to 26.6 °C (79.9 °F). Yearly rainfall is approximately 2,400 millimetres (90 in), although it has varied from 1,356 millimetres (53.4 in) to 3,183 millimetres (125.3 in) in the period 1901–2015.
Economy
Saint Kitts and Nevis is a twin-island federation whose economy is characterised by its dominant tourism, agriculture, and light manufacturing industries. Sugar was the primary export from the 1940s on, but rising production costs, low world market prices, and the government's efforts to reduce dependence on it have led to a growing diversification of the agricultural sector. In 2005, the government decided to close down the state-owned sugar company, which had experienced losses and was a significant contributor to the fiscal deficit.
St Kitts and Nevis is heavily dependent upon tourism to drive its economy, a sector which has expanded significantly since the 1970s. In 2009 there were 587,479 arrivals to Saint Kitts compared to 379,473 in 2007, an increase of just under 40% in a two-year period, however the tourist sector decreased during the Global financial crisis and has only recently returned to pre-crash levels. In recent years the government has sought to diversify the economy via agriculture, tourism, export-oriented manufacturing, and offshore banking.
In July 2015, St Kitts & Nevis and the Republic of Ireland signed a tax agreement to "promote international co-operation in tax matters through exchange of information." The agreement was developed by the OECD Global Forum Working Group on Effective Exchange of Information, which consisted of representatives from OECD member countries and 11 other countries in the Caribbean and other parts of the world.
Economic citizenship by investment
St Kitts allows foreigners to obtain the status of St Kitts citizen by means of a government sponsored investment programme called Citizenship-by-Investment. Established in 1984, St Kitts's citizenship programme is the oldest prevailing economic citizenship programme of this kind in the world. However, while the programme is the oldest in the world, it only catapulted in 2006 when Henley & Partners, a global citizenship advisory firm, became involved in the restructuring of the programme to incorporate donations to the country's sugar industry.
Citizenship-by-Investment Programmes have been criticised by some researchers due to the risks of corruption, money laundering and tax evasion. According to the official website of St Kitts's Citizenship-by-Investment Programme they offer multiple benefits: "When you acquire citizenship under the St Kitts & Nevis citizenship programme, you and your family enjoy full citizenship for life, which can be passed on to future generations by descent. As citizens of St Kitts & Nevis, you and your family are issued with passports which allow visa-free travel to more than 140 countries and territories worldwide, including all of the EU. Of course you have the right to take up residence in St Kitts & Nevis as well as in most of the CARICOM member countries at any time and for any length of time".
Each candidate must go through several legal steps and make a qualifying investment into the country and should complete certain legal requirements to qualify for citizenship under the investment programme. The applicant must make at least a minimum investment in either approved real estate, the Sugar Industry Diversification Foundation (SDIF), or the Sustainable Growth Fund (SGF) to qualify for the economic citizenship of St Kitts and Nevis.
According to Henley & Partners, the requirements are as follows:
According to Imperial & Legal, from 1 April 2018 St Kitts and Nevis government implemented a new investment option – Contribution to Sustainable Growth Fund (SGF). To qualify for citizenship of St Kitts & Nevis, applicants who choose to invest in SGF will need to make a once-off non-refundable contribution of $150,000 plus due diligence fees.
About us









































Cliff Jacobs (Nat Dpl Hotel Man (UJ). MPRE. GA Level 5 TEFL) Managing Principal / CEO Exquisite Hotel Consultants (Pty) Ltd Mobile: +27 (0) 67 587 2532 (voice calls) Mobile: +27 (0) 84 413 1071 (WhatsApp voice calls and chats only) / +27 (0) 61 716 6951 (WhatsApp voice calls and chats only) Email: cliff@exquisitehotelconsultants.com Web: https://www.exquisitehotelconsultants.com © All rights reserved Terms and Conditions apply Scroll down to view our Hospitality Properties and Businesses for sale or lease or lease-to-buy or partnership arrangement or management agreement arrangement.